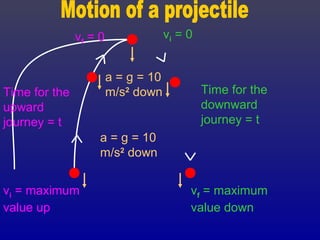
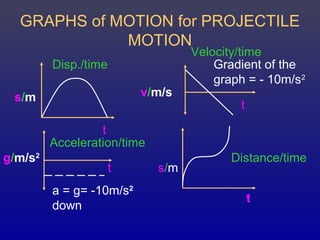
This document discusses vertical projectile motion and free fall. It explains that during vertical projectile motion, an object thrown upwards experiences maximum velocity on release, slows as it rises, stops at the top of its path, and then speeds up as it descends. The acceleration due to gravity causes the downward motion and is always 10 m/s^2. Equations of motion can be used to analyze the path of a vertically thrown object. When objects fall through air, air resistance reduces their acceleration until they reach terminal velocity, where acceleration equals zero and the object falls at a constant speed.