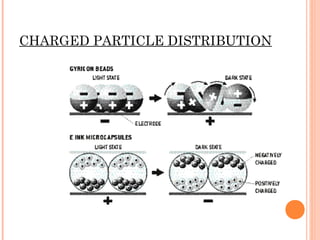
E-paper is a display technology that mimics the appearance of ordinary ink on paper. It was developed in the 1970s and uses microcapsules filled with charged pigment particles. When an electric field is applied, the particles move to the top or bottom, allowing the color to be changed. E-paper has advantages over LCD displays in having a wide viewing angle, being readable in sunlight, and not requiring power to hold an image. It is used in e-readers, e-newspapers, mobile displays, and could replace paper in the future.