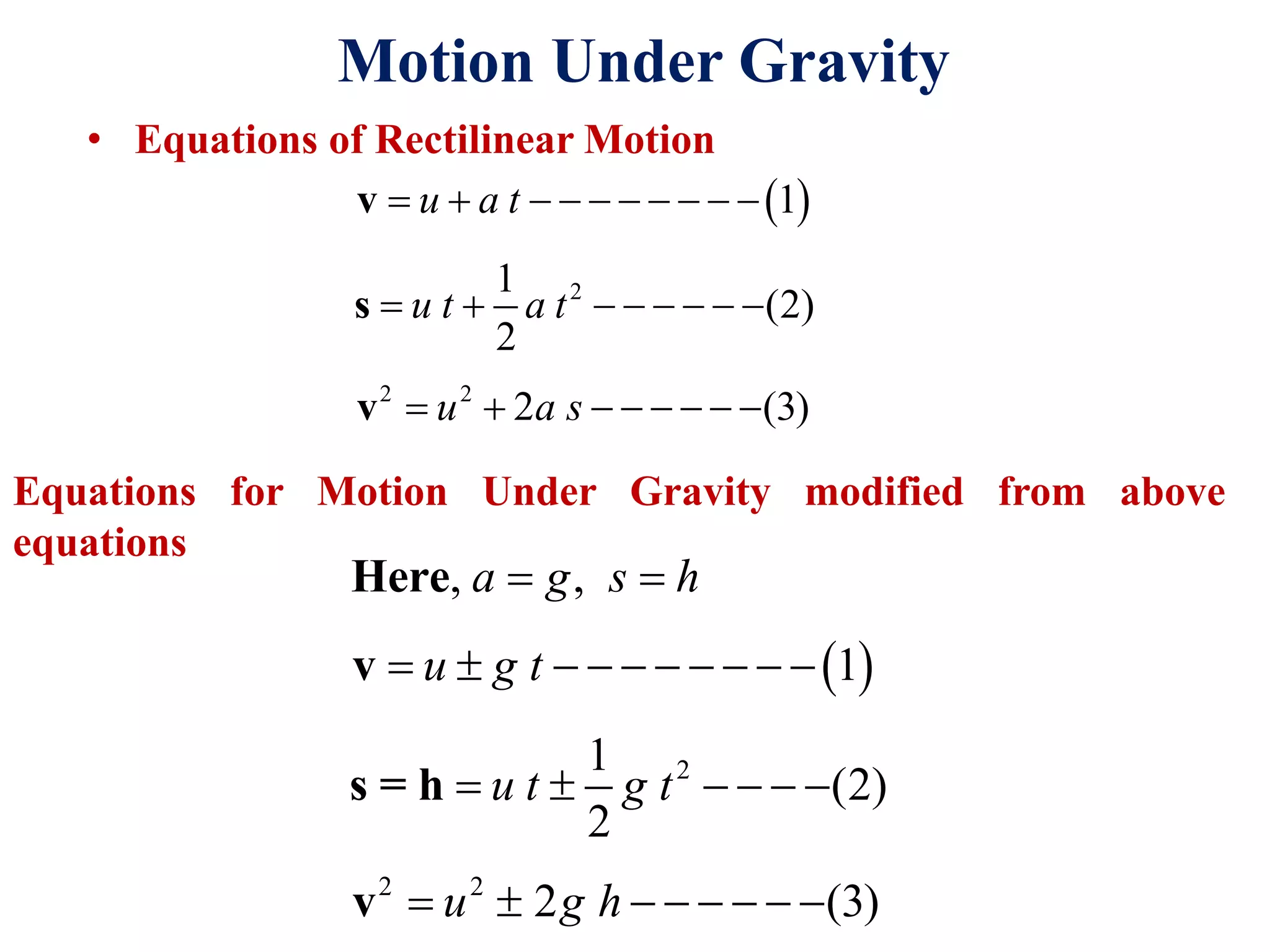
This document discusses rectilinear motion under gravity. It defines motion under gravity as motion of a particle projected vertically in air under the influence of gravitational force. It presents the equations of rectilinear motion and modifies them for motion under gravity. It notes that time of flight is the total time an object remains in air, which is the sum of time for upward and downward journeys. It provides examples calculating the time and velocity at which two objects crossing paths under gravity conditions.