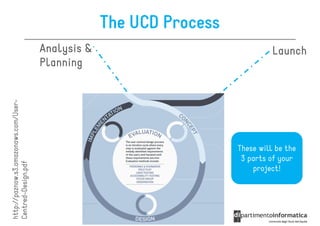
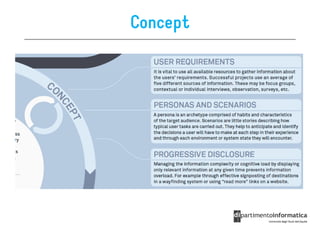
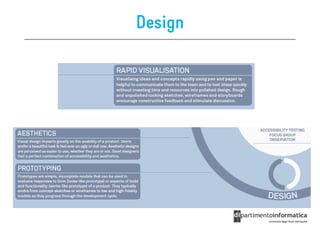
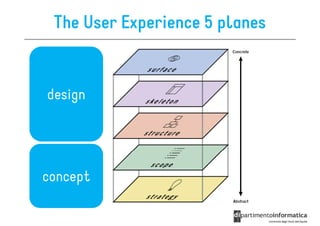
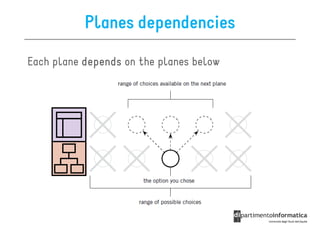
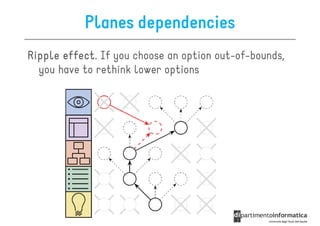
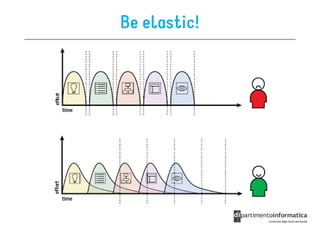
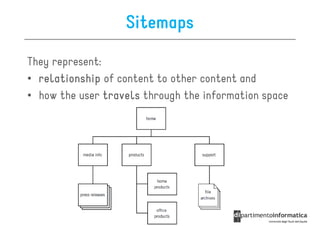
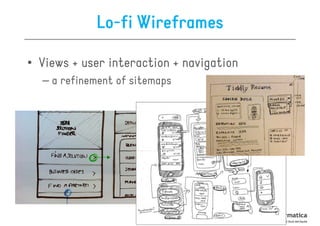
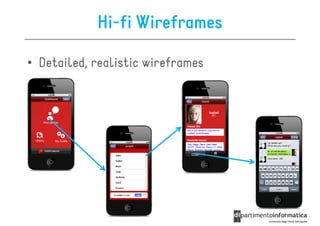
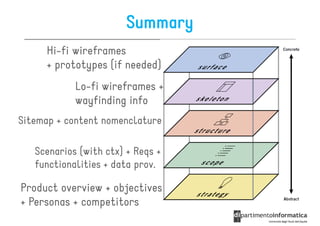
The document discusses user-centered design (UCD), which is a design philosophy focusing on the end user's needs, wants, and limitations during the design process to ensure high usability. It outlines various stages of the UCD process including user analysis, testing, and the creation of personas, as well as the key elements that contribute to an effective user experience. Additionally, it explores the importance of prototyping and the different types of wireframes used to visualize and test design concepts.