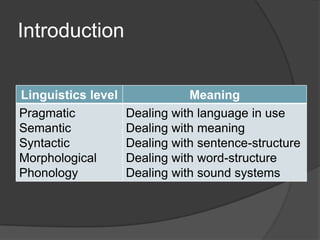
This document discusses the linguistic level of morphology. It defines morphology as the study of word structures, especially in terms of morphemes. Morphology examines how words are formed through the combination of morphemes. The document outlines the different types of morphemes such as free morphemes like root words that can stand alone and bound morphemes like affixes that cannot be used alone. It also discusses how morphology interfaces with other linguistic levels like phonology and syntax.