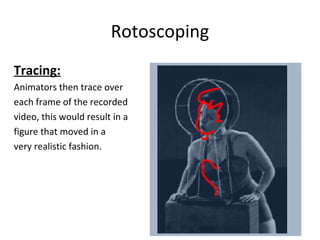
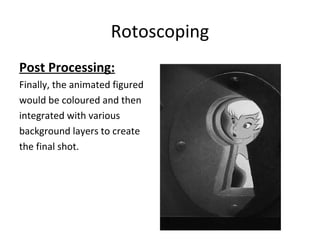
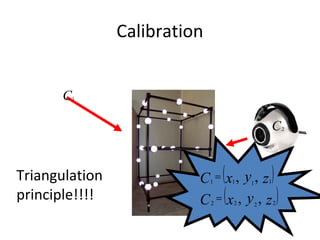
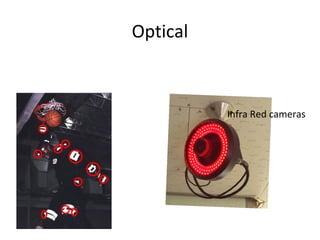
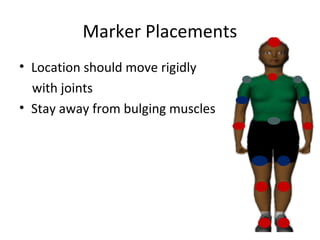
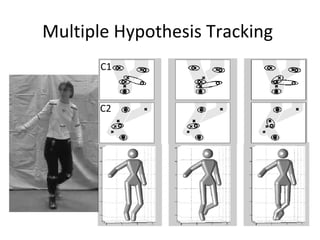
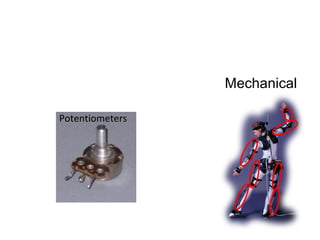
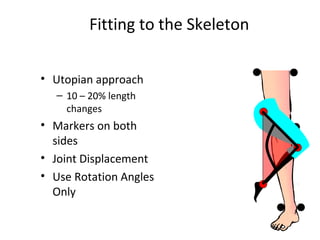
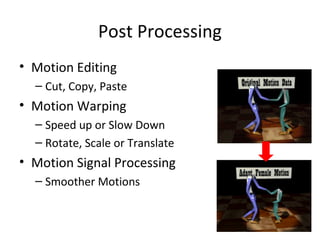
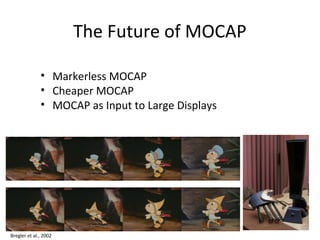
Motion capture technology involves recording human movement through specialized cameras and mapping it onto digital character models. Historically, rotoscoping was used, which involved animators tracing live-action footage frame-by-frame. Now, motion capture uses optical, magnetic, or mechanical techniques to track markers on an actor's body in real-time. The captured motion data is then fitted to a digital skeleton and can be edited or processed before being applied to animations. Motion capture has applications in entertainment, medicine, education, science, engineering, and more.