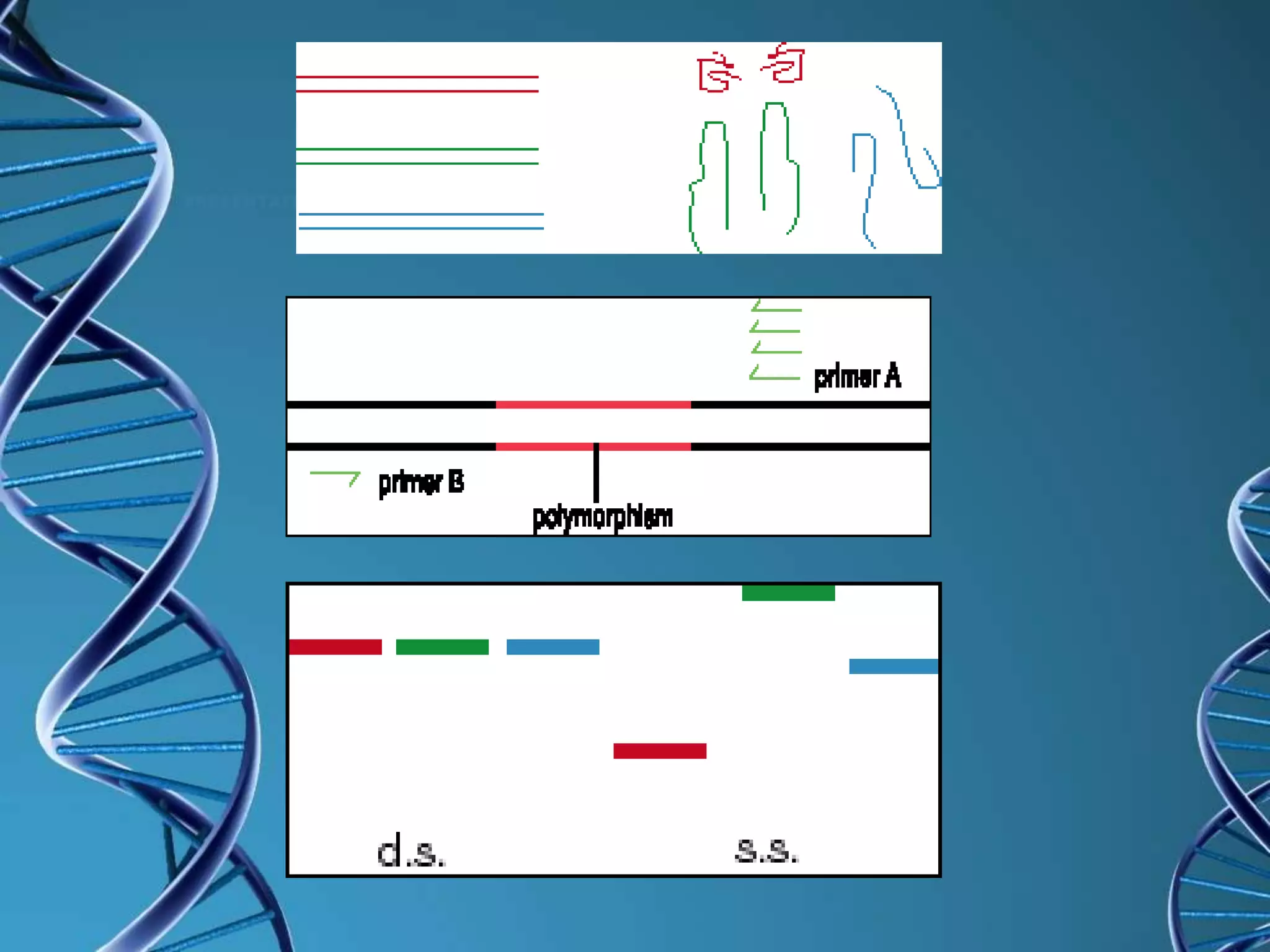
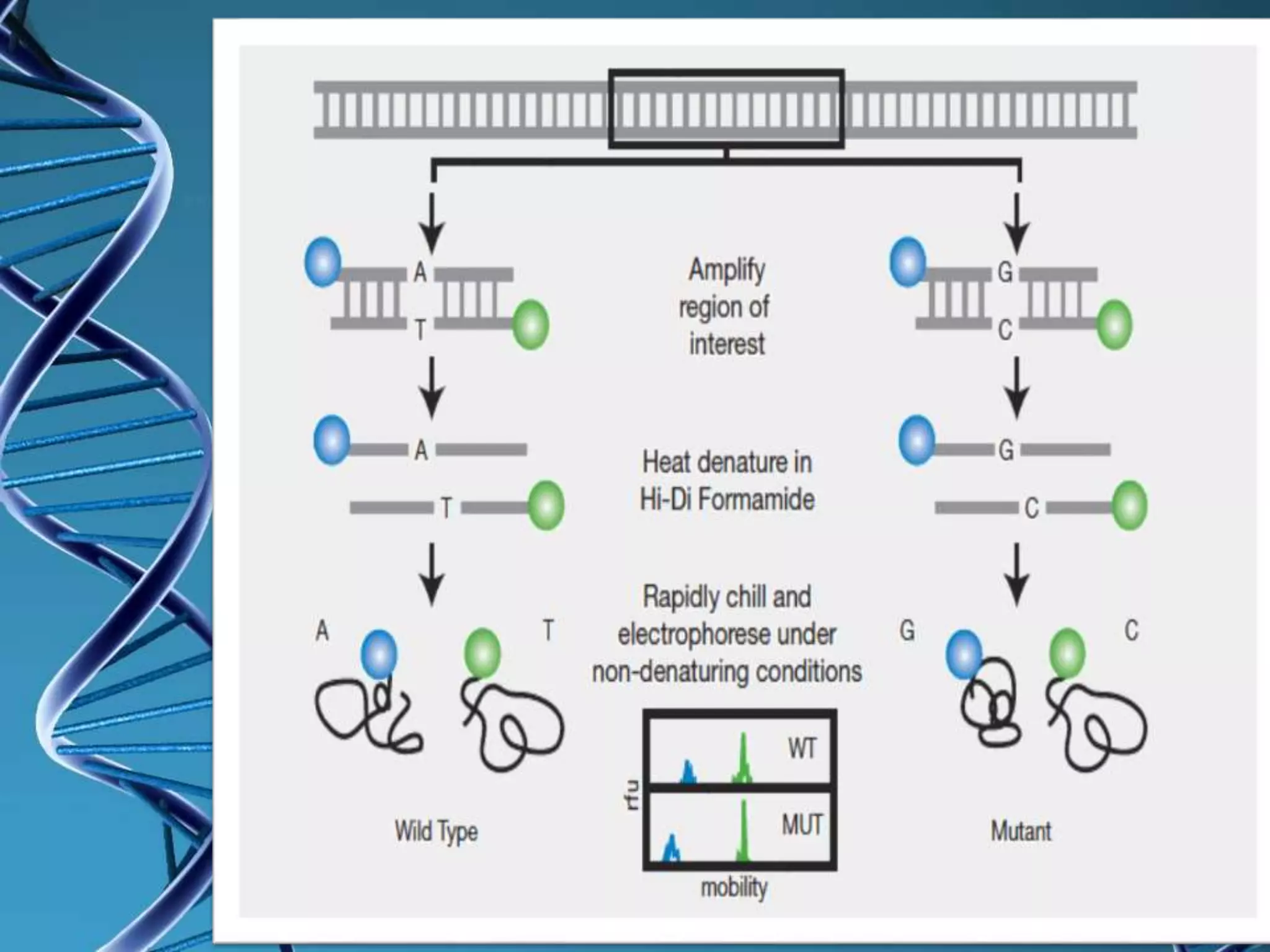
Single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) is a technique that detects differences in the secondary structure of single-stranded DNA fragments caused by variations in their nucleotide sequence. SSCP analysis involves digesting DNA, separating the strands, running electrophoresis on a gel, and comparing the mobility of single strands - strands with different sequences will have different conformations and mobilities. SSCP is useful for detecting genetic variations and mutations, and has applications in genotyping, viral strain identification, and medical diagnosis.