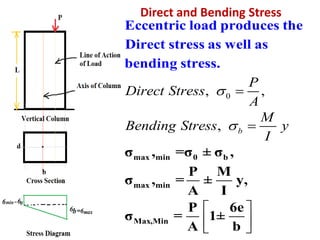
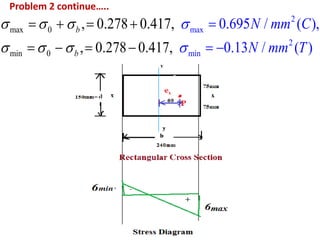
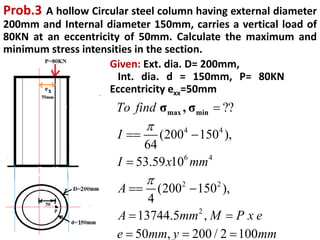
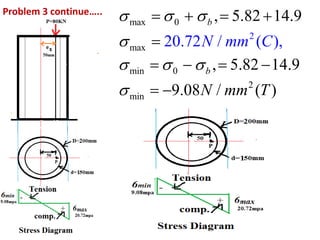
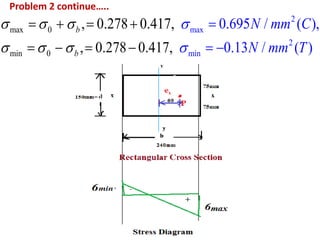
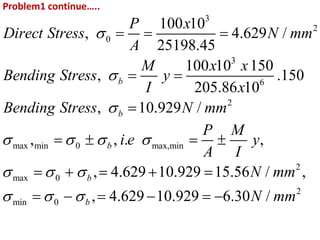1) Eccentrically loaded columns experience both direct stress from the applied load as well as bending stress due to the eccentricity of the load. The maximum and minimum stresses are calculated as the sum and difference of these direct and bending stresses.
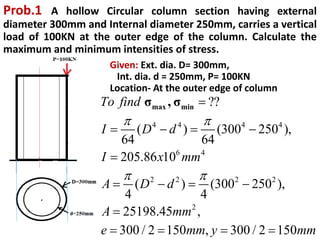
2) Three examples of eccentrically loaded columns are provided: a hollow circular column, a rectangular column, and another hollow circular column. The maximum and minimum stresses are calculated for each example by determining the direct and bending stresses from the given load, dimensions, and eccentricity, and summing or differencing as required.
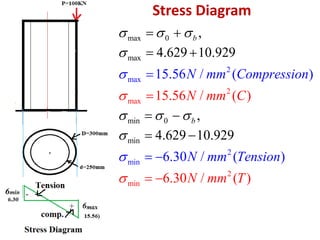
3) Stress diagrams are shown for each example, indicating the variation of compressive and tensile stress across the cross section due to the eccentric