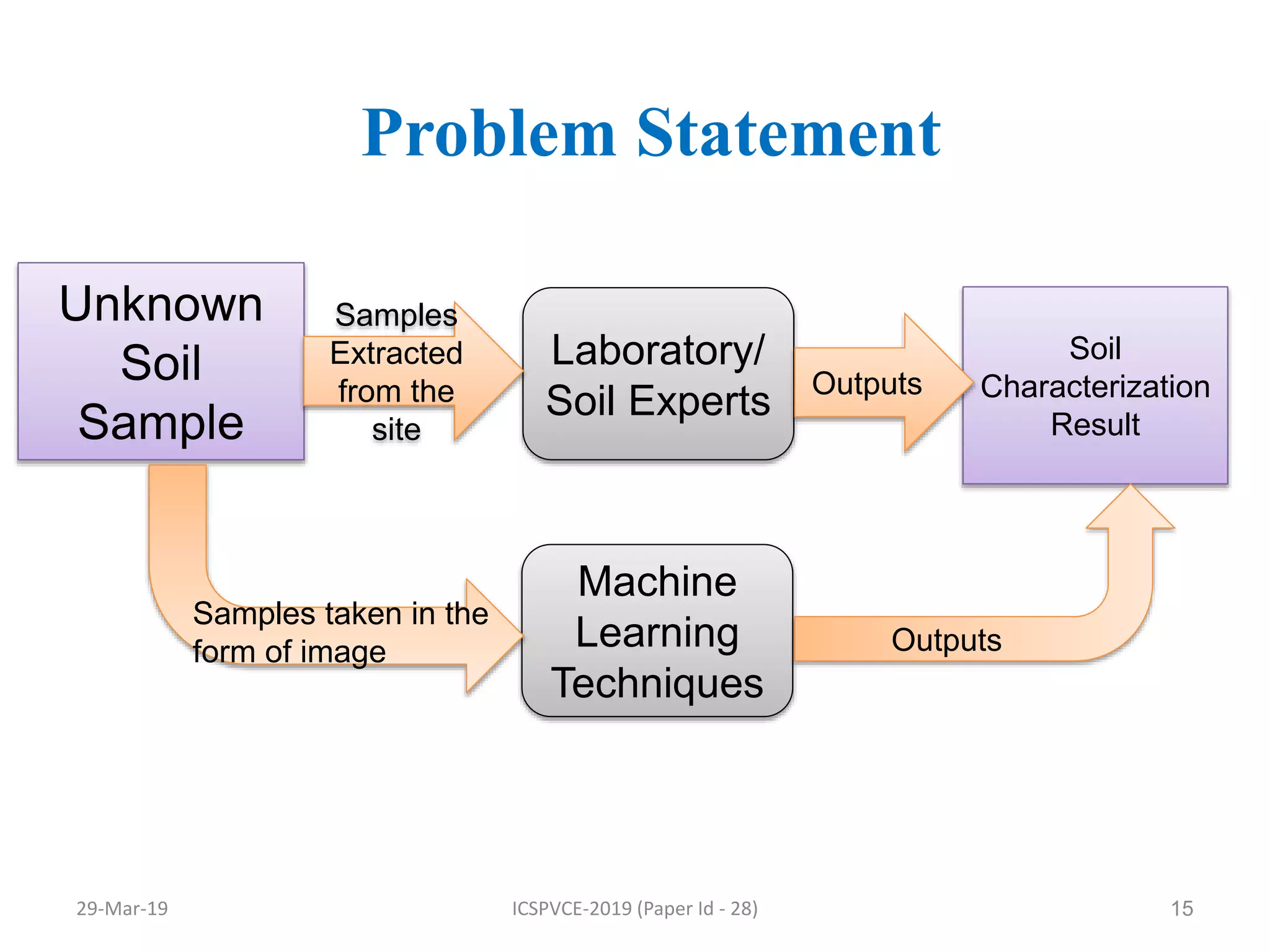
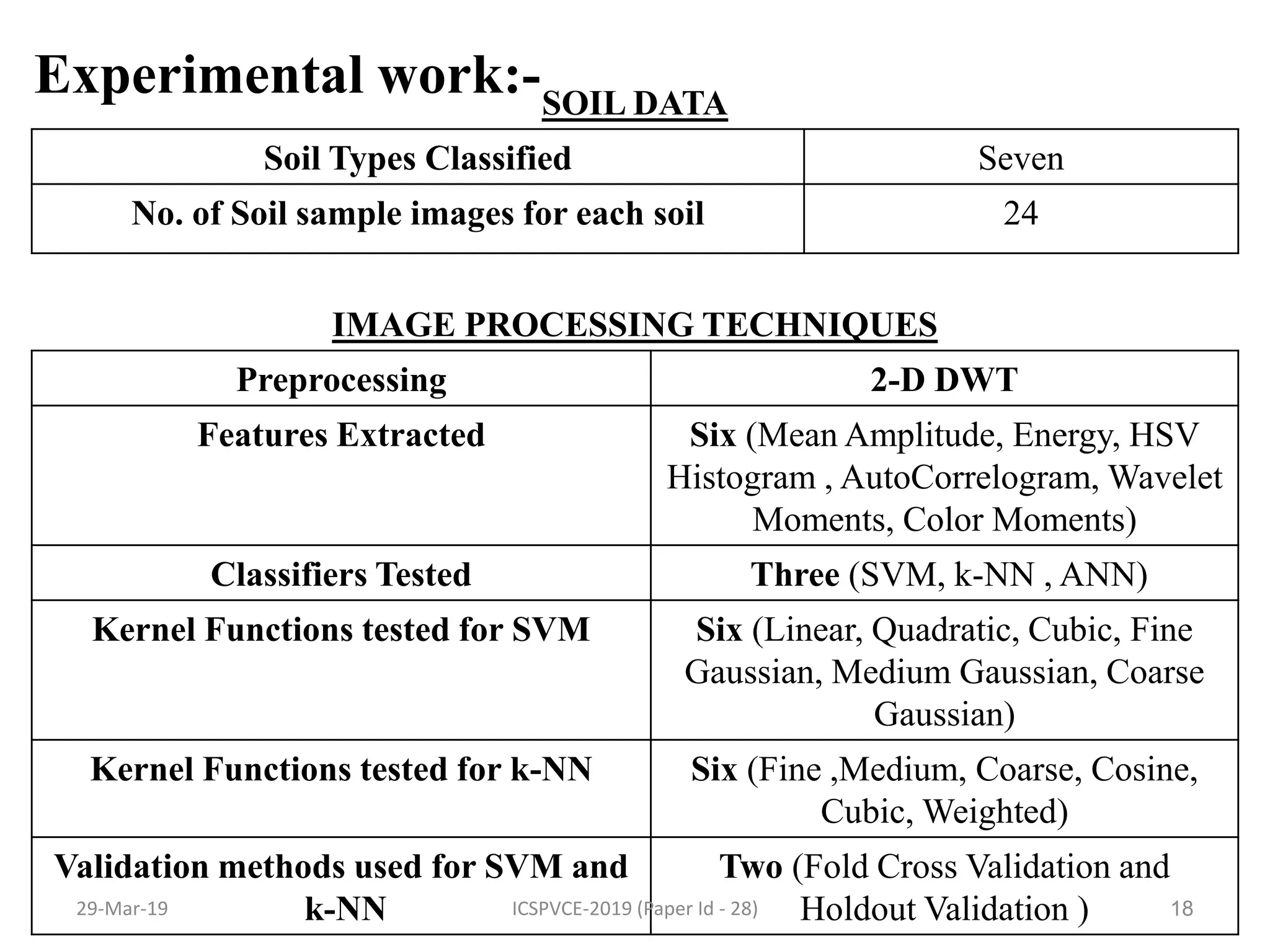
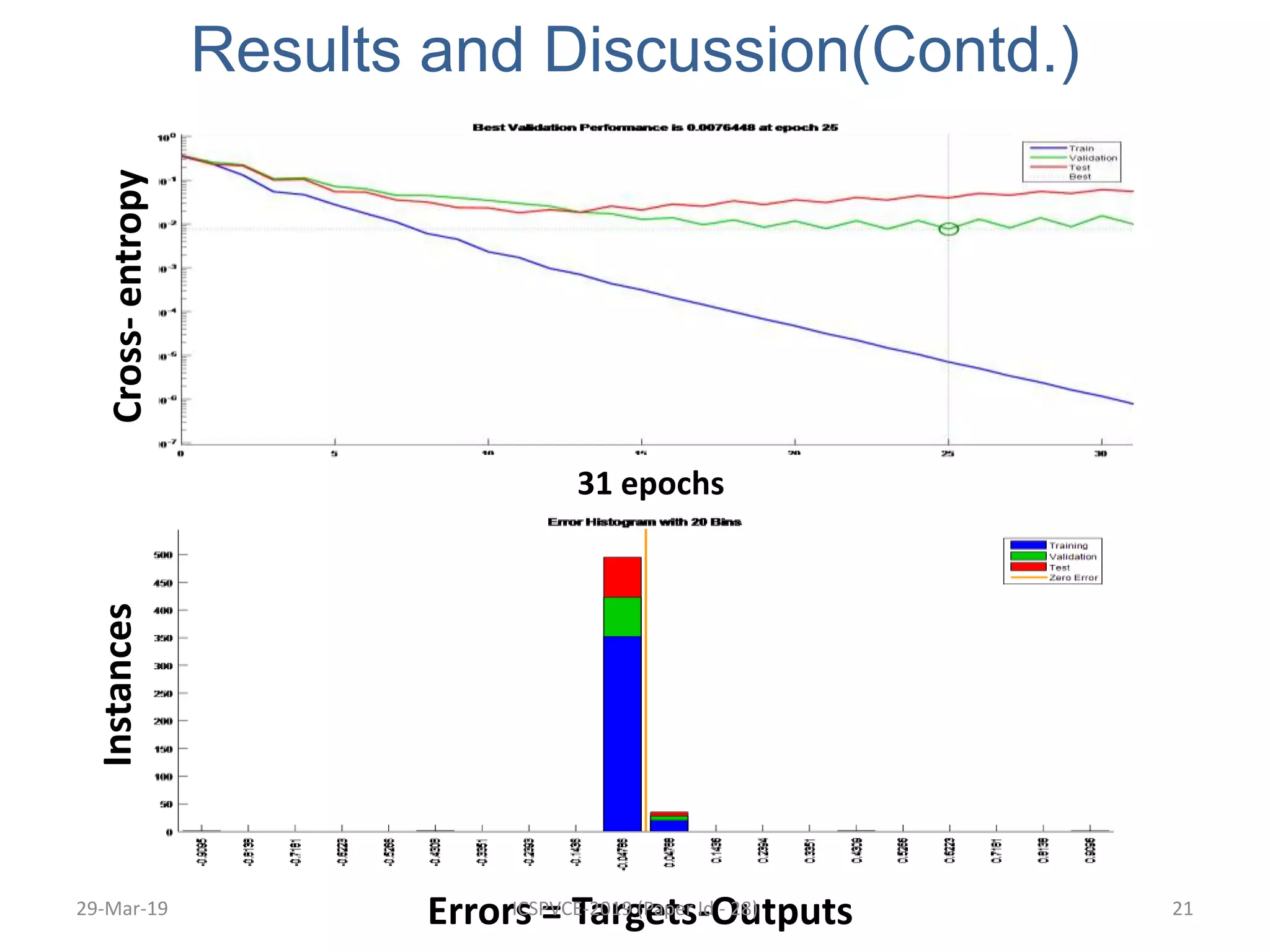
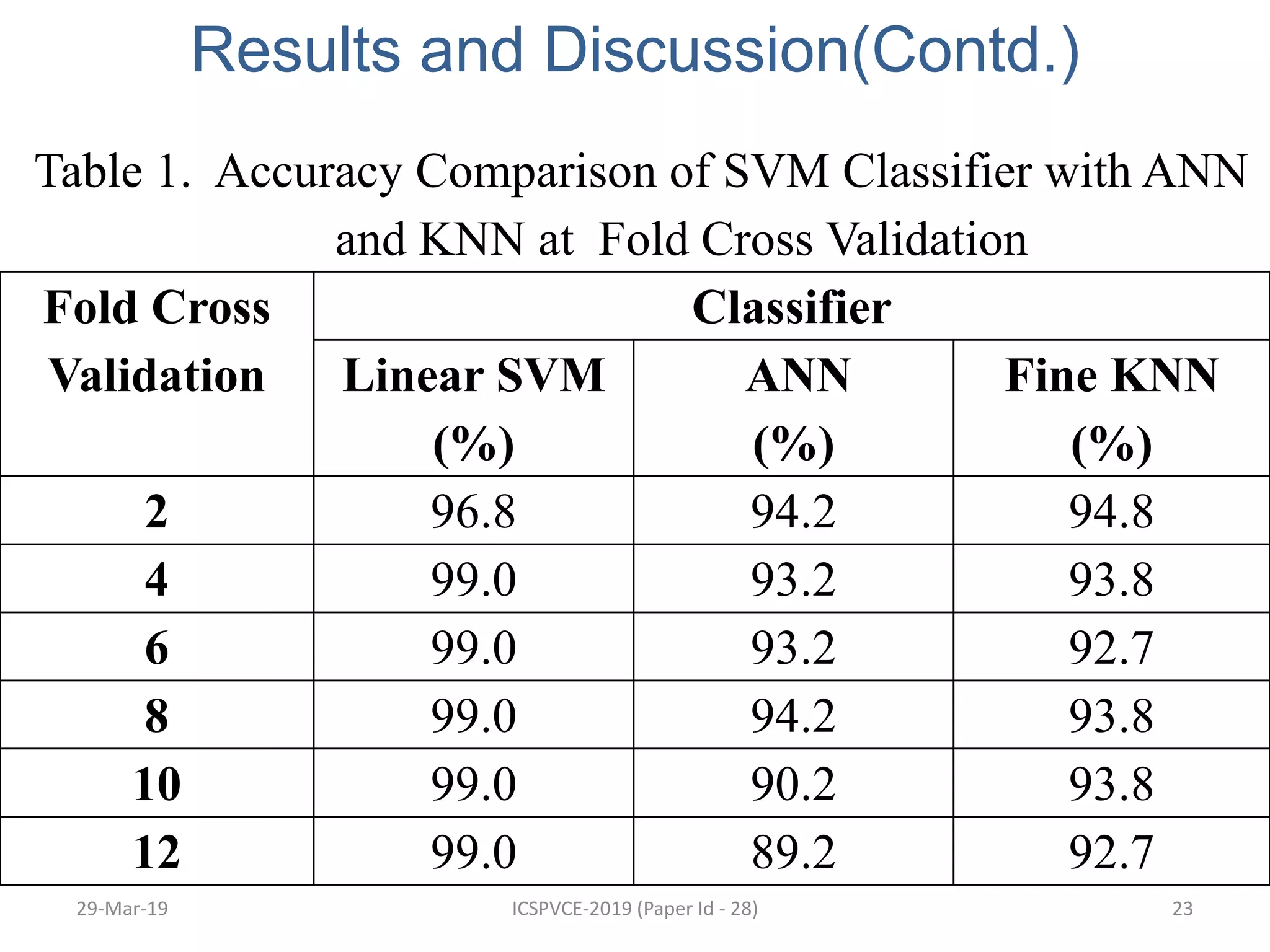
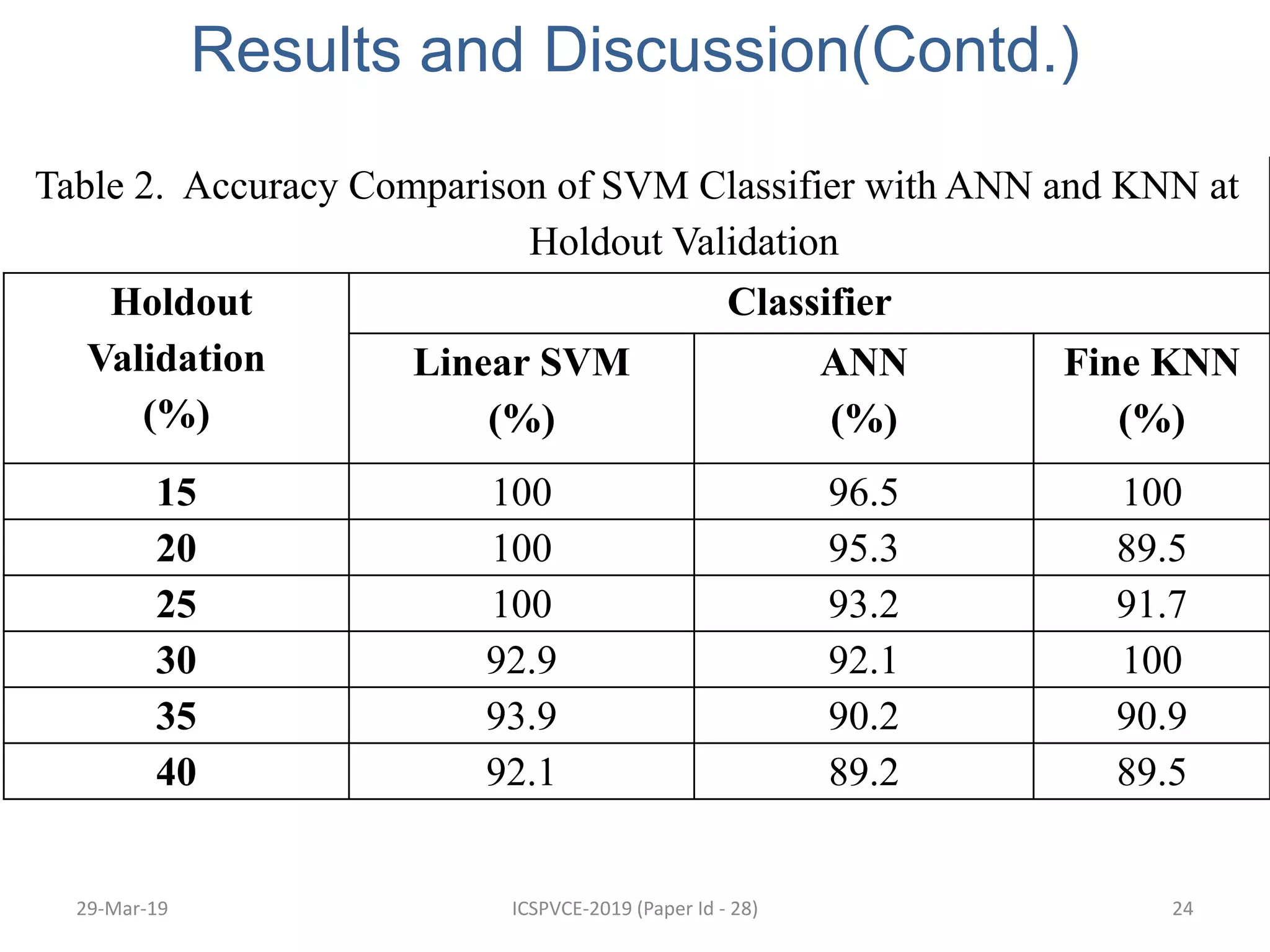
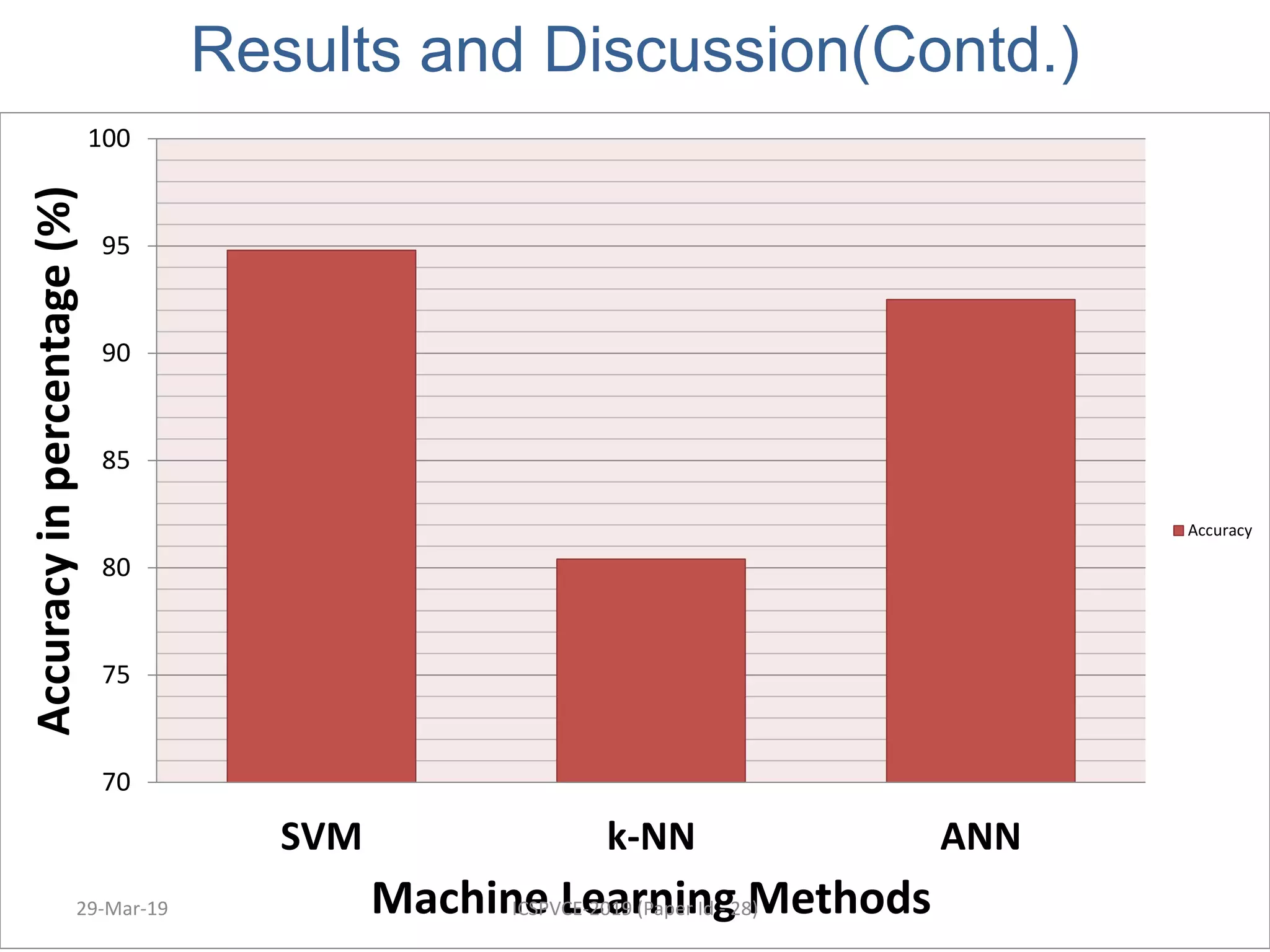
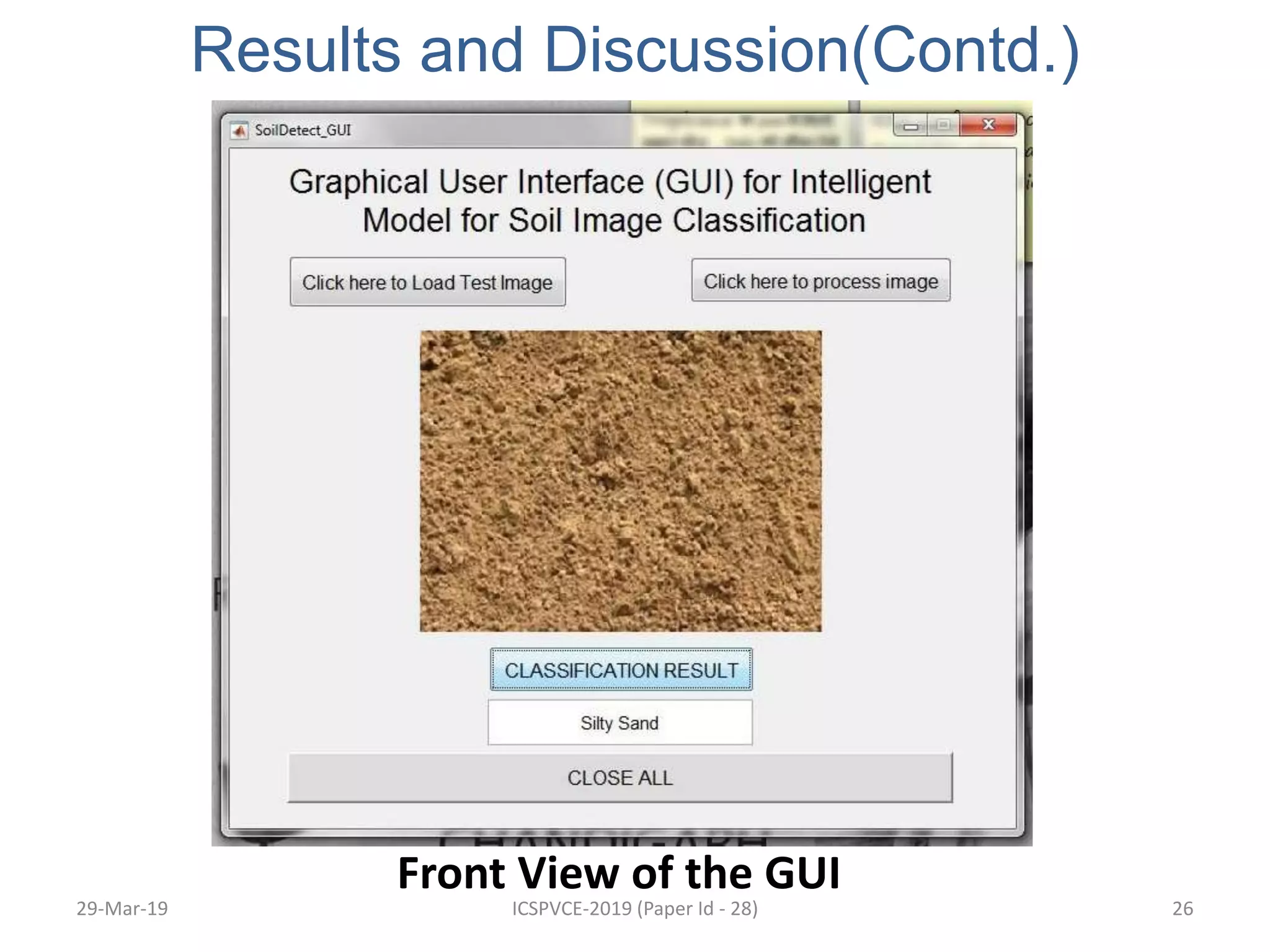
The document presents a machine learning model for soil image classification. It introduces soil classification and machine learning techniques like supervised and unsupervised learning. Feature extraction from soil images and classifiers like SVM, k-NN and ANN are discussed. Experimental results show SVM achieved highest accuracy of 99% for classifying 7 soil types, outperforming ANN and k-NN. A GUI was developed for easy soil classification using the model.




![13
Initial findings from Literature
Review
Prior to the construction of engineering structures,
it is required to inspect the site to determine its
suitability for the intended structure[1].
Four major in situ tests include Standard
Penetration Test (SPT)[2], Cone Penetration Test
(CPT)[3], Pressure Meter Test (PMT)[4], and Vane
Shear Test (VST).
Image classification using ML refers to the process
of labeling a wide set of images into a number of
predefined categories, decided by the user’s
requirement[5].
29-Mar-19 ICSPVCE-2019 (Paper Id - 28)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptpaperid28-190401110001/75/AN-INTELLIGENT-MACHINE-LEARNING-MODEL-FOR-SOIL-IMAGE-CLASSIFICATION-13-2048.jpg)
![14
Inferences Drawn out of
Literature Review
With the advancement of image
classification research procedures, many
advance techniques for classification such as
ANN, SVM, Fuzzy classification and k-NN
have been developed[6][7].
SVM has been identified as a better method
than ANN and k-NN for classification[8].
29-Mar-19 ICSPVCE-2019 (Paper Id - 28)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptpaperid28-190401110001/75/AN-INTELLIGENT-MACHINE-LEARNING-MODEL-FOR-SOIL-IMAGE-CLASSIFICATION-14-2048.jpg)






![28
References
[1]. BB Mishra. “Indian System of Soil Classification: A way
Forward”, Agri Res & Tech, vol. 3, no.2, 2016.
[2]. Wazoh, H. and Mallo, “Standard Penetration Test in
Engineering Geological Site Investigations – A Review”, The
International Journal Of Engineering And Science, vol 3, no.
7, pp. 40-48, 2014
[3]. Adrian-Traian Iliesi, Ana-Luciana Tofan And Diego Lo
Presti .2012. “Use Of Cone Penetration Tests And Cone
Penetration Tests With Porewater Pressure Measurement
For Difficult Soils Profiling”, Bul. Inst. Polit. Iaşi, T. Lviii ,Vol.
3,2012
[4]. Frikha, Wissem & burlon, Sebastien & Monaco, Paola,”
Session report: Pressure meter and Dilatometer” , 2016.
29-Mar-19 ICSPVCE-2019 (Paper Id - 28)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptpaperid28-190401110001/75/AN-INTELLIGENT-MACHINE-LEARNING-MODEL-FOR-SOIL-IMAGE-CLASSIFICATION-28-2048.jpg)
![29
References (Contd.)
[5]. Bhattacharya, Biswanath, and Dimitri P. Solomatine.
"Machine learning in soil classification", Neural networks ,
vol.19, no.2, pp.186-195,2006.
[6]. Ashwini Rao, Janhavi, Abhishek Gowda, Manjunath,
Mrs. Rafega Beham, “Machine Learning in Soil Classification
and Crop Detection”, International Journal for Scientific
Research & Development, Vol. 4, No. 1, 2016
[7]. MilošKovačević ,BranislavBajat, Boško Gajić, “Soil type
classification and estimation of soil properties using support
vector machines”, Geoderma, Vol. 154, pp. 340–347, 2010
[8]. Małgorzata Charytanowicz and Piotr Kulczycki, An
Image Analysis Algorithm for Soil Structure Identification,
Intelligent Systems, Vol. 323, pp. 681-691, 2015
29-Mar-19 ICSPVCE-2019 (Paper Id - 28)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptpaperid28-190401110001/75/AN-INTELLIGENT-MACHINE-LEARNING-MODEL-FOR-SOIL-IMAGE-CLASSIFICATION-29-2048.jpg)
