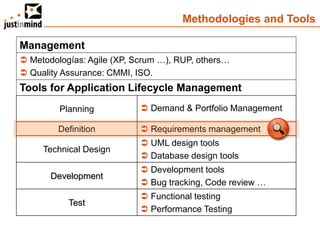
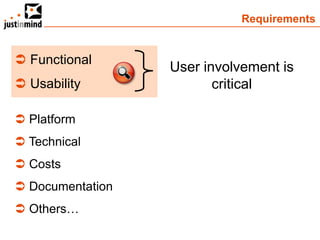
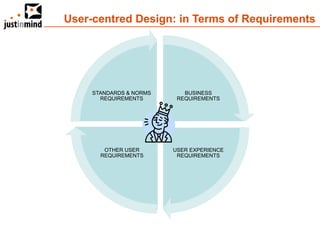
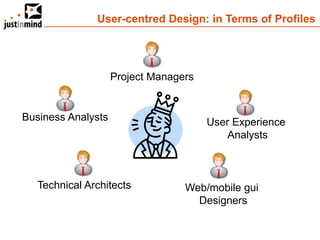
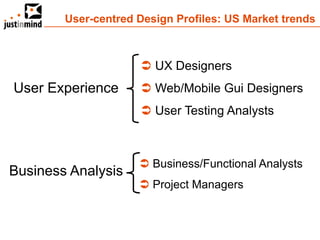
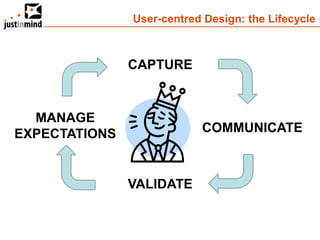
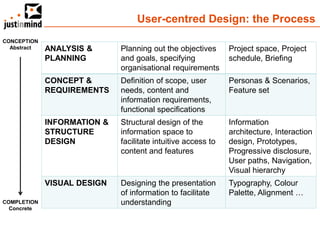
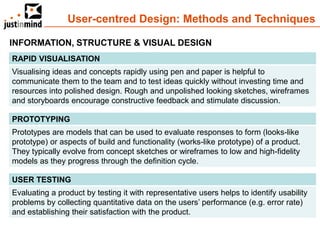
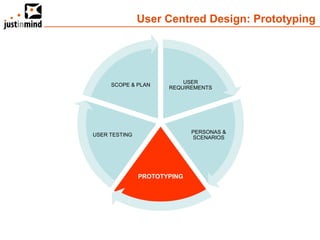
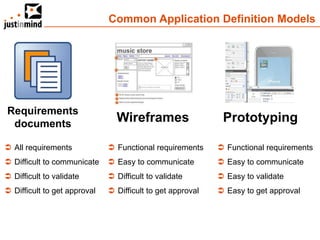
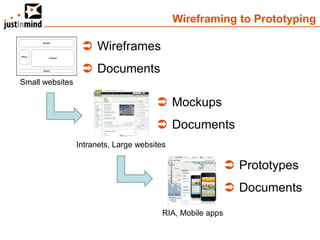
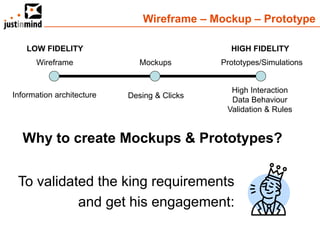
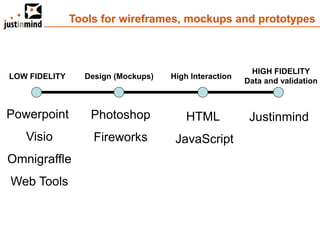
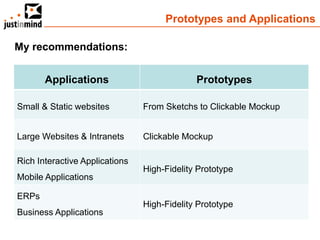
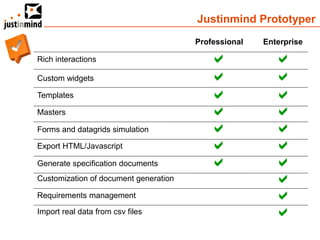
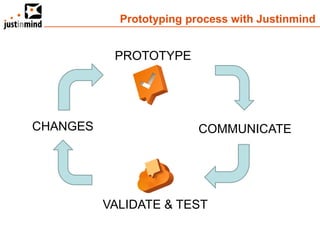
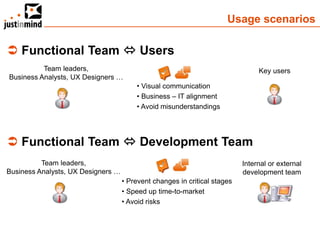
The document discusses user-centered design and the importance of prototyping in software development. It notes that user-centered design is a process that gives extensive attention to end users' needs, wants and limitations at each stage of the design process. Effective prototyping methods like creating clickable mockups and high-fidelity prototypes are recommended to validate functional requirements with users and gain approval for applications. Prototyping helps reduce costs, risks and time to market compared to relying only on requirements documents or wireframes.