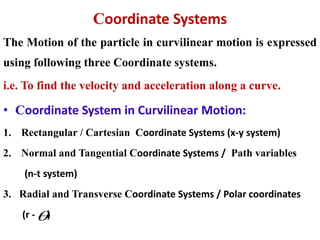
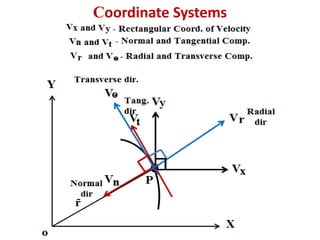
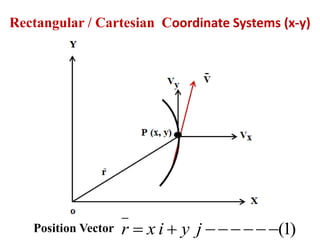
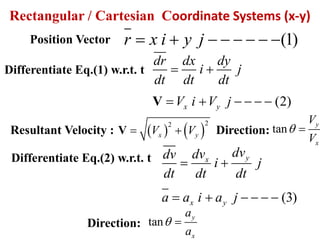
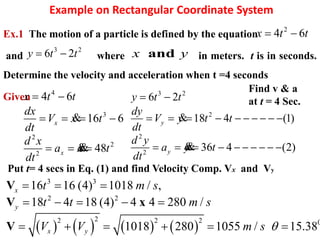
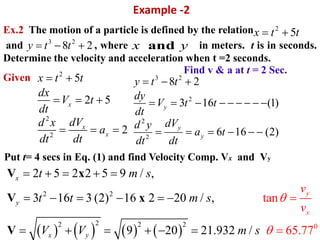
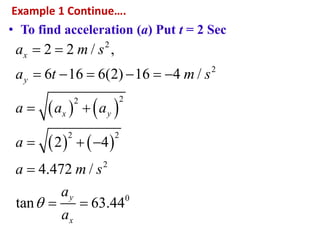
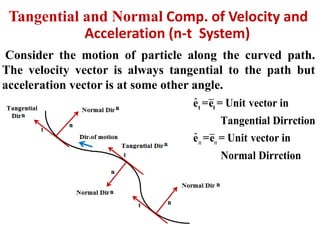
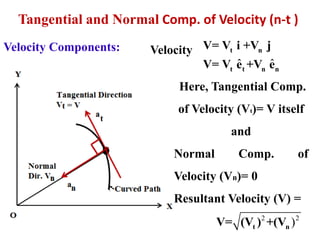
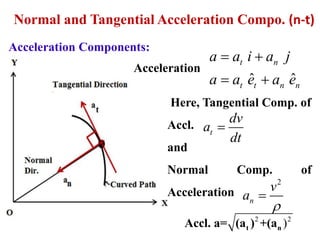
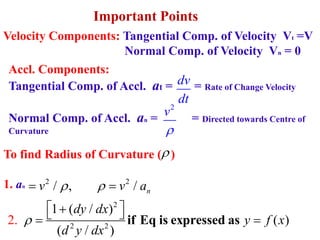
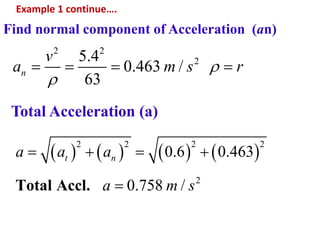
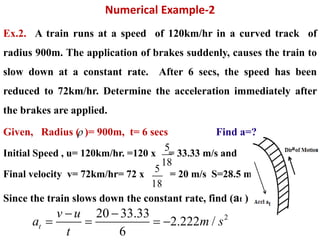
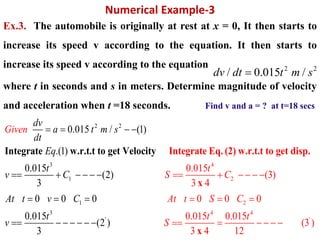
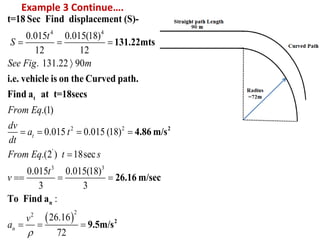
This document discusses coordinate systems used to describe curvilinear motion. It describes three coordinate systems: 1) Rectangular/Cartesian (x-y) where position, velocity and acceleration vectors are defined, 2) Normal and tangential where velocity has a tangential component and acceleration has tangential and normal components, 3) Radial and transverse/polar where position is defined by radial and transverse coordinates. It also provides examples of calculating velocity and acceleration in rectangular coordinates and normal-tangential coordinates for curvilinear motion problems.