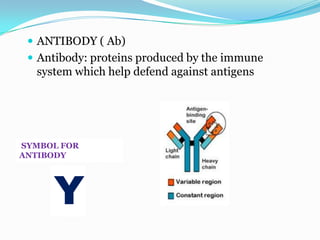
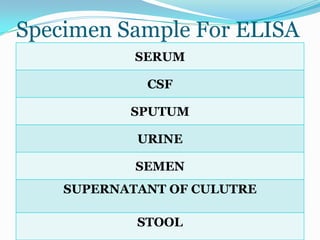
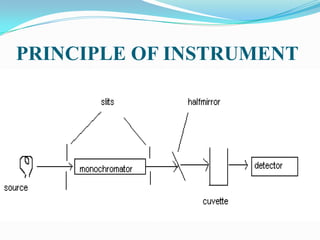
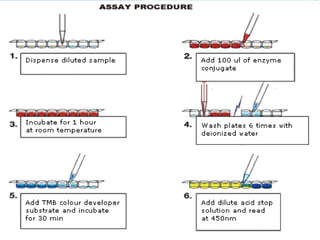
This document provides an introduction and overview of the ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) technique. It explains that ELISA uses an enzyme to detect the binding of antigens and antibodies, with the enzyme converting a colorless substrate to a colored product. The document outlines the basic principles and steps of ELISA, including coating a plate with antigens, adding primary and secondary antibodies, adding an enzyme substrate, and measuring the color change produced. It also discusses the different types of ELISA (e.g. indirect sandwich, competitive), materials needed, and applications for detecting various targets like hormones, proteins, infectious agents, and more.