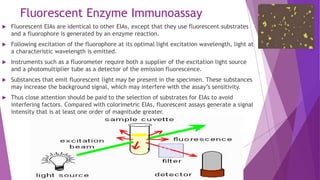
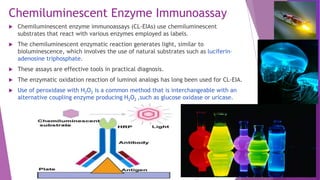
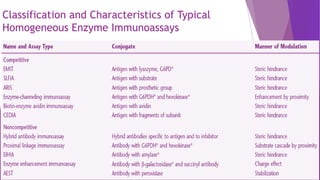
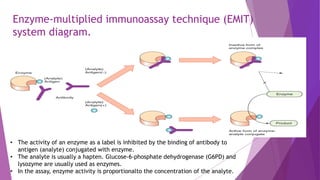
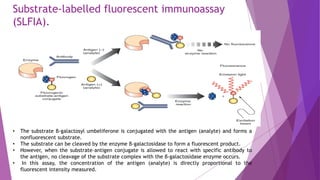
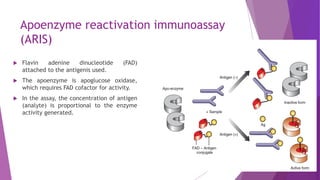
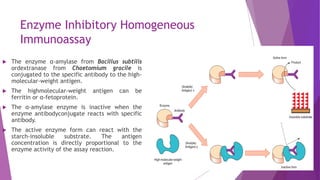
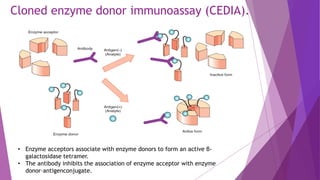
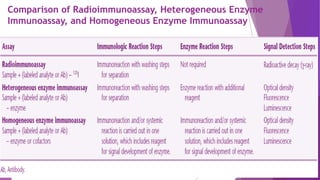
Radioimmunoassay (RIA) and enzyme immunoassay (EIA) techniques allow for the quantitative detection of analytes at trace levels. RIA uses radioisotopes as labels, while EIA uses enzymes. Both techniques can be formatted competitively or non-competitively. Variations include immunoradiometric assays, enzyme-multiplied immunoassay technique (EMIT), substrate-labeled fluorescent immunoassay (SLFIA), and apoenzyme reactivation immunoassay (ARIS). These assays find wide application in research, clinical medicine, and drug monitoring due to their high sensitivity and specificity.

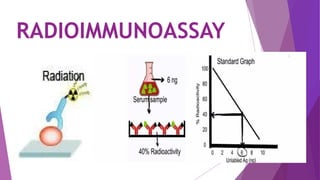


![RADIOIMMUNOASSAY
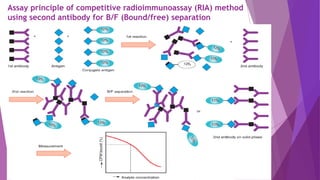
• The competitive assay follows:
THE LAW OF MASS ACTION
• The Scatchard plot of the ratio of bound to
free antibody to analyte concentration is
commonly used to evaluate antibody
performance.
• Kinetics of Antigen-Antibody Reaction section,
from the following equation:
B/F = Ka ([Ab]t − B)
Where, B = bound antigen or analyte
F = free antigen
• y-axis - B/F ratio that is proportional to free
[Ab] from [Ab]t − B , equal to free [Ag].
• Ka represents the slope of the plot.
Figure: Scatchard plot for
cyclosporine determination
The affinity constant Ka is 8.1 × 109 L/M
for the antibody specific to
cyclosporine.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immunoassaysdak-200404082423/85/Immunoassays-5-320.jpg)







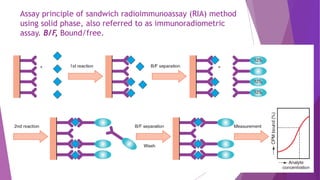





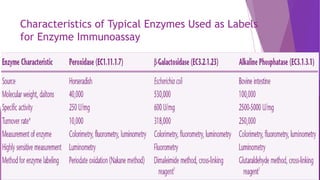

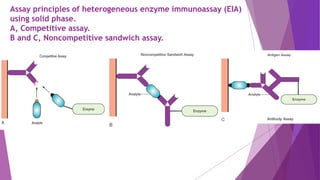
![Colorimetric Enzyme Immunoassay
In this assay, enzyme reaction is performed by using chromogenic
substrates to develop a color by prime catalytic reaction.
Example:
horseradish peroxidase, catalyzing ABTS (diammonium salt of 2,2′-
azinodi[{ 3-ethyl-benzothiazoline-6-sulfonate}]) with H2O2 to form a
green color
alkaline phosphatase specific to the p-nitrophenyl phosphate to form a
yellow color.
Both enzymes are the most commonly used types of colorimetric enzyme
immunoassays.
A spectrophotometer is used to measure the optical density of the
resulting chromogen.
Many instruments are available for the measurement of optical density in
tubes or microtiter plates, ranging from a fully automated system that
performs sample pipetting and data printout to simpler manual devices.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/immunoassaysdak-200404082423/85/Immunoassays-24-320.jpg)