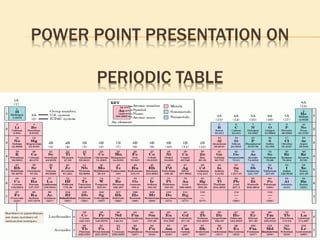
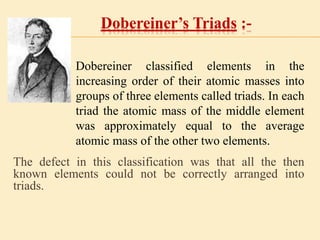
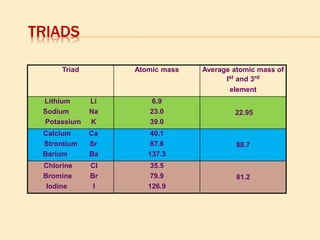
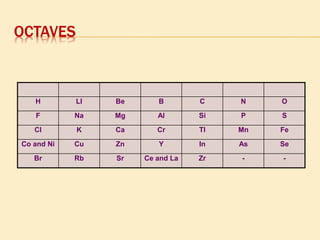
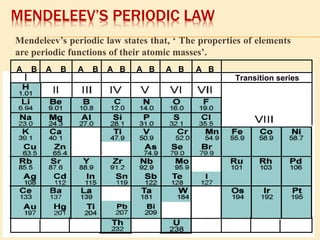
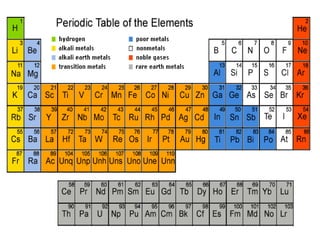
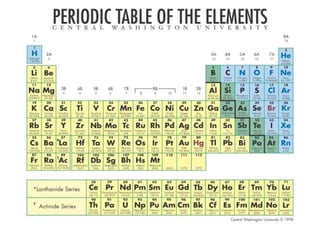
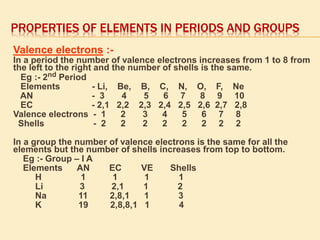
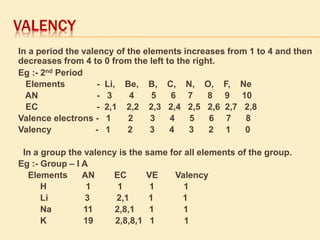
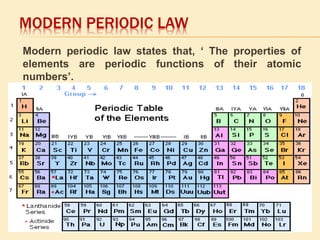
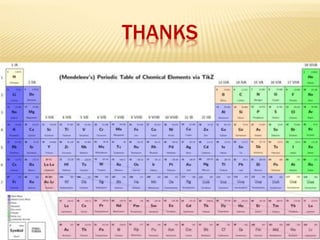
This document is a PowerPoint presentation on the periodic table submitted by a student named Sreekala T. It provides a brief history of how the periodic table developed from early classifications by scientists like Lavoisier, Dobereiner, and Newlands. It describes Mendeleev's periodic table and the improvements made in the modern periodic table, which arranges elements by atomic number instead of mass. Key aspects of the periodic table like periods, groups, valence electrons, and periodic trends in properties are summarized.