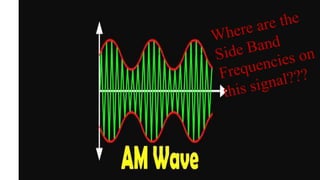
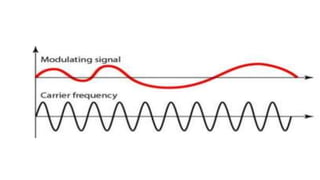
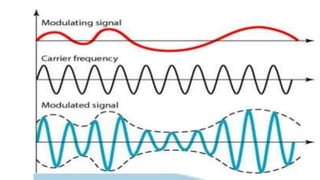
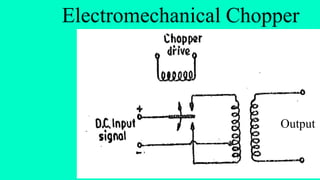
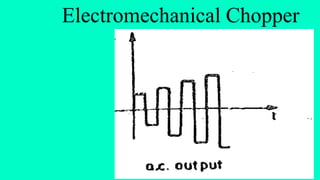
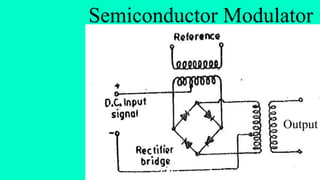
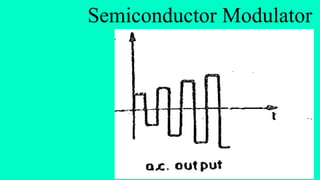
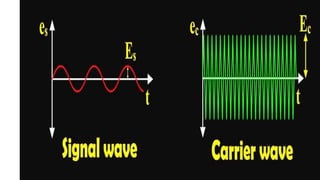
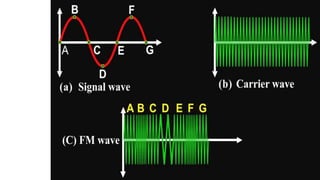
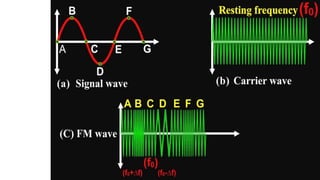
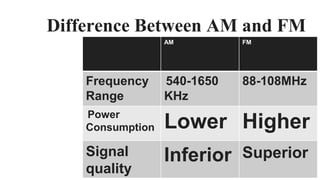
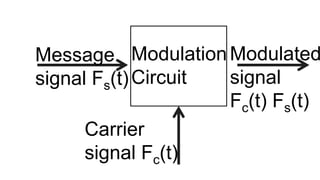
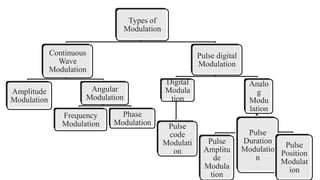
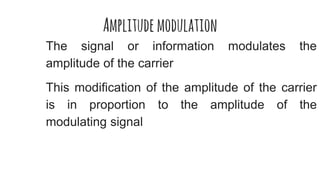
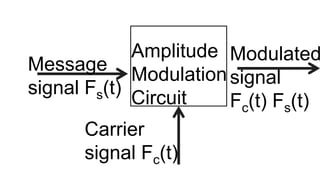
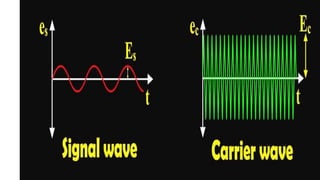
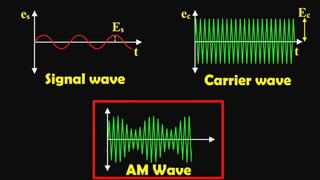
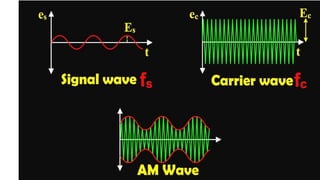
The document discusses modulation techniques. Modulation involves imposing information onto a carrier signal by varying its amplitude, frequency, or phase. Specifically, it describes amplitude modulation where the amplitude of the carrier wave is varied proportionally to the amplitude of the message signal. It provides the mathematical representations of the carrier and message signals and how they are multiplied to generate the modulated signal. It also discusses uses of amplitude modulation in applications like air band radio.









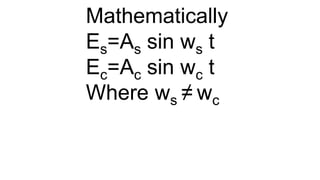
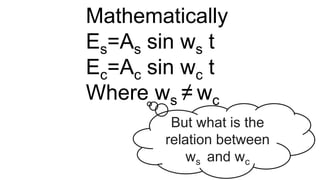
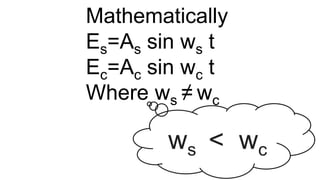
![Output = (As sin ws t)( Ac sin wc t)
= AsAc [cos(wc-ws)t – cos (wc+ws)t]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulation-190427205138/85/Modulation-23-320.jpg)
![Output = (As sin ws t)( Ac sin wc t)
= AsAc [cos(wc-ws)t – cos (wc+ws)t]
2
Side Band Frequencies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulation-190427205138/85/Modulation-24-320.jpg)