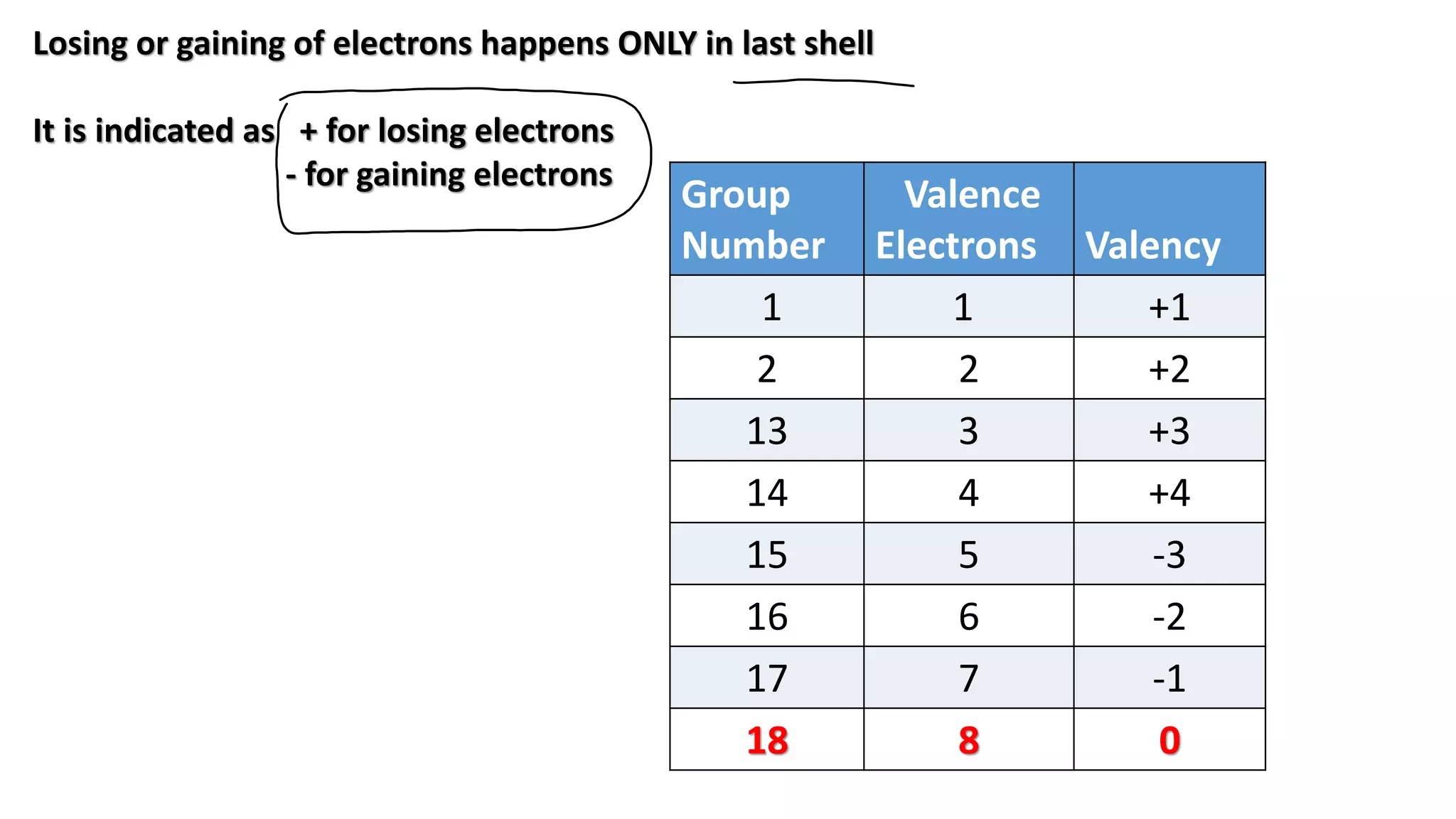
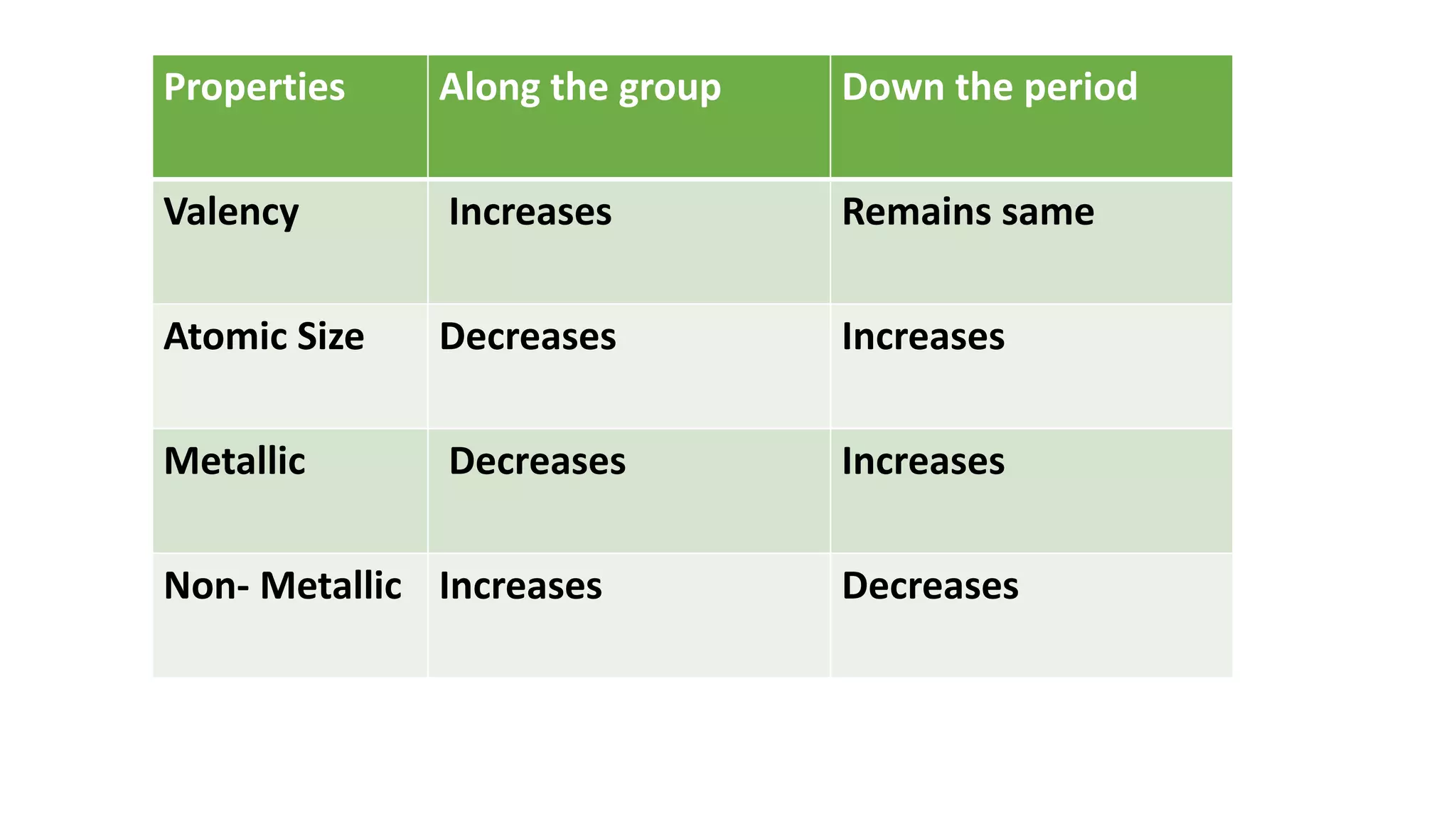
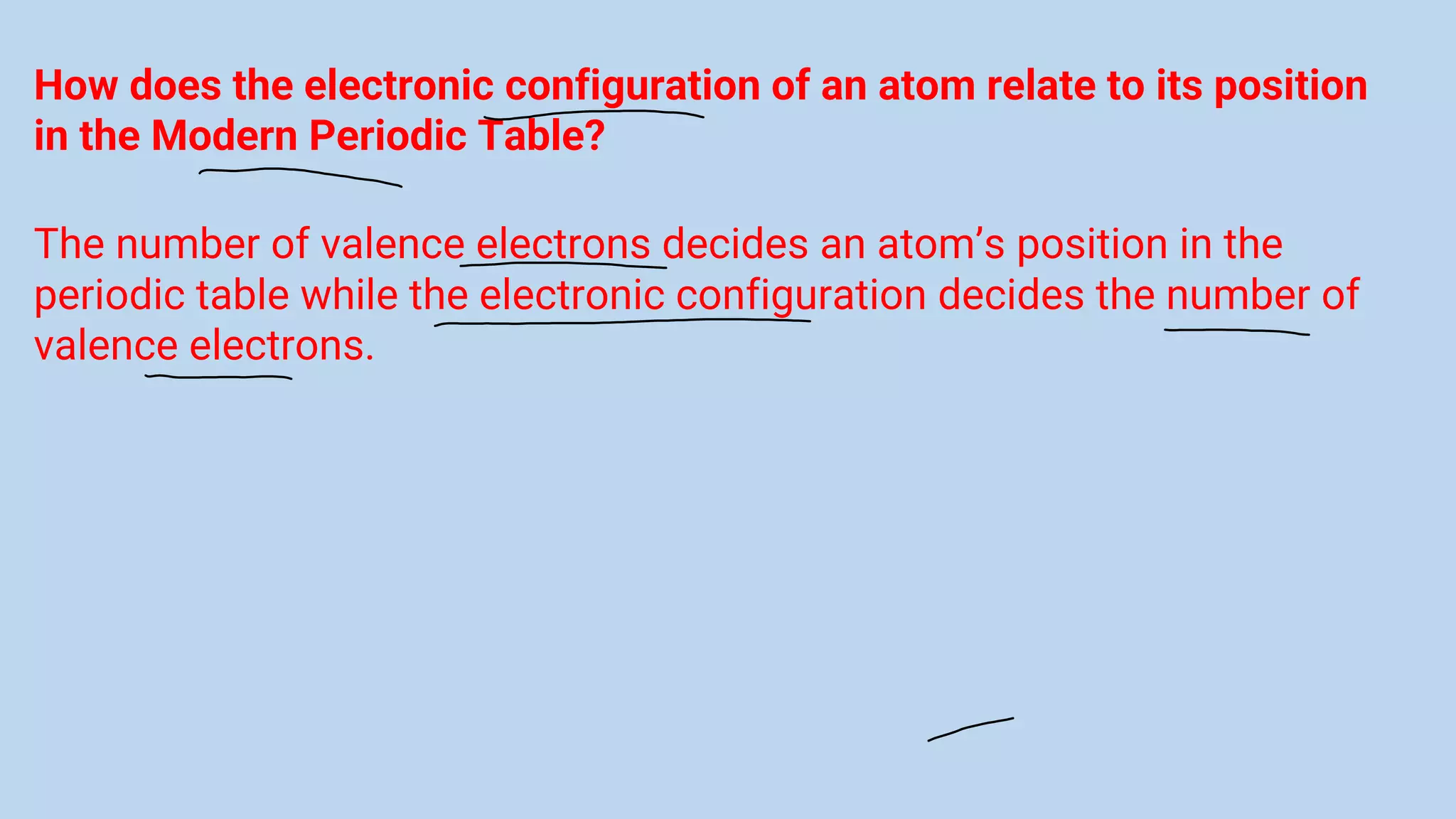
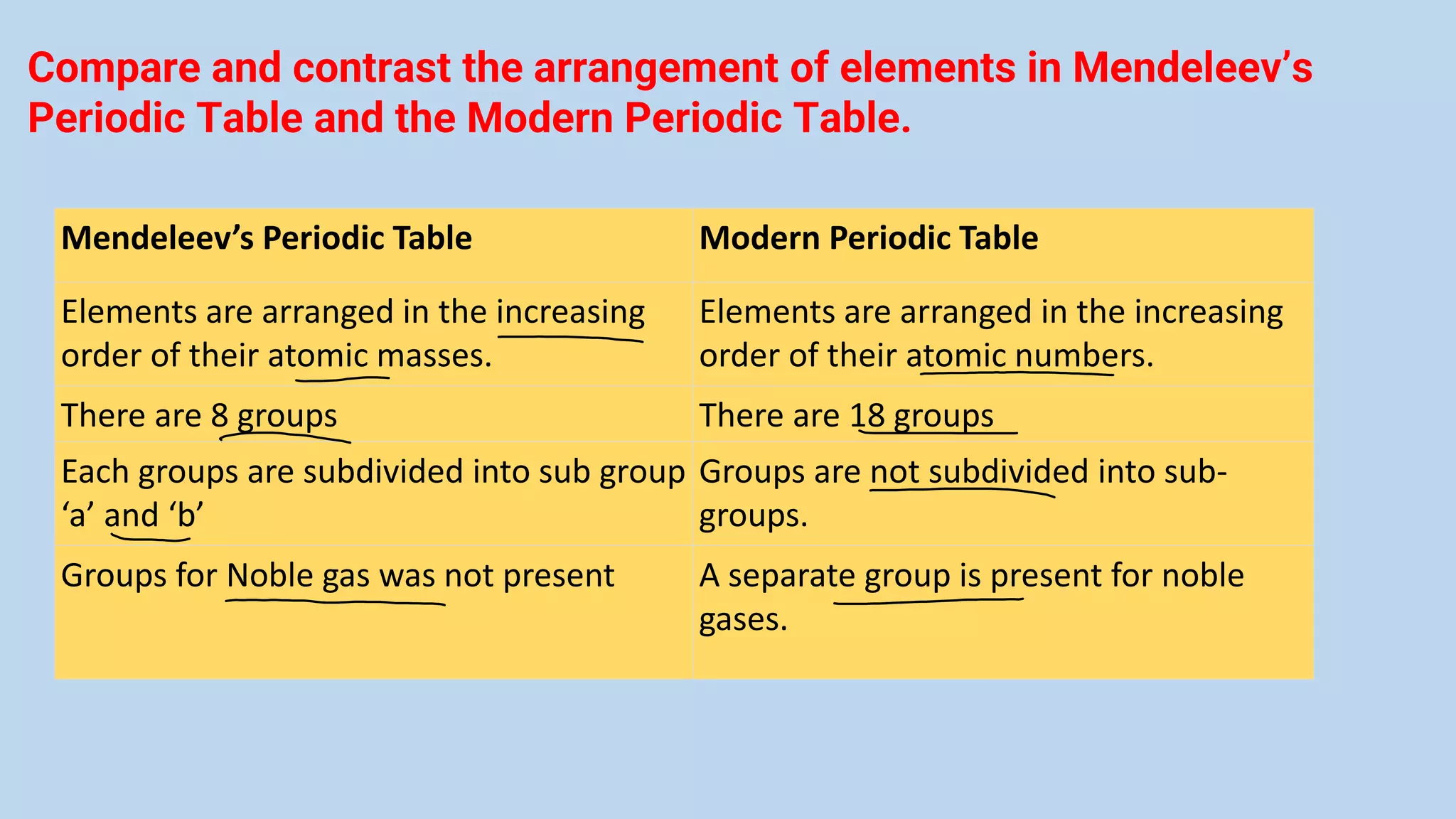
The document discusses the modern periodic table, highlighting its structure with 18 groups and 7 periods, and key concepts such as periodicity, valency, atomic size, and the properties of elements. It contrasts Mendeleev’s periodic table, which was based on atomic mass, with the modern table that uses atomic number, also explaining trends like metallic and non-metallic character. Additionally, it provides probable exam questions related to periodic law and the arrangement of elements.