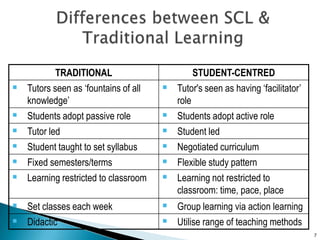
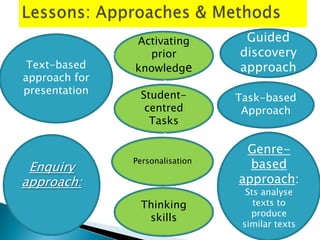
The document discusses approaches to student-centered learning and lesson planning. It describes student-centered learning as an approach where students are responsible for planning the curriculum or participating in choosing it. The document then outlines several approaches that can be used in student-centered lesson planning, including activating prior knowledge, guided discovery, enquiry approaches, task-based approaches, and genre-based approaches. It emphasizes learning by doing and using real-world tasks.