Embed presentation
Downloaded 86 times




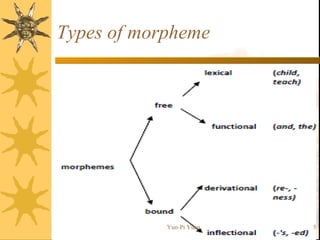


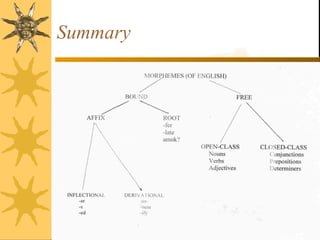


The document discusses morphology, which is the study of how words are formed from morphemes. It defines a morpheme as the smallest unit of language that carries meaning. There are two basic types of morphemes: free morphemes, which can stand alone as words, and bound morphemes, which must be attached to other morphemes. Free morphemes are further divided into lexical morphemes (content words) and functional morphemes (function words). Bound morphemes are divided into derivational morphemes, which can change a word's syntactic class, and inflectional morphemes, which express different forms of the same word.









