Embed presentation
Download to read offline
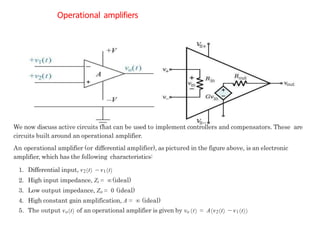
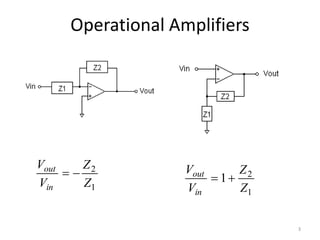
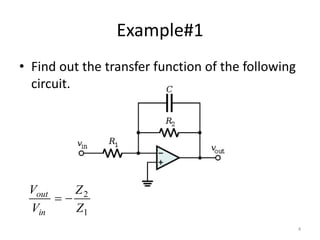
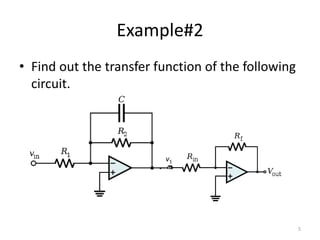
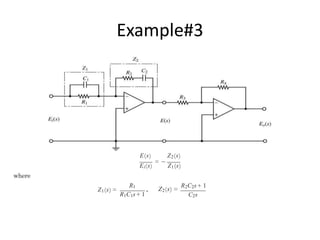
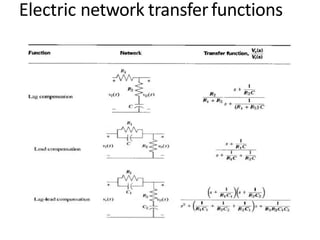
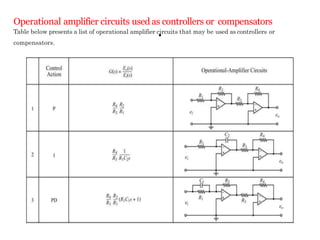
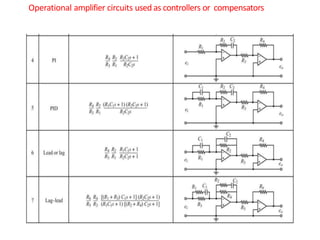

This document discusses modeling electronic systems using operational amplifiers. It provides operational amplifier basics, examples of calculating transfer functions of operational amplifier circuits, and discusses using operational amplifiers for lead/lag compensation and PID controllers. Specifically, it gives examples of calculating transfer functions, discusses electric network transfer functions, and provides a table of common operational amplifier circuits that can be used as controllers or compensators.








