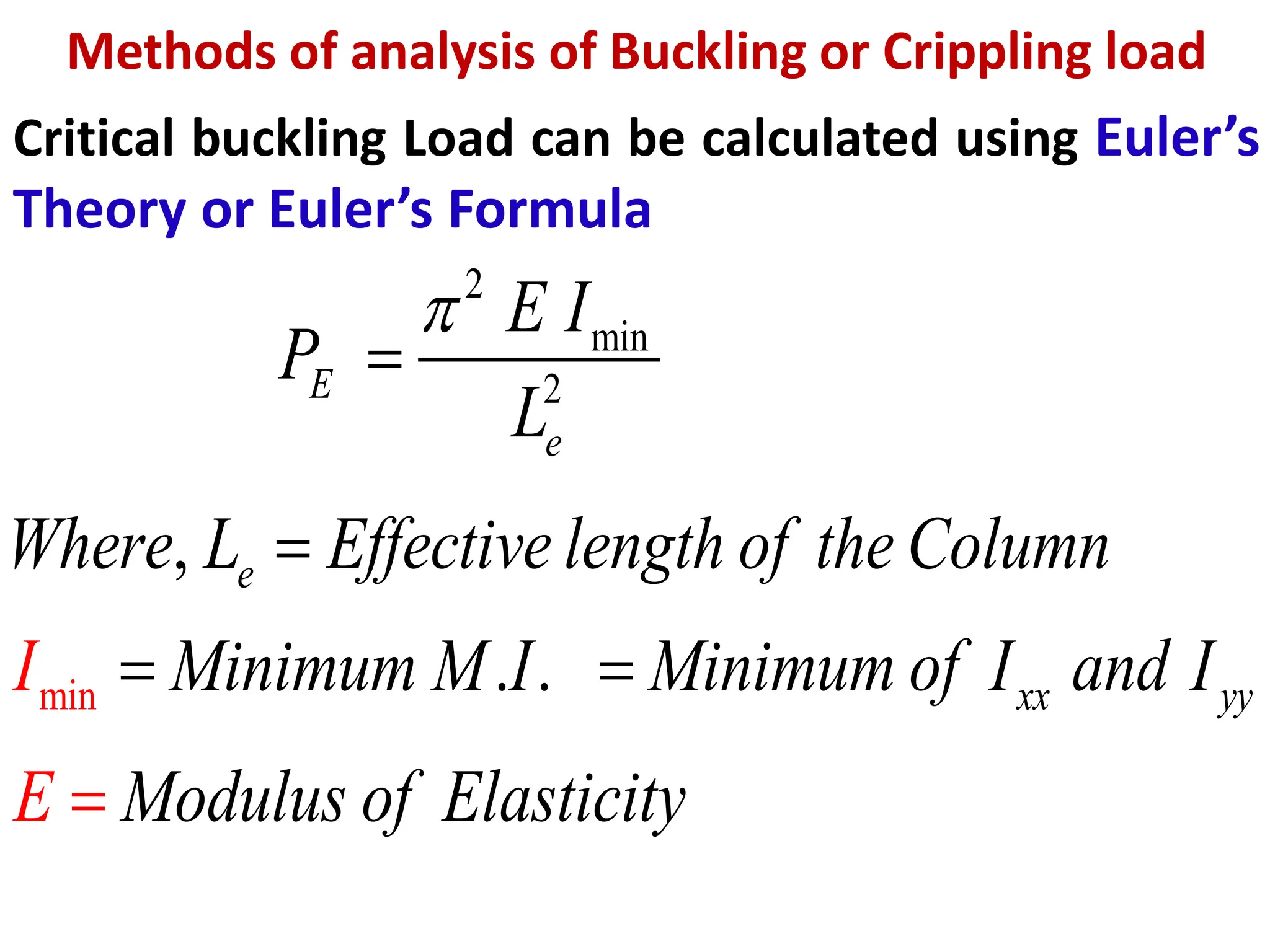
This document contains 4 numerical problems related to calculating the buckling or crippling load of columns using Euler's formula. Problem 1 calculates the safe load capacity of an alloy tube column with one end fixed and the other hinged. Problem 2 finds the crippling load of a T-section strut with both ends hinged. Problem 3 determines the crippling load of an I-section joist with both ends fixed. Problem 4 compares the strength ratio of a solid column section to a hollow column section with the same cross-sectional area and length, both with pinned ends. The document provides step-by-step working and uses Euler's formula to calculate the critical buckling loads.