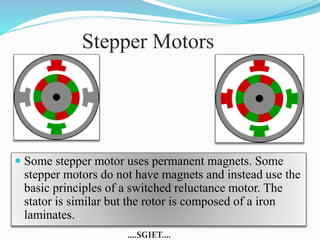
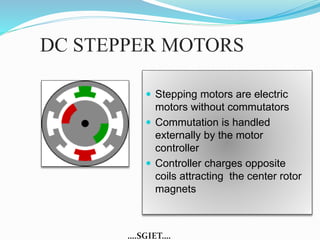
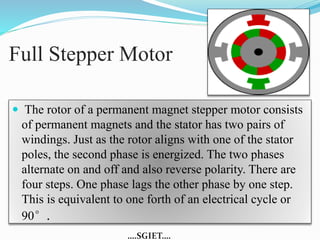
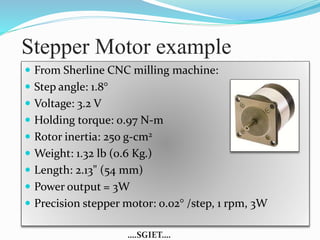
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on stepper motors. It describes the basic components and operating principles of stepper motors, including the different types (permanent magnet, variable reluctance, and hybrid). It also discusses identifying motor wires, the differences between full-step and half-step motors, provides an example of stepper motor specifications, and lists some common applications of stepper motors.