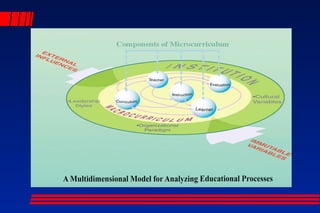
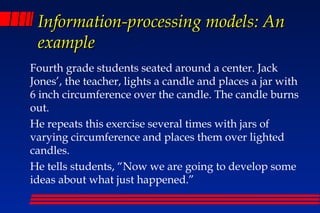
This document discusses models of teaching and their benefits. It describes four families of teaching models: information processing, social, personal, and behavioral. Each family is designed to achieve different purposes and outcomes. Models of teaching provide a framework to guide lesson planning and instruction, promote a common language among teachers and administrators, and help eliminate achievement gaps. They can accelerate learning by tailoring instruction to student needs. Both teachers and students benefit, as models of teaching improve instruction quality and increase student engagement, aptitude, and academic self-esteem. While models do not replace expertise, using a variety when planning lessons can meet diverse learning needs.