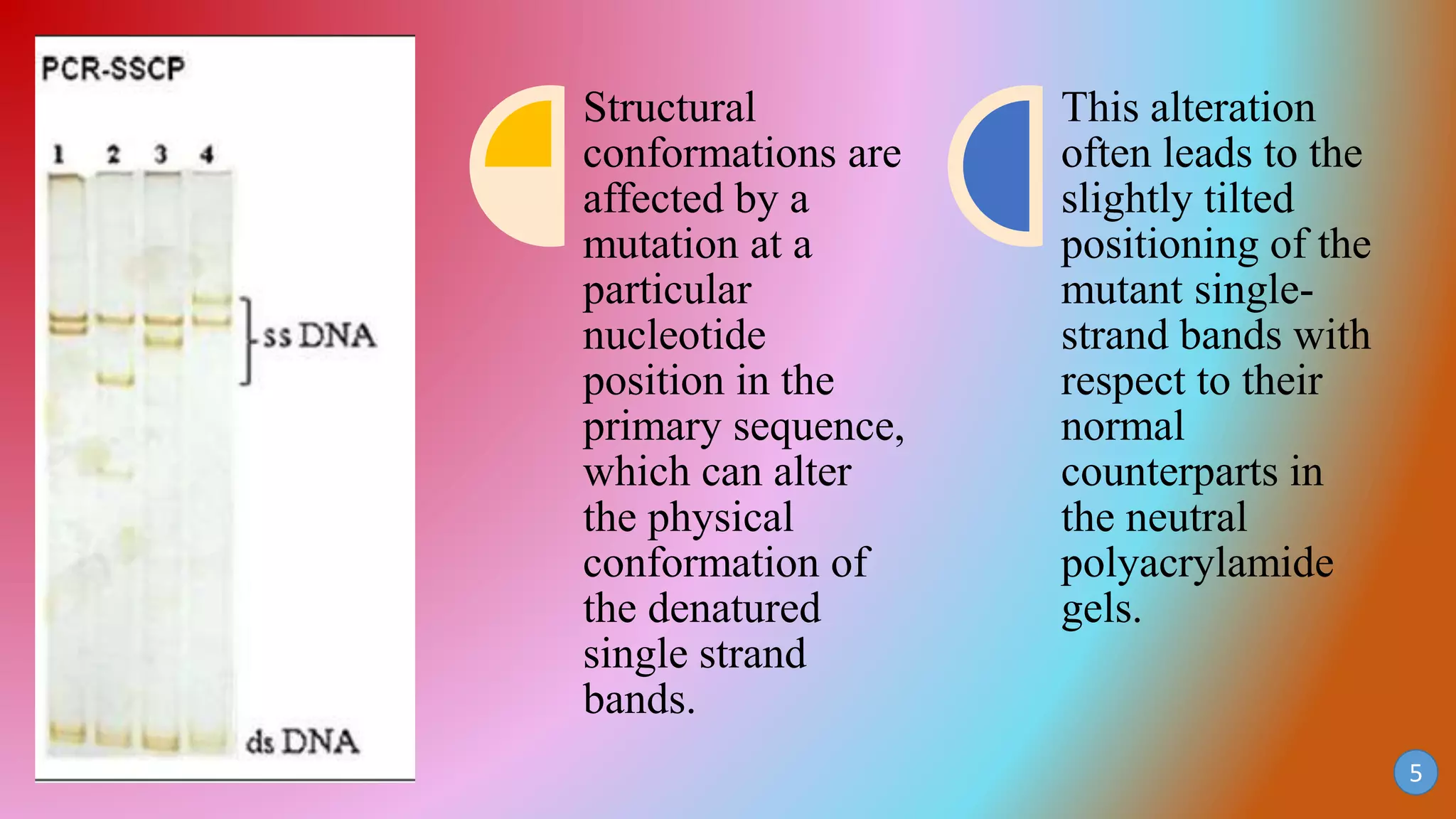
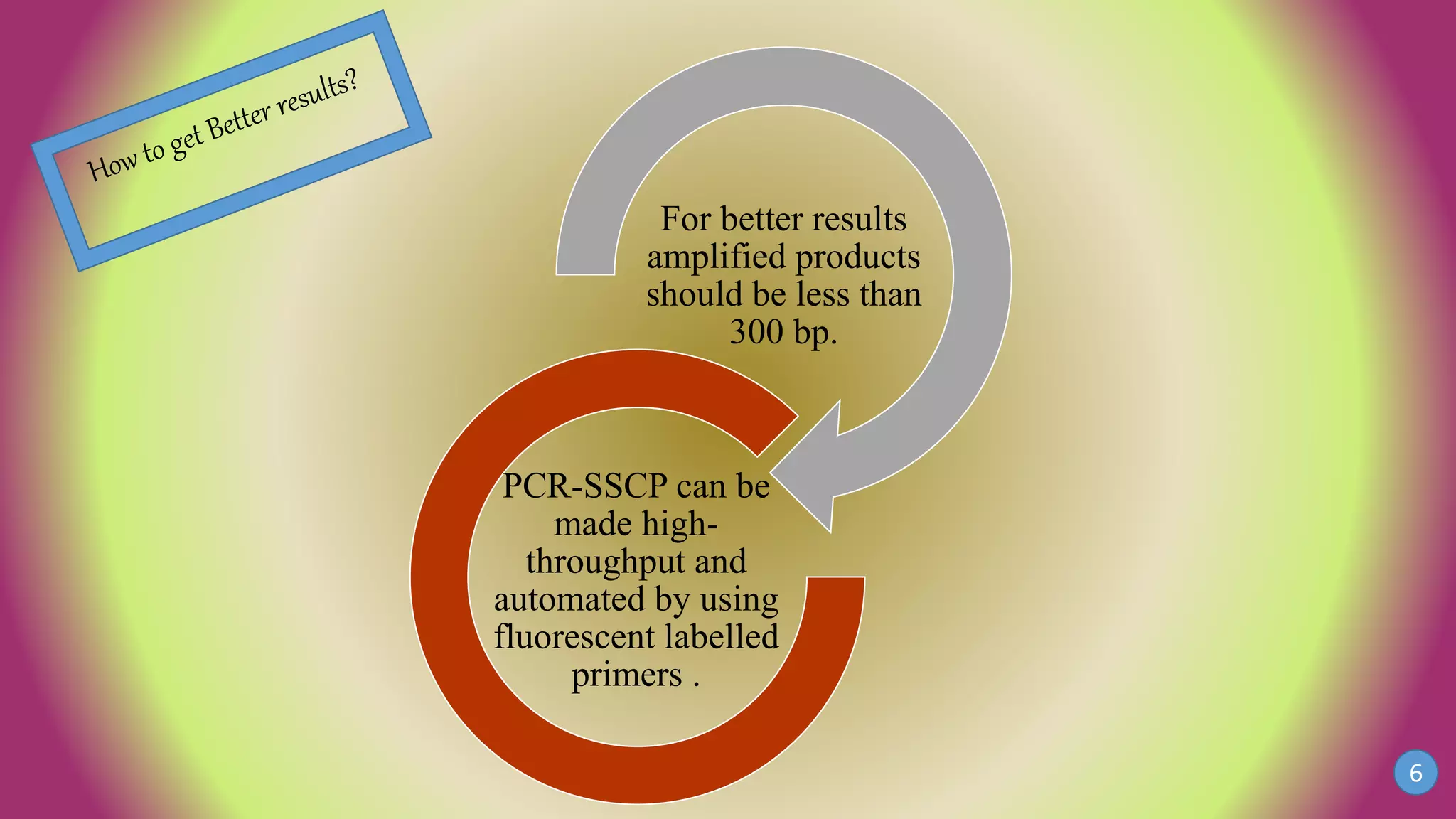
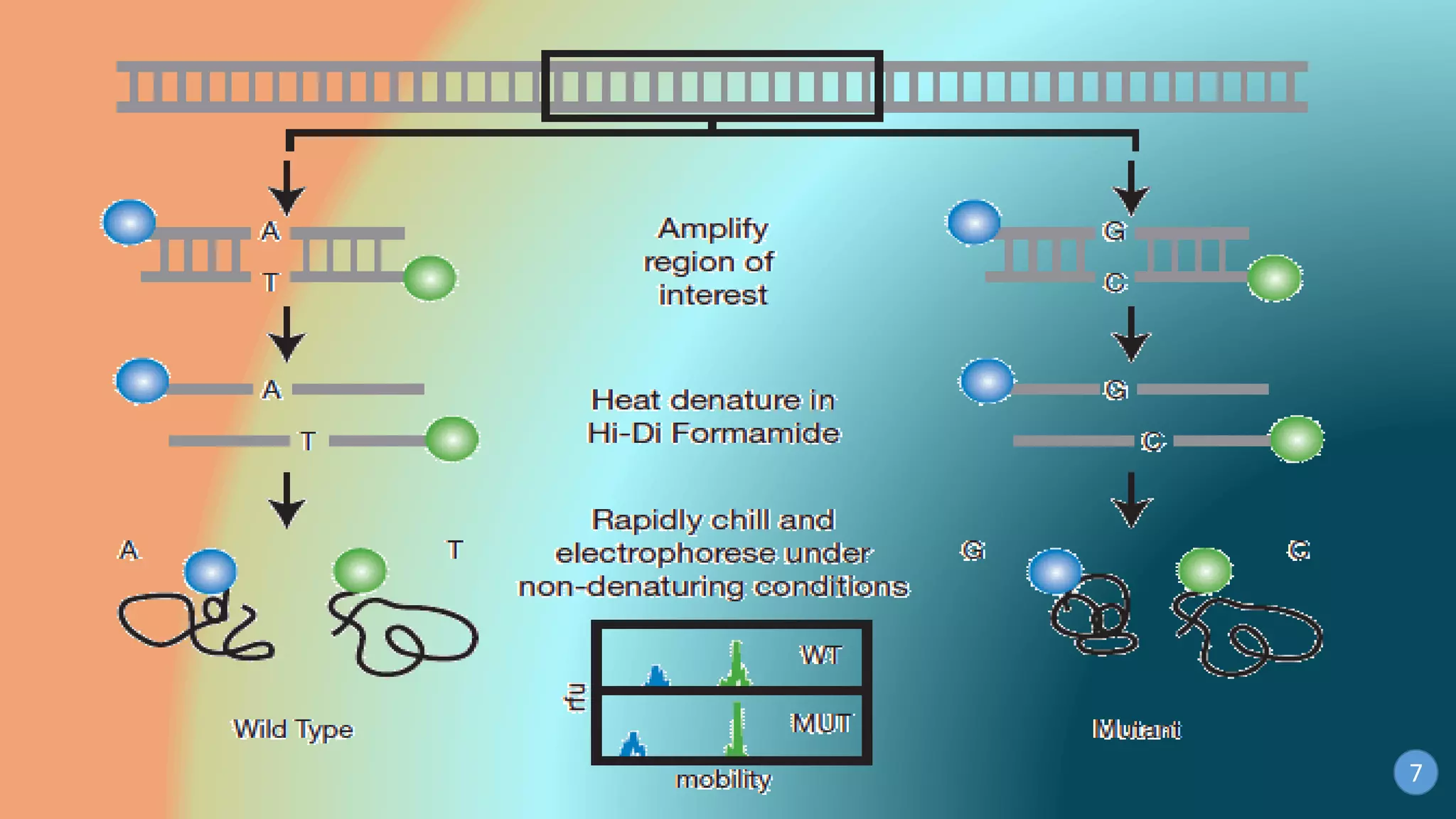
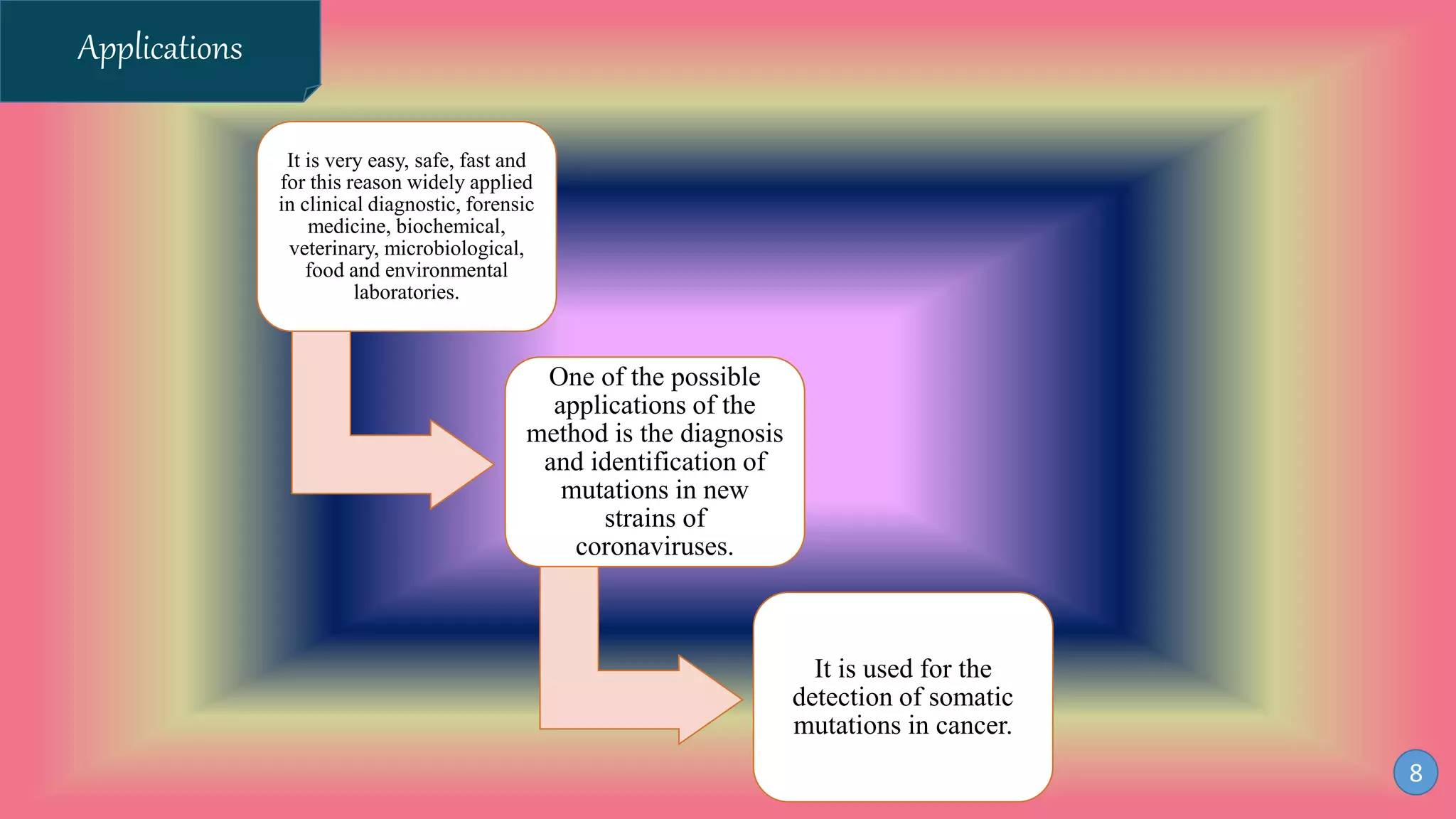
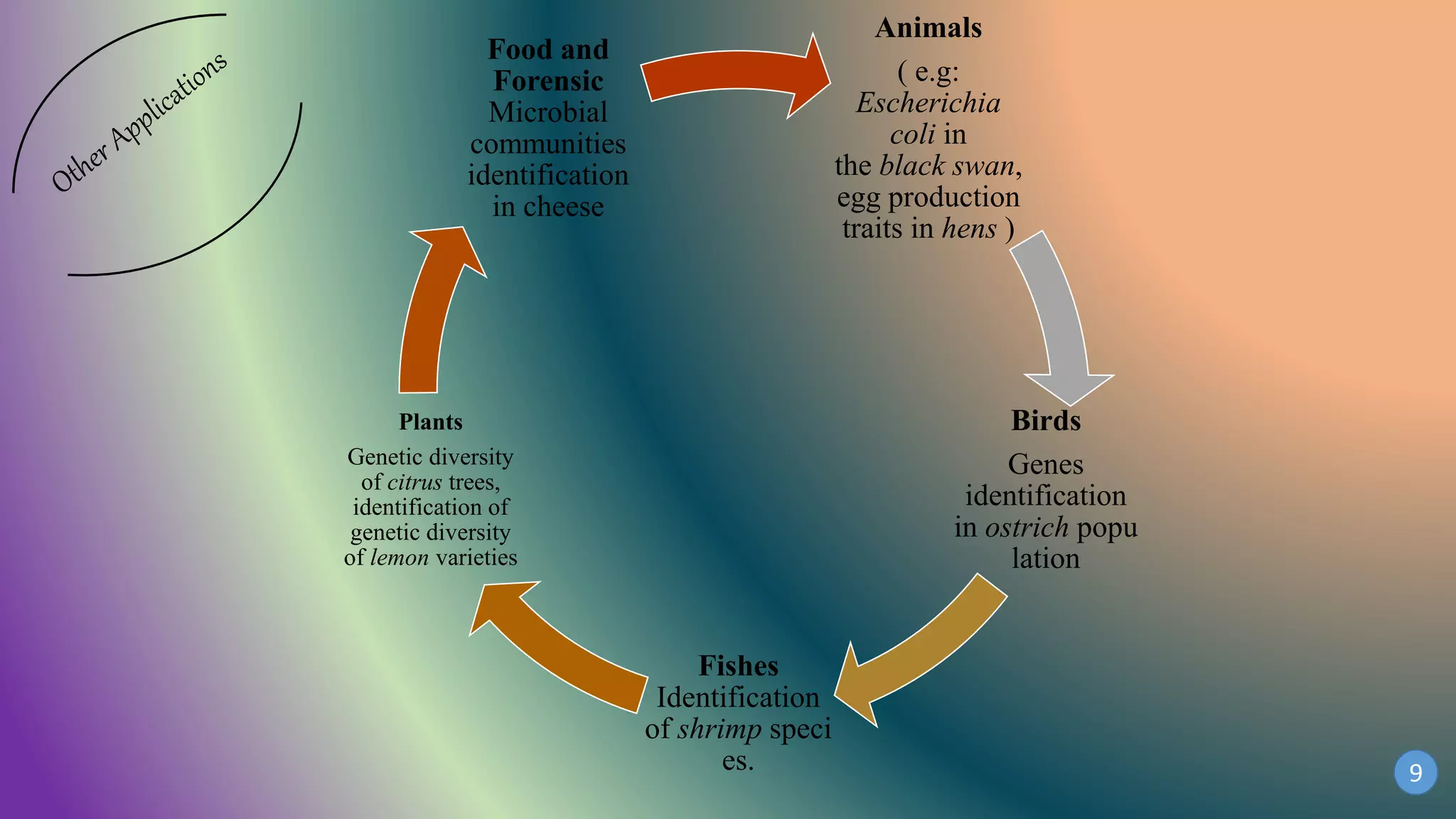
This document discusses PCR-SSCP (single-strand conformation polymorphism) analysis, which is a sensitive technique for detecting mutations. It works by separating double-stranded PCR products into single strands, which take on conformations depending on their sequence. Minor mutations can alter the conformation and cause bands to shift on a gel. The technique is useful for detecting unknown single nucleotide polymorphisms and has various applications in clinical diagnosis, forensics, and studying genetics in animals, plants, and microbes.