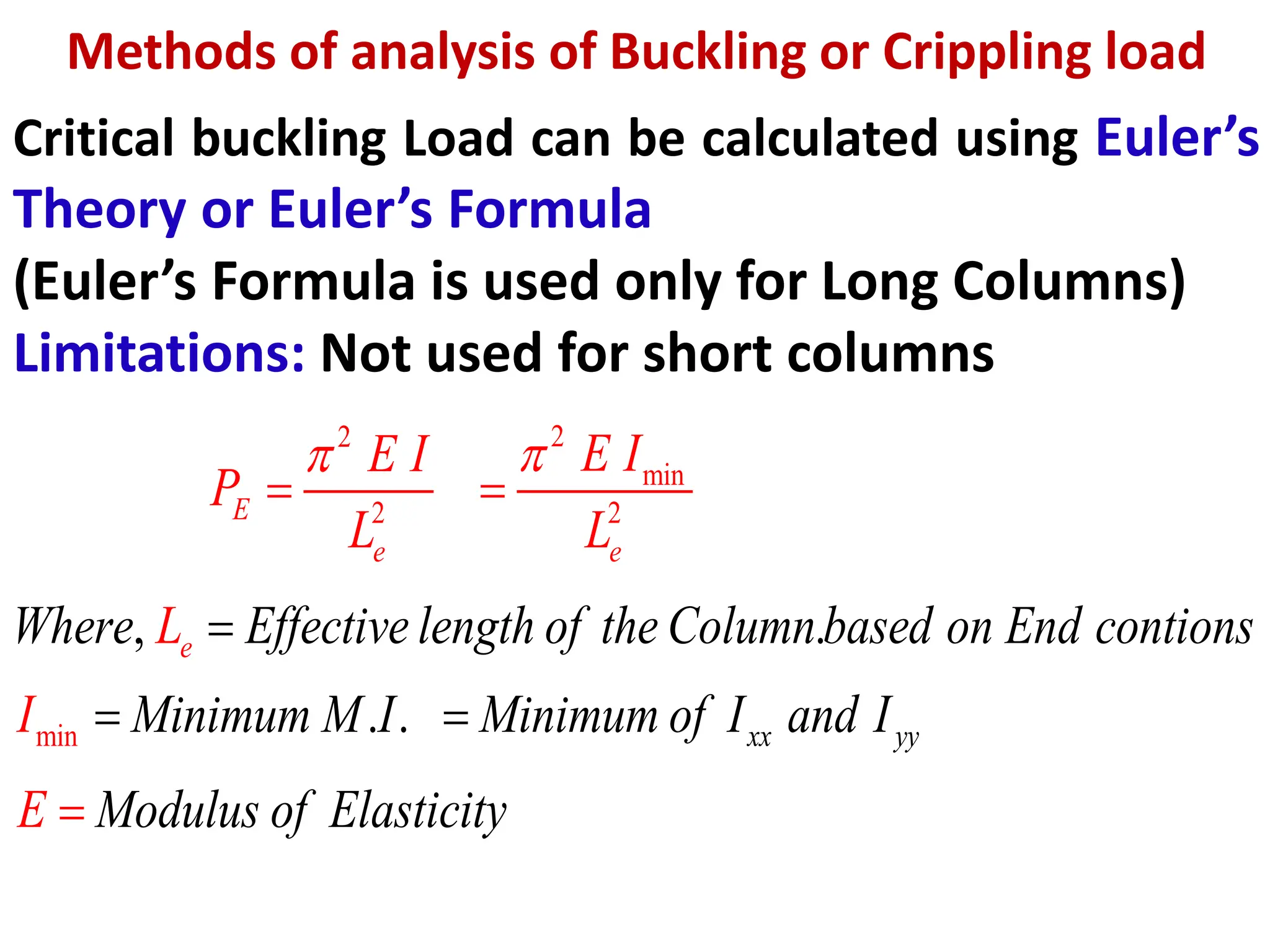
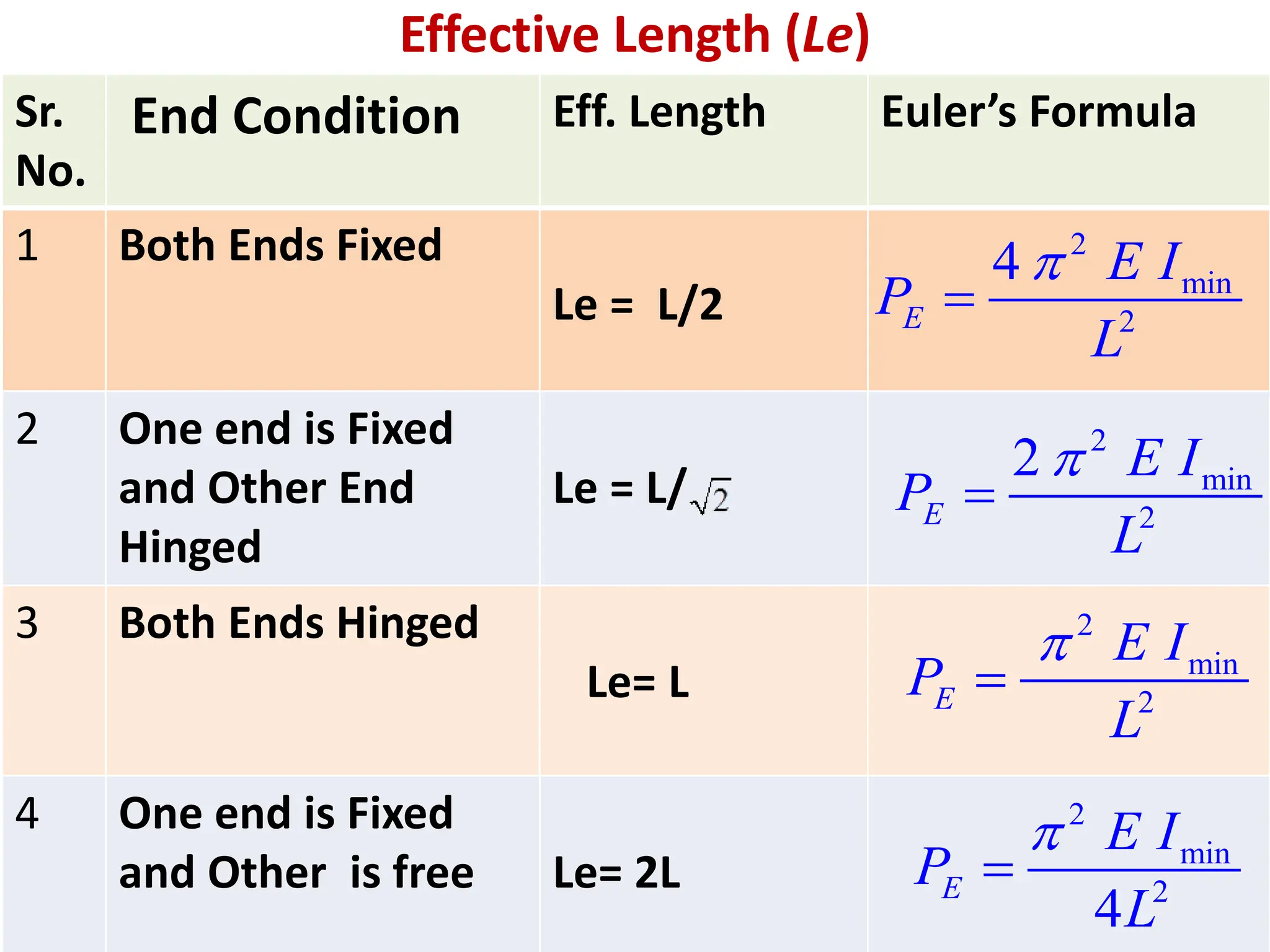
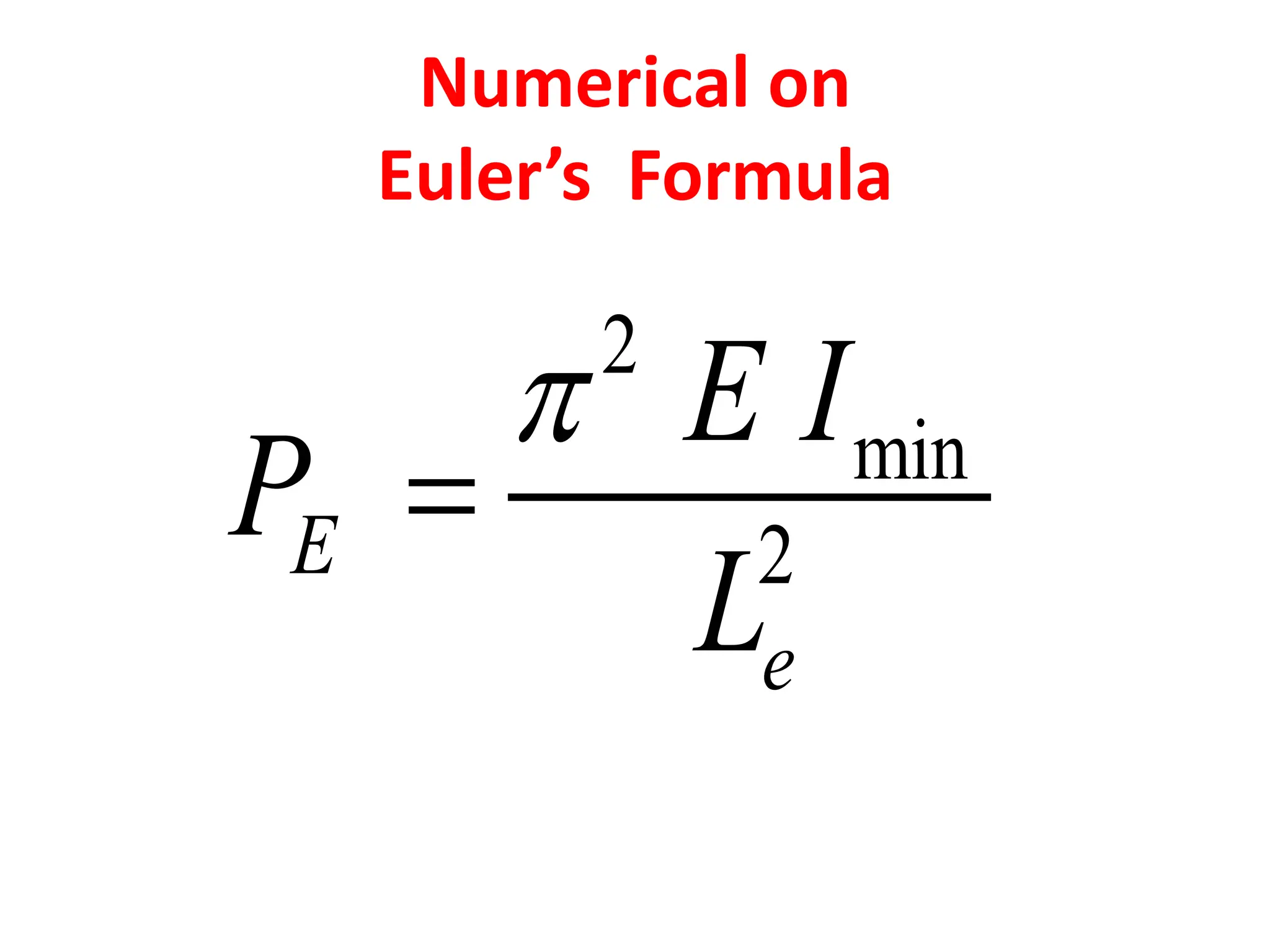
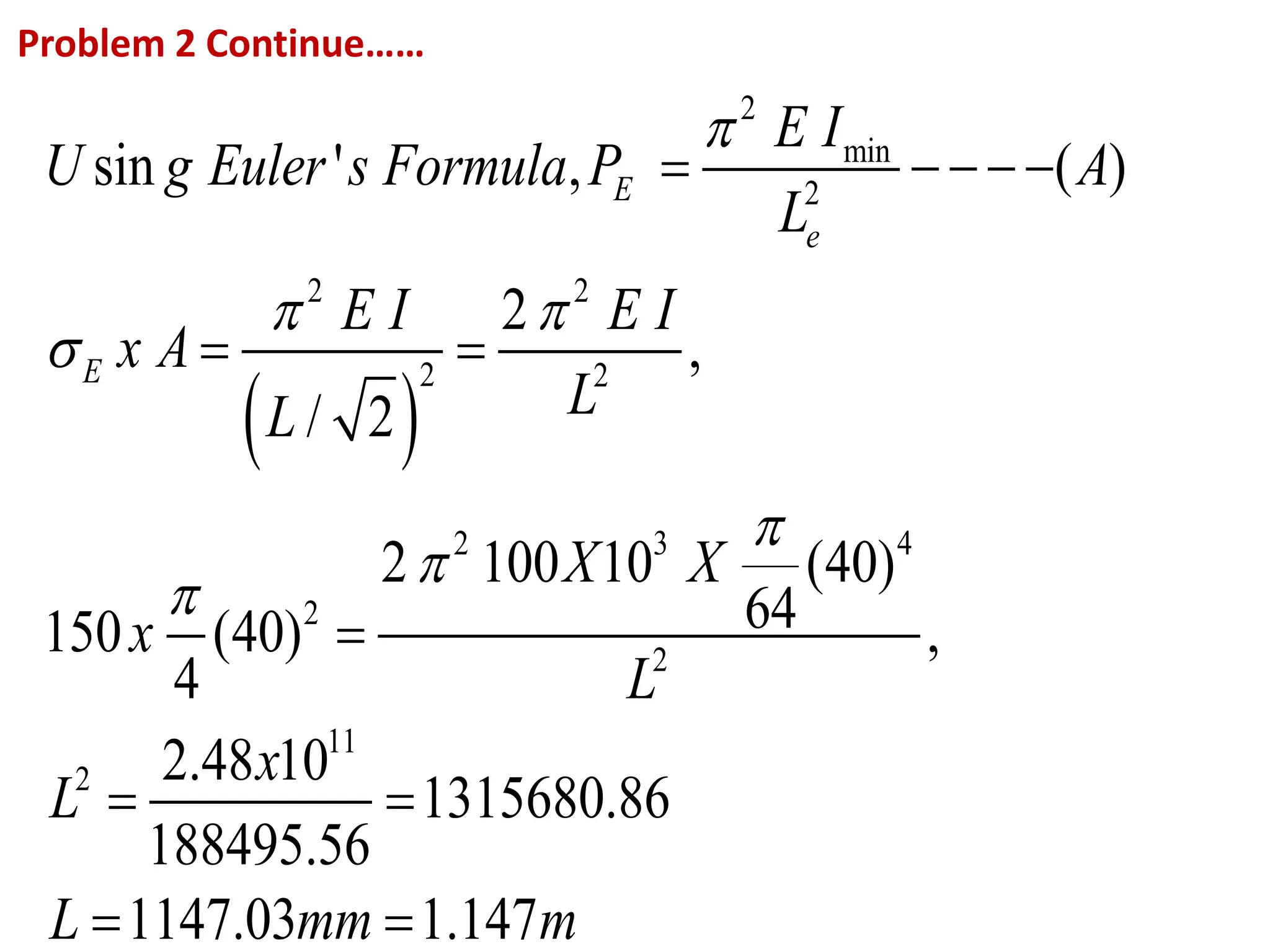
This document discusses the use of Euler's formula to calculate the buckling or critical load of columns. It provides the following key points:
1. Euler's formula can be used to calculate the critical buckling load of long columns based on the column's effective length, which depends on its end conditions, and its minimum moment of inertia.
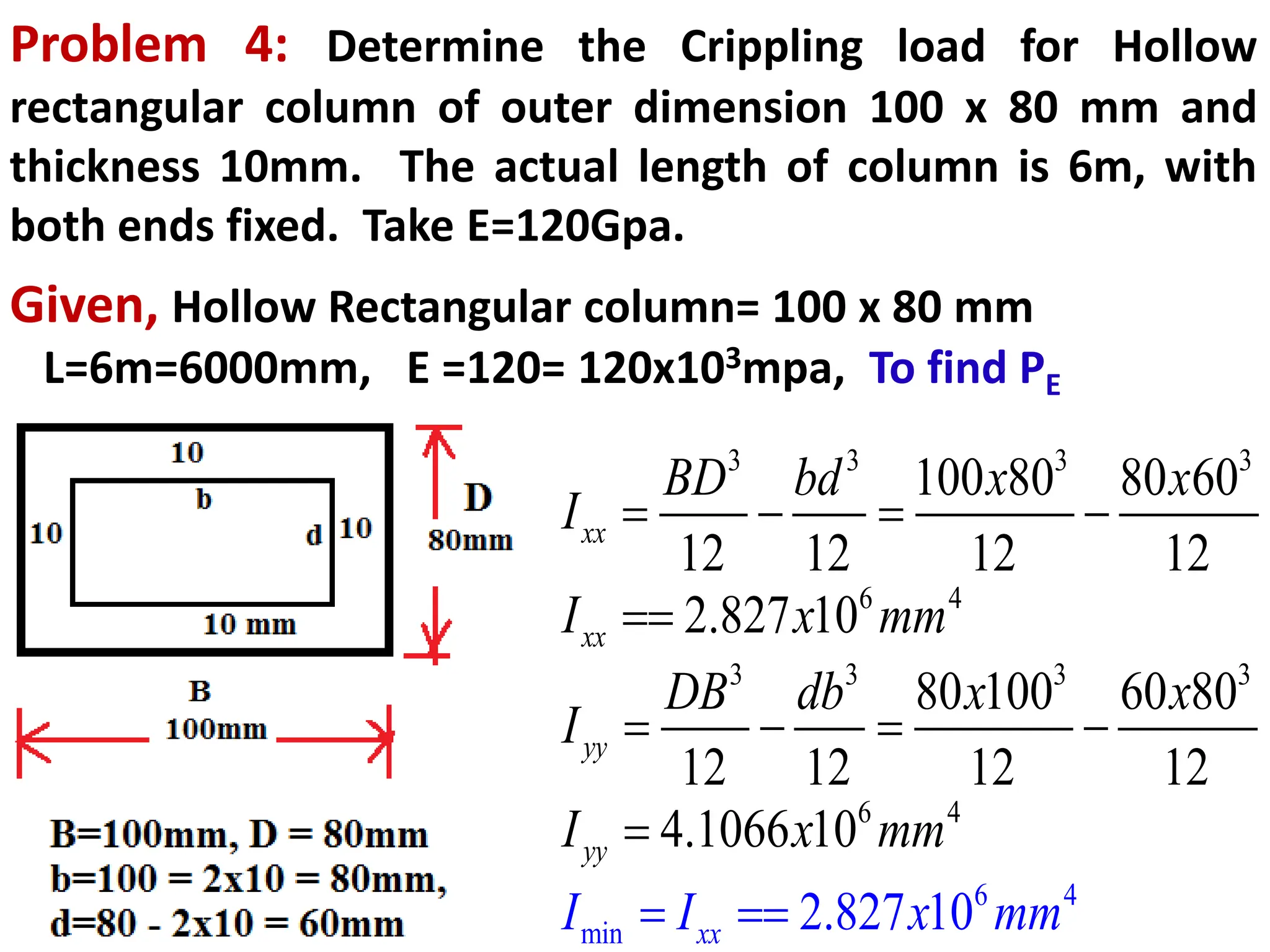
2. Several examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the slenderness ratio and critical load of columns with different cross-sections, lengths, materials and end conditions using Euler's formula. The examples analyze columns that are circular, hollow circular, hollow rectangular, and tubular.
3. Parameters that must be provided to use Euler's formula include the column's dimensions, length