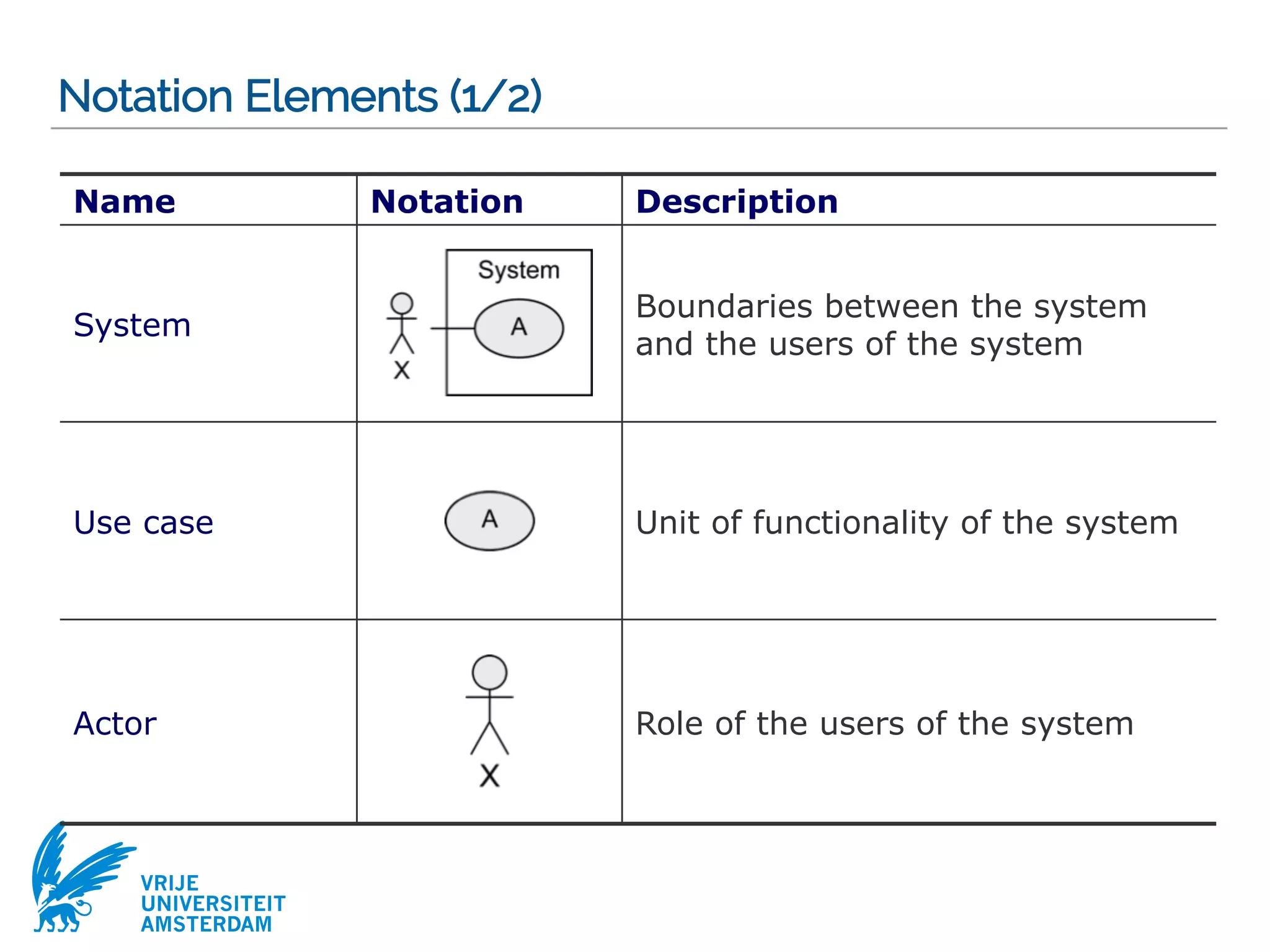
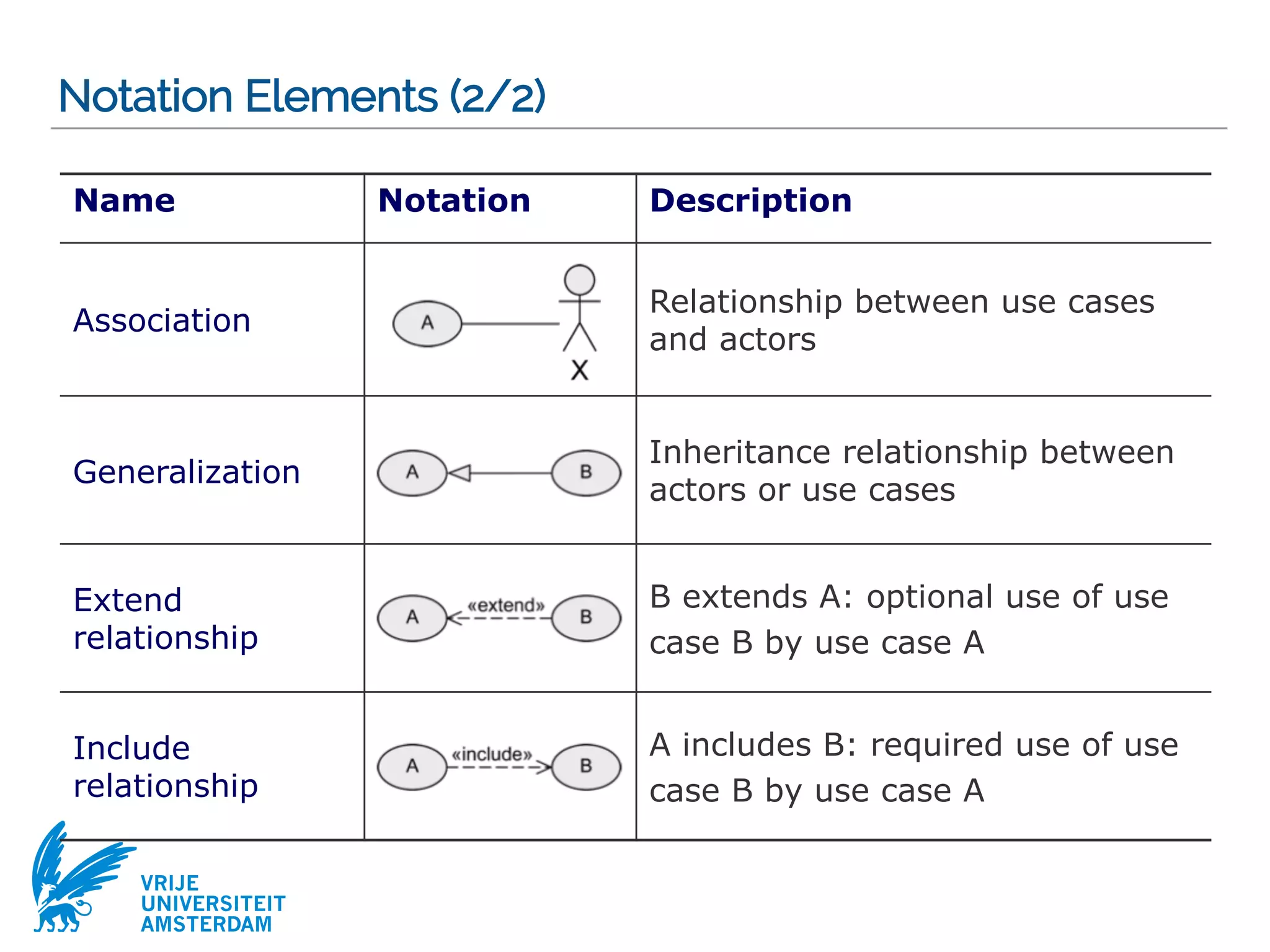
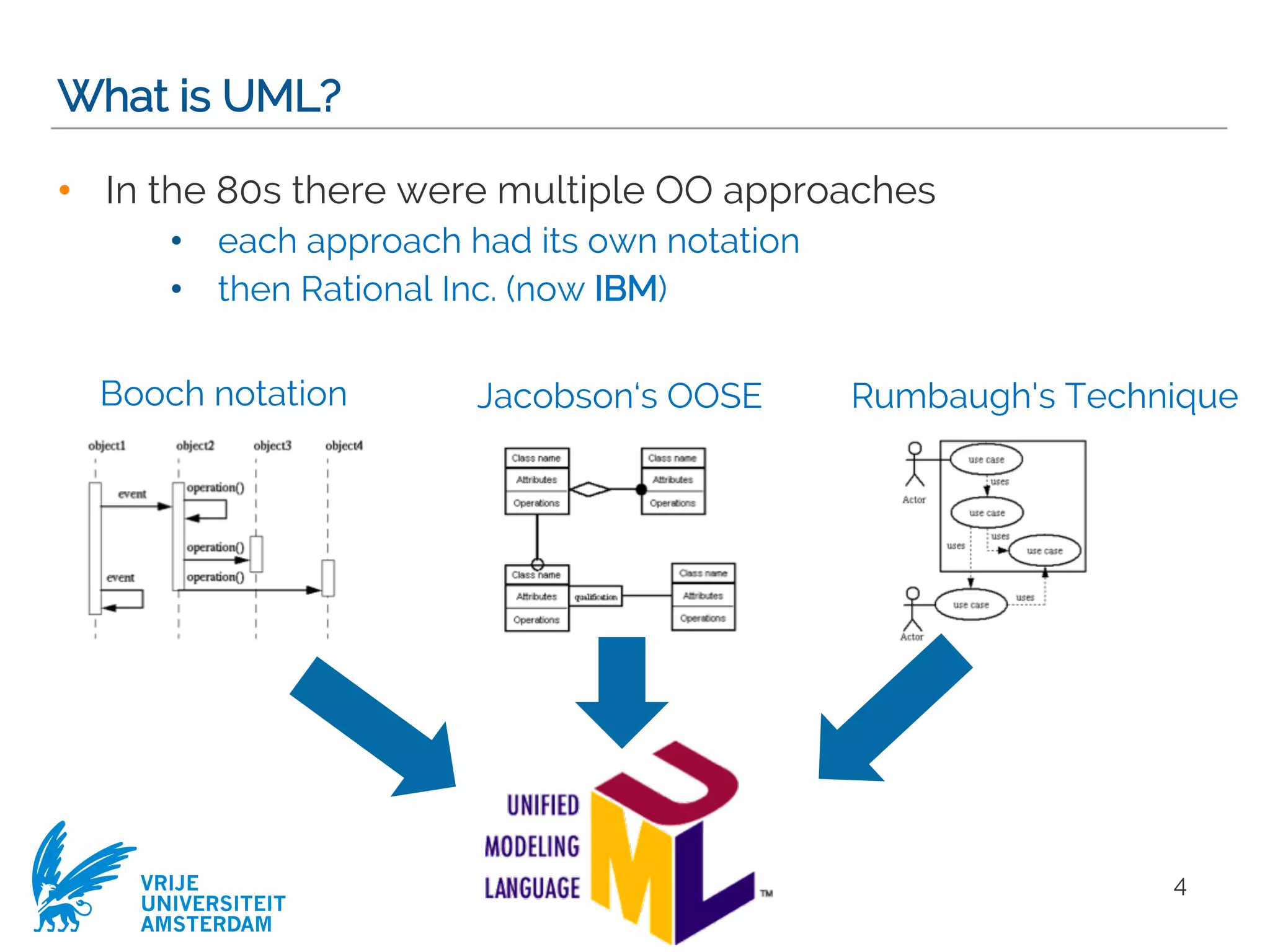
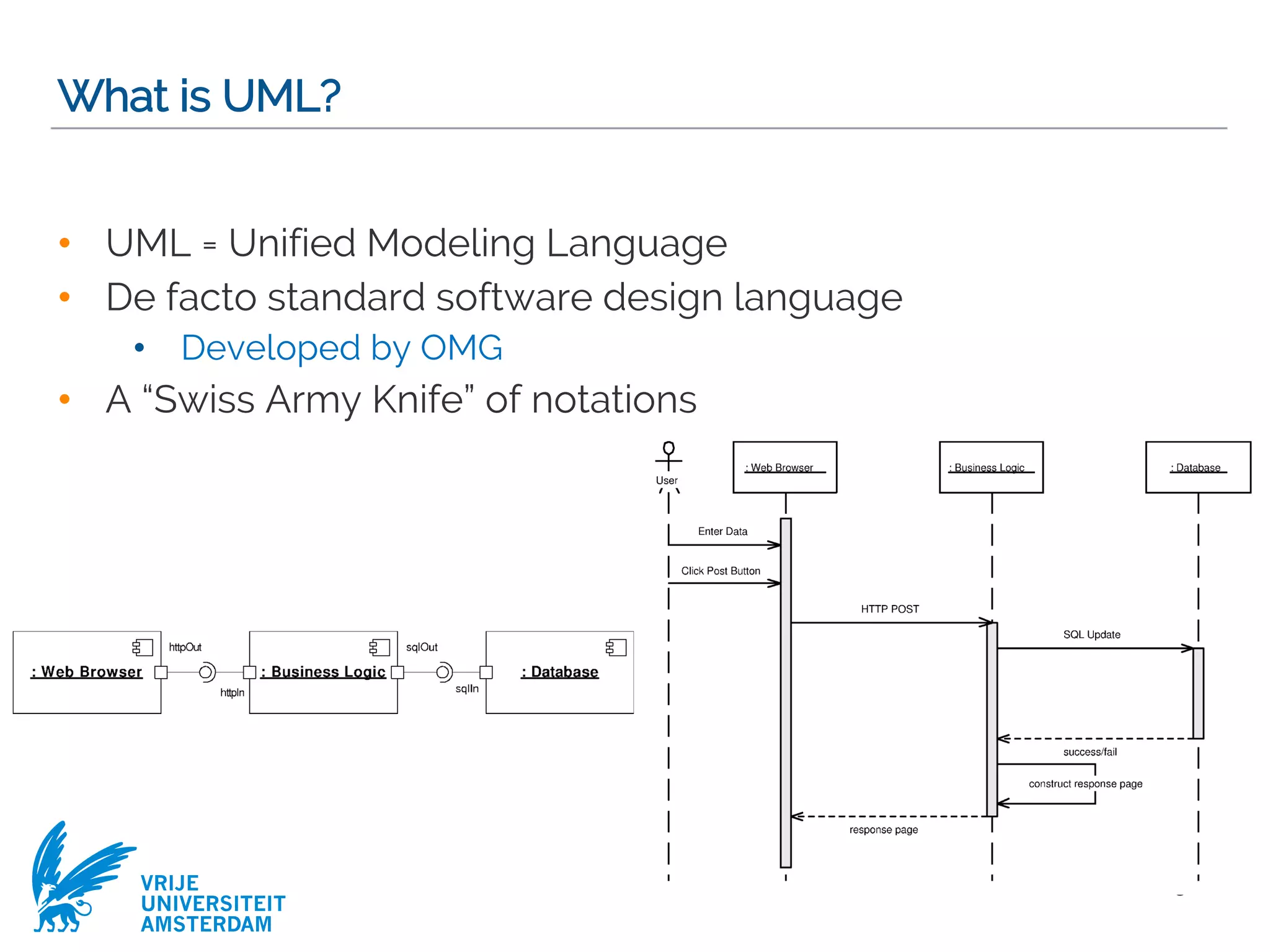
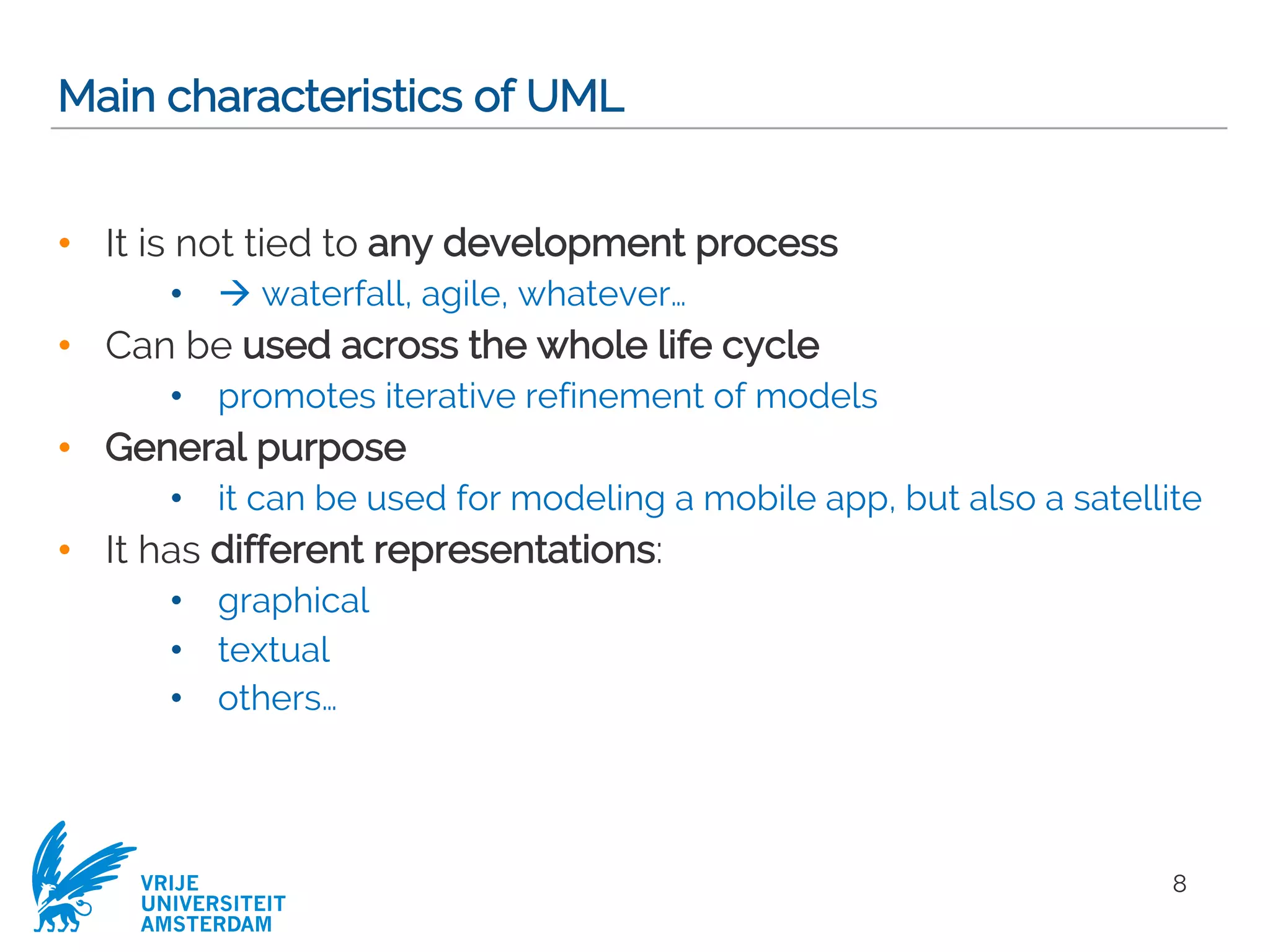
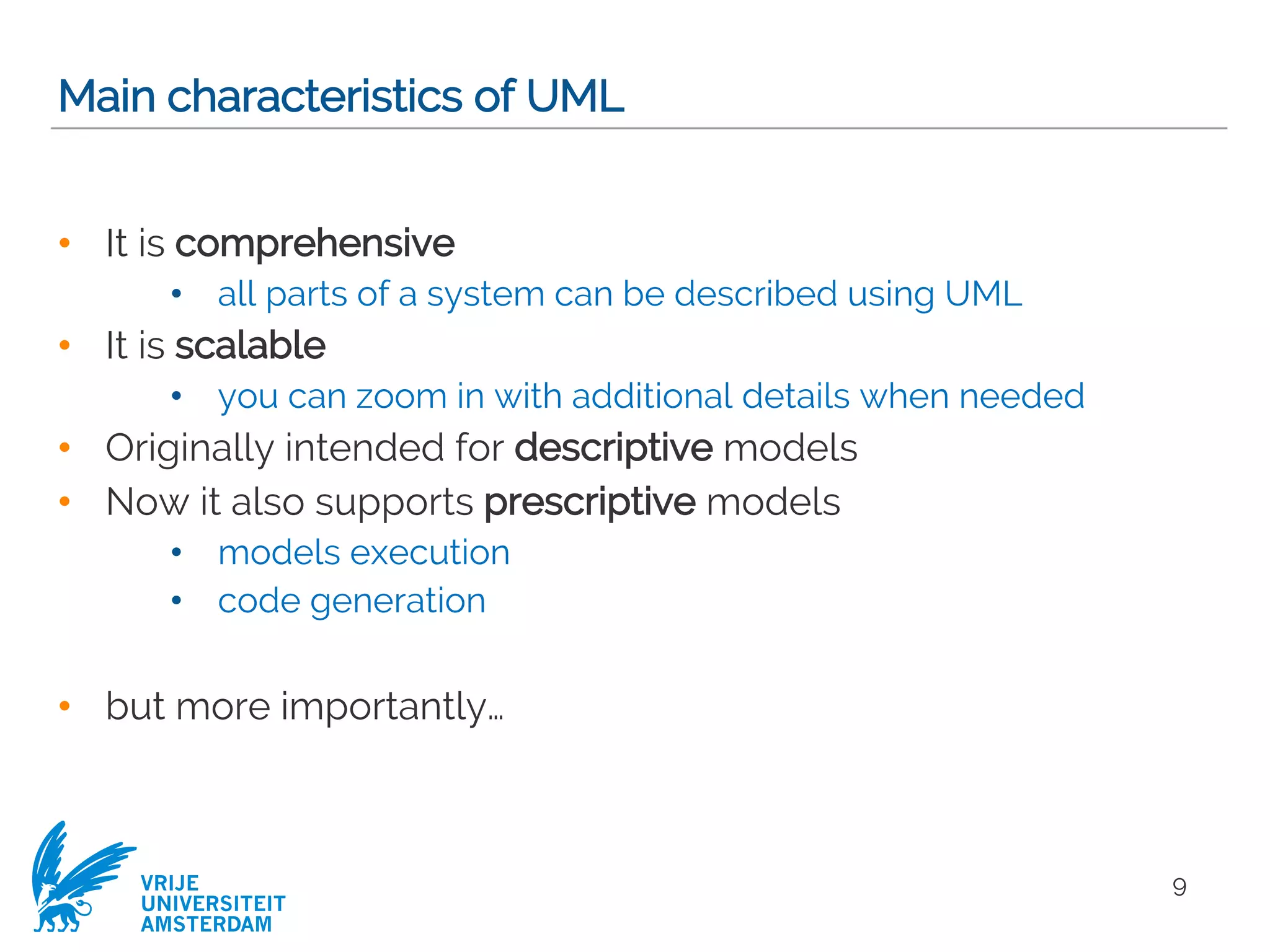
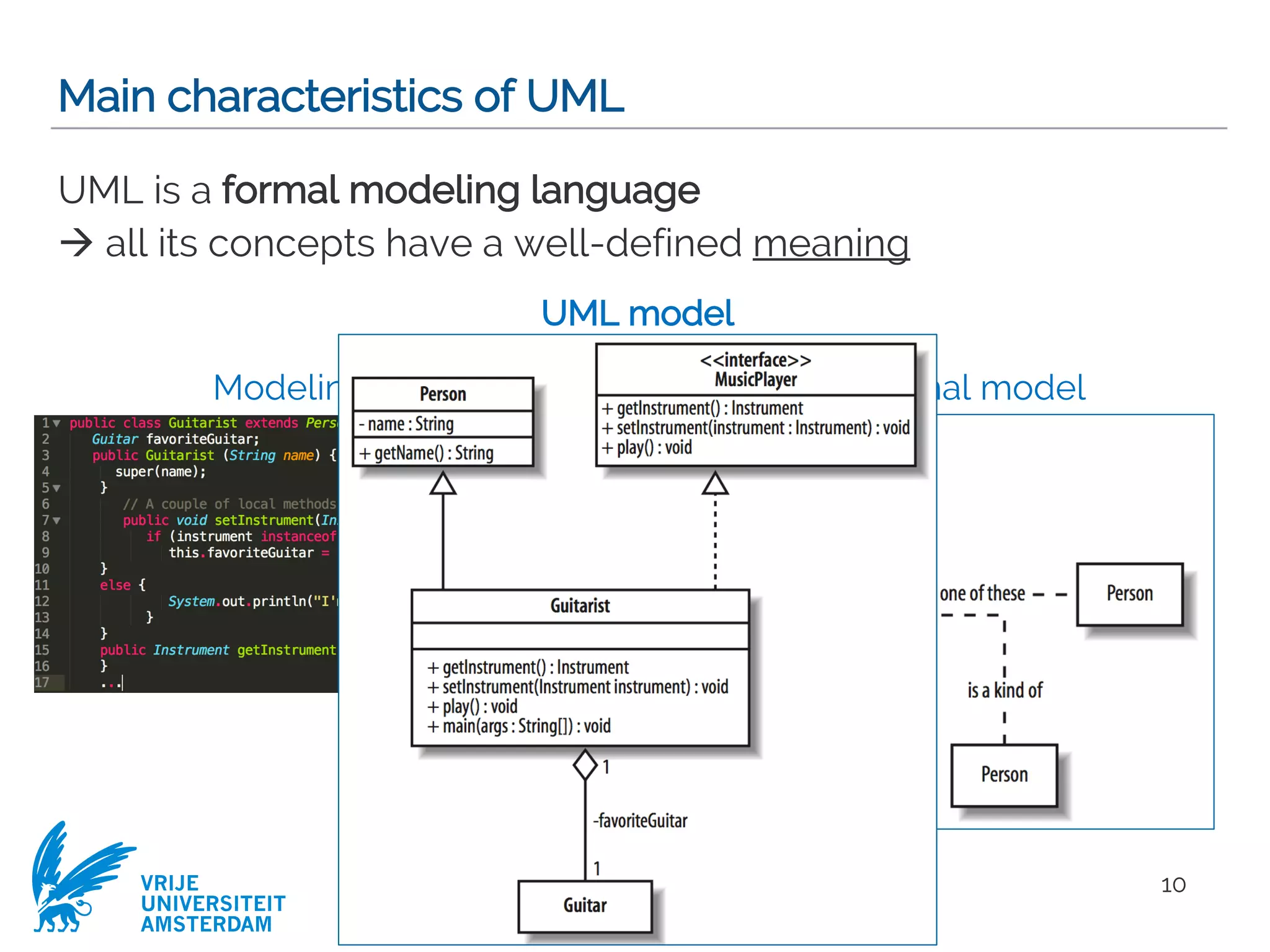
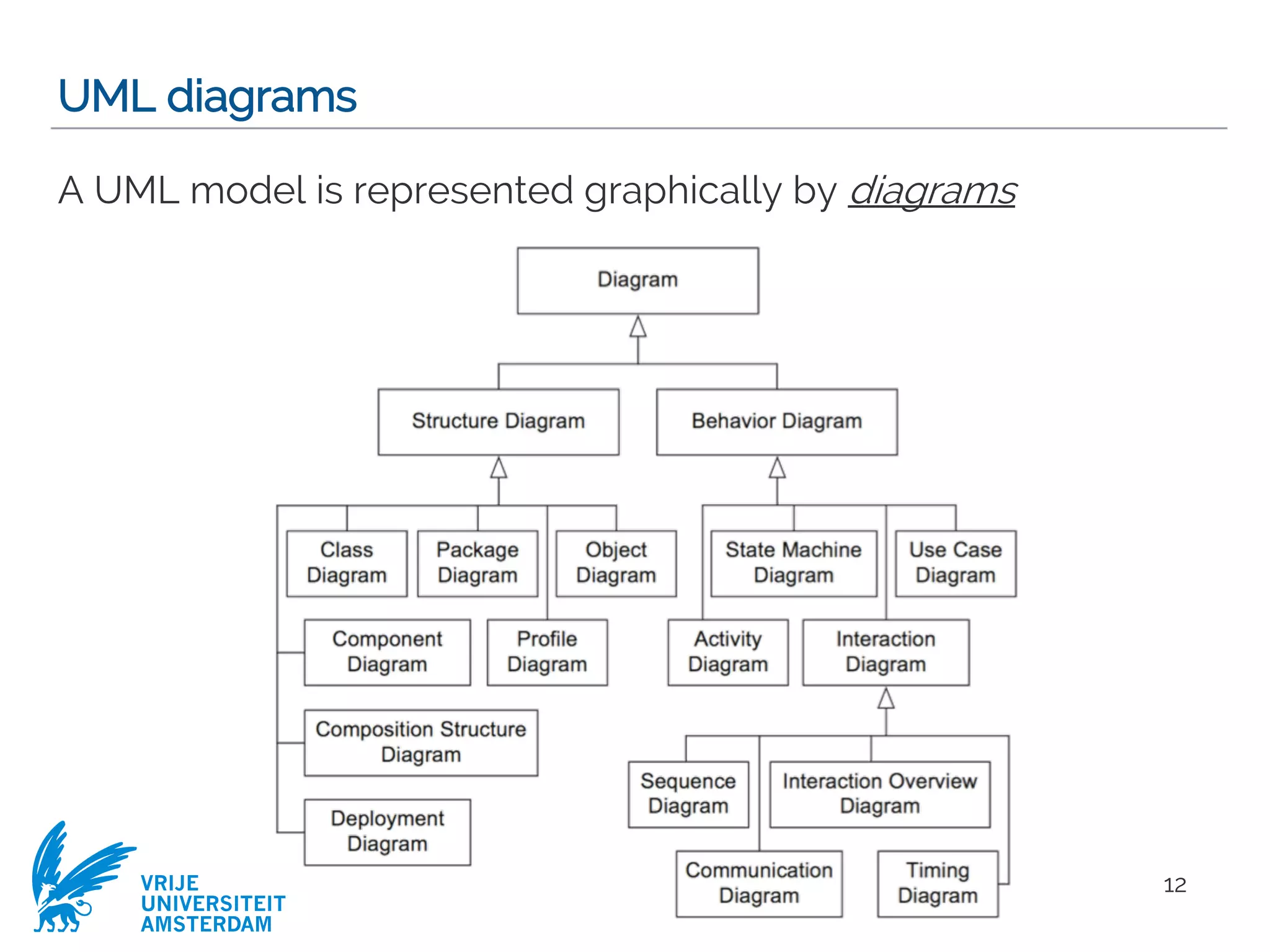
This document provides a comprehensive overview of the Unified Modeling Language (UML) and its application in requirements engineering and software design, emphasizing its importance in modeling software systems. It outlines key characteristics of UML, including its non-reliance on any specific development process, and covers various diagram types such as use case diagrams, class diagrams, and state machine diagrams. Furthermore, it discusses the differentiation between functional and non-functional requirements, and best practices for writing and validating requirements specifications.












![VRIJE
UNIVERSITEIT
AMSTERDAM
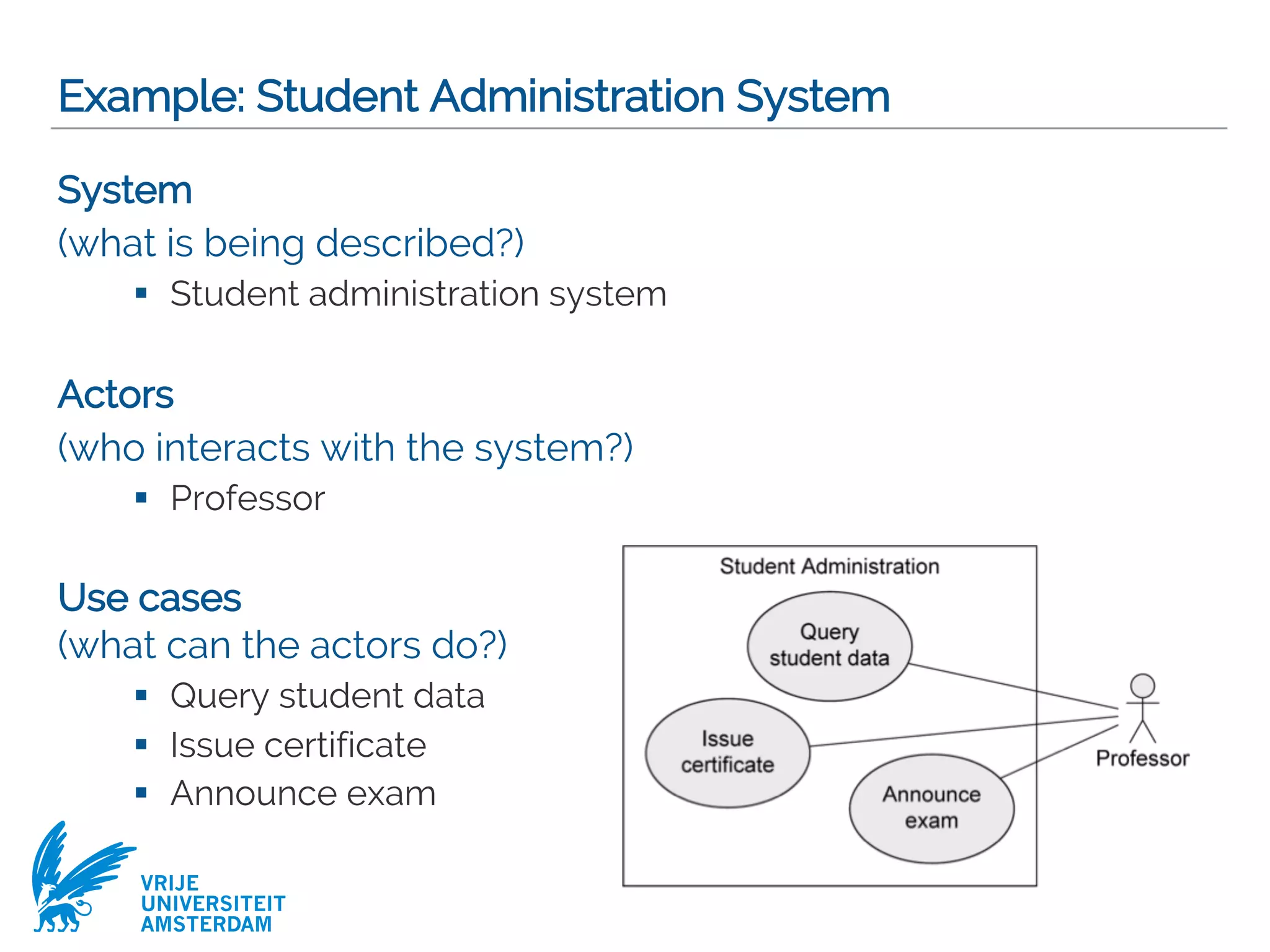
Description of Use Cases
Structured approach
§ Name
§ Short description
§ Precondition: prerequisite for successful execution
§ Postcondition: system state after successful execution
§ Error situations: errors relevant to the problem domain
§ System state on the occurrence of an error
§ Actors that communicate with the use case
§ Trigger: events which initiate/start the use case
§ Standard process: individual steps to be taken
§ Alternative processes: deviations from the standard process
[A. Cockburn: Writing Effective Use Cases, Addison Wesley,
2000]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02requirements-180213083117/75/Requirements-engineering-with-UML-Software-Design-Computer-Science-Vrije-Universiteit-Amsterdam-2017-2018-43-2048.jpg)