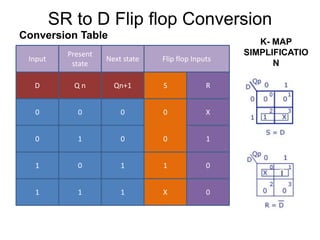
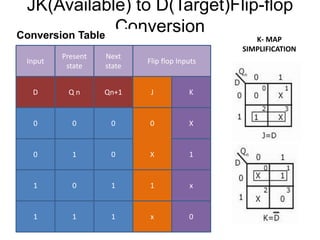
This document describes procedures for converting different types of flip-flops, including SR, JK, D, and T flip-flops. The procedures involve drawing block diagrams of the target flip-flop, writing truth tables, writing excitation tables, drawing K-maps, and developing conversion tables and logic diagrams. Examples are provided for converting an SR flip-flop to a D flip-flop, an SR flip-flop to a JK flip-flop, and several other common flip-flop conversions.