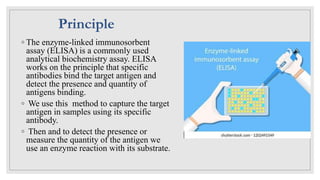
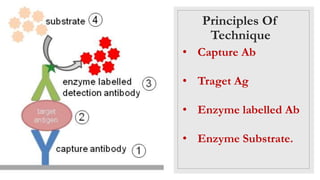
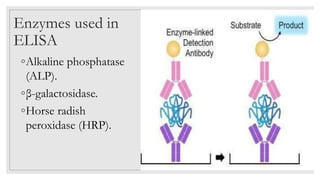
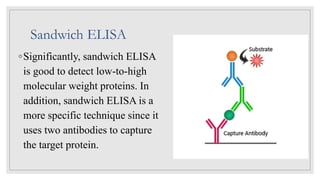
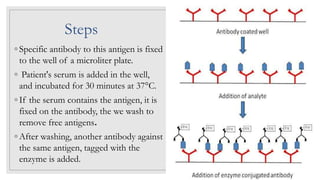
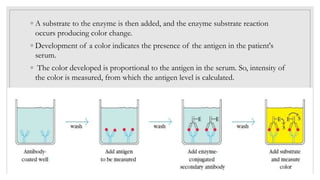
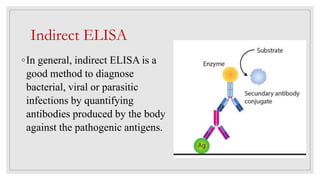
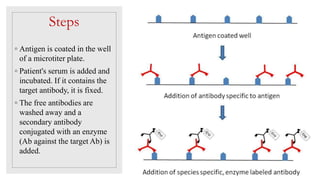
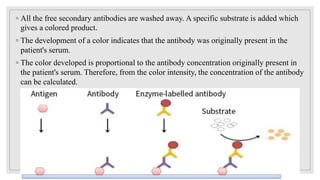
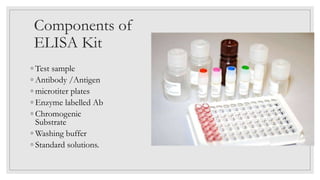
The document discusses the ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) technique. ELISA is used to detect the presence and quantity of antigens or antibodies in samples. It works by capturing the target antigen or antibody using specific antibodies attached to a microwell plate. An enzyme-linked antibody is then used to detect the captured target, and a color change reaction indicates a positive result. Common applications include detecting hormones, viruses, bacteria, and antibodies in blood samples. There are two main types: indirect ELISA detects antibodies, while sandwich ELISA detects antigens.