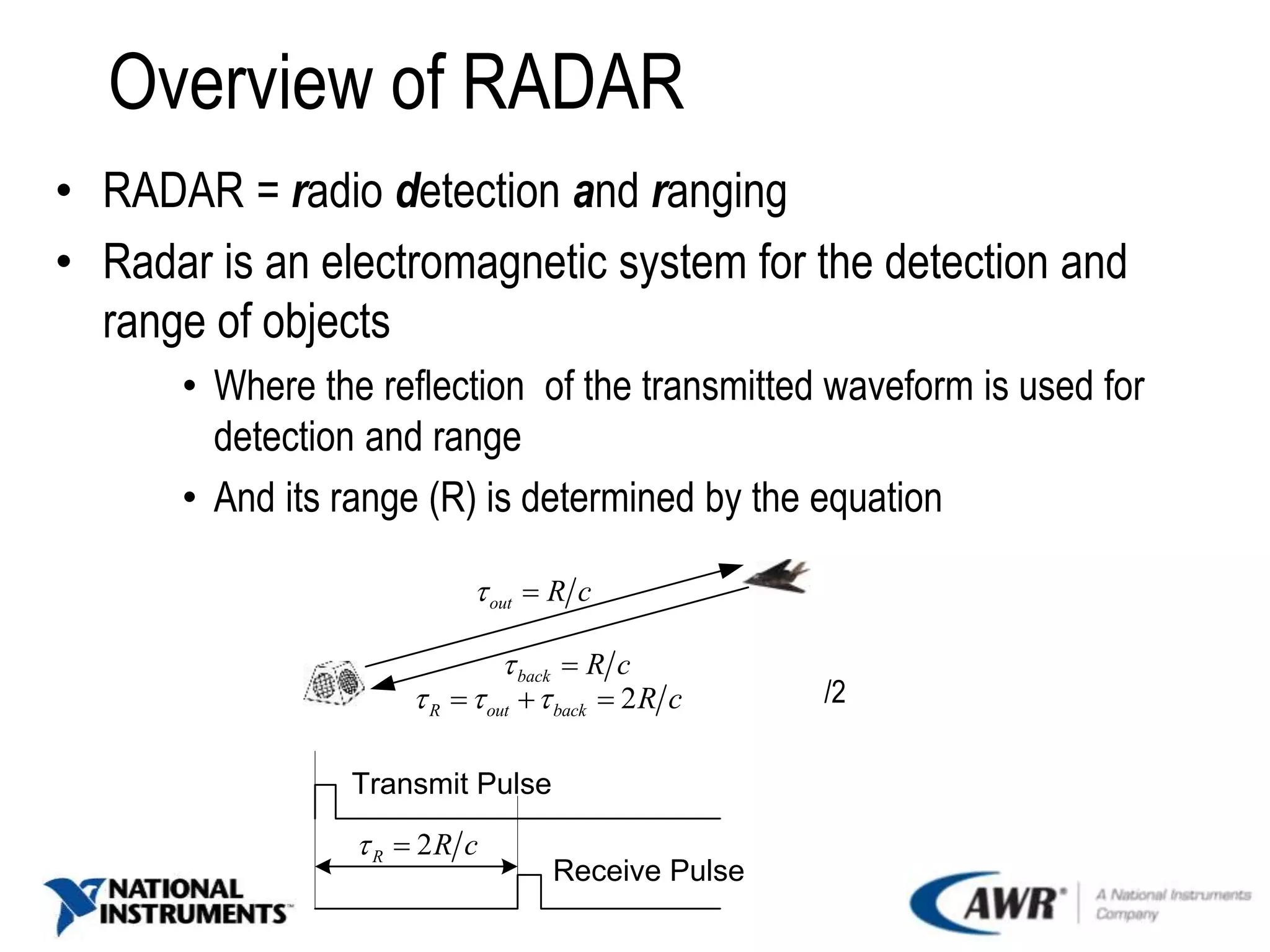
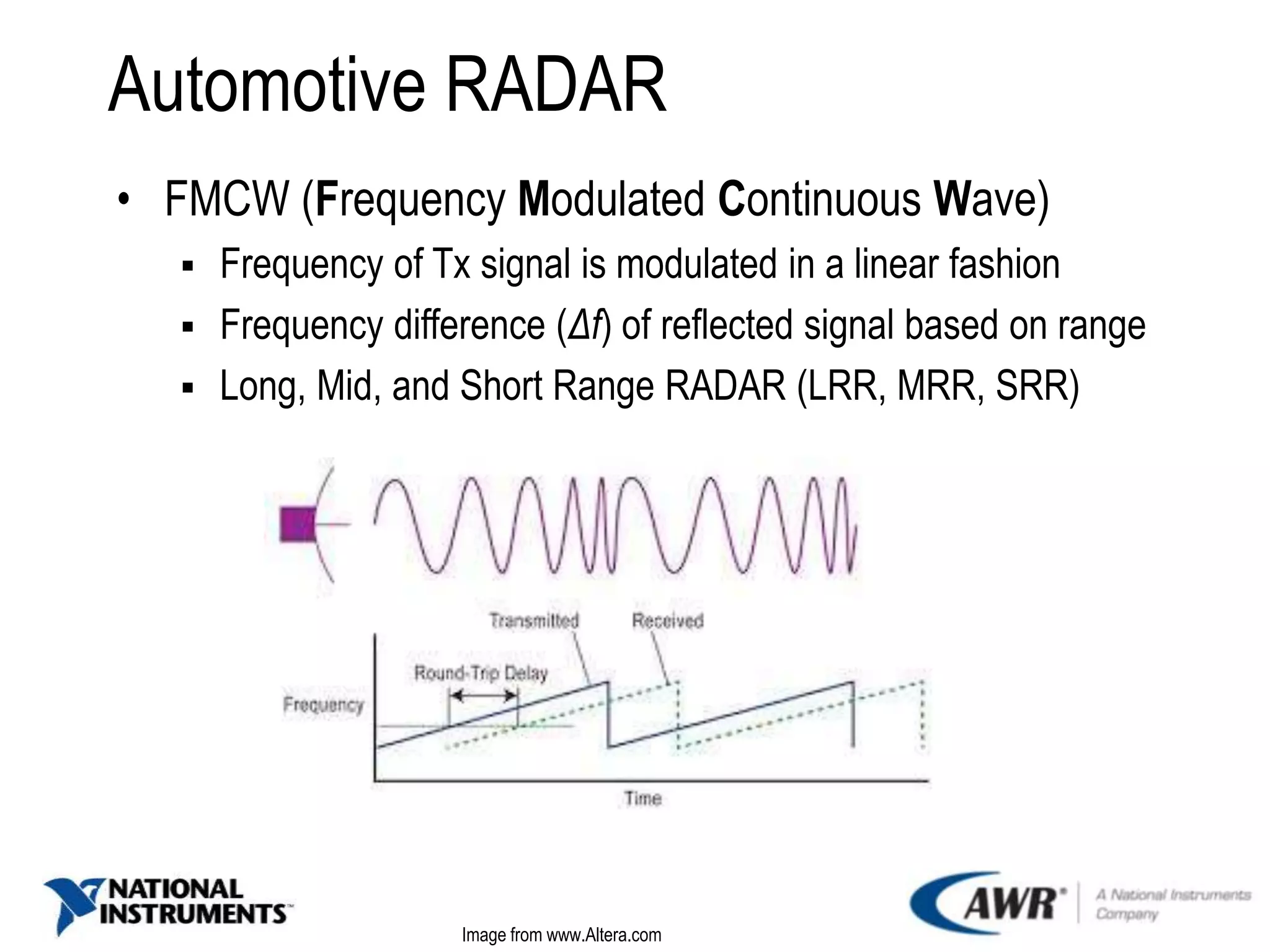
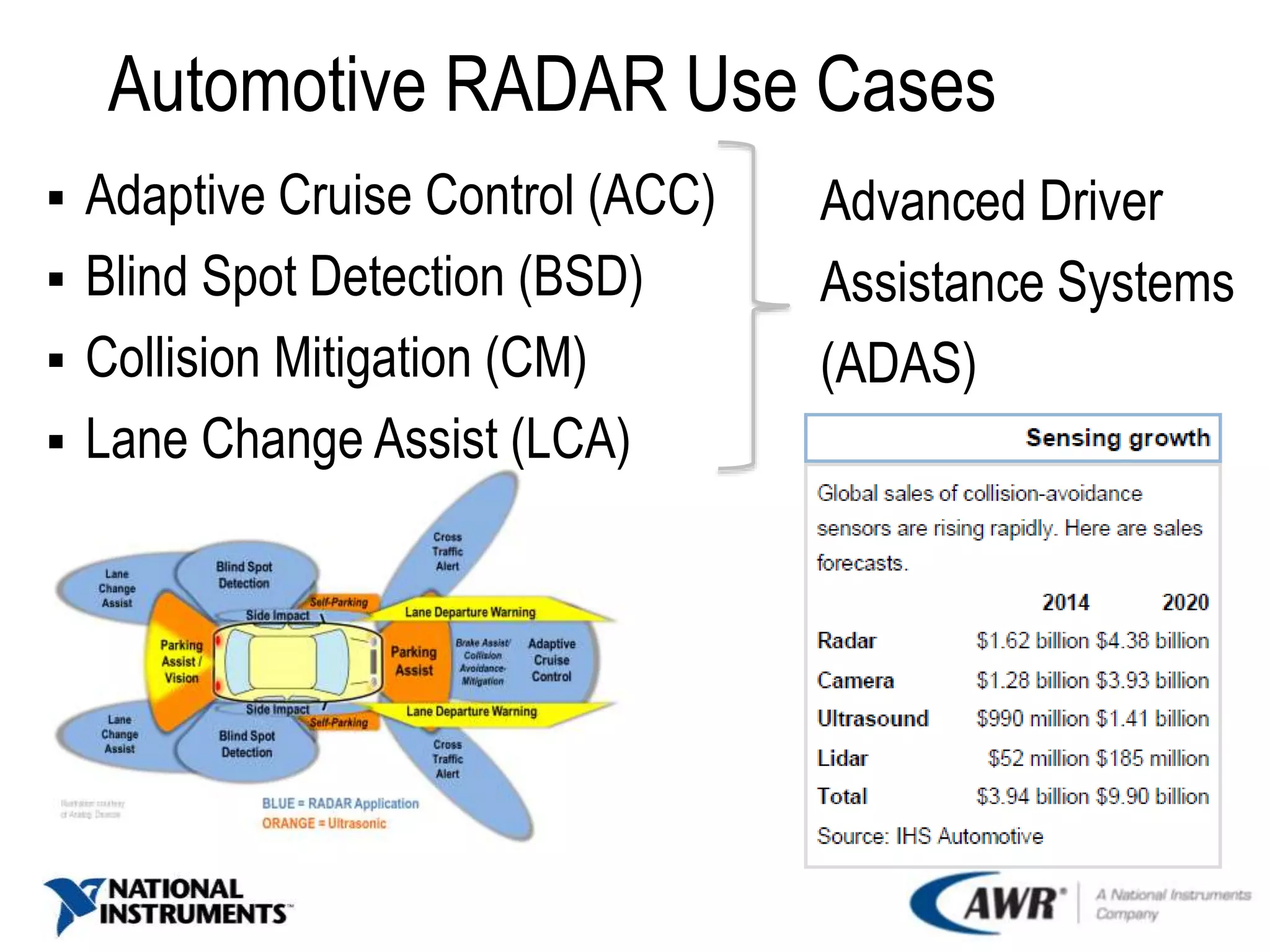
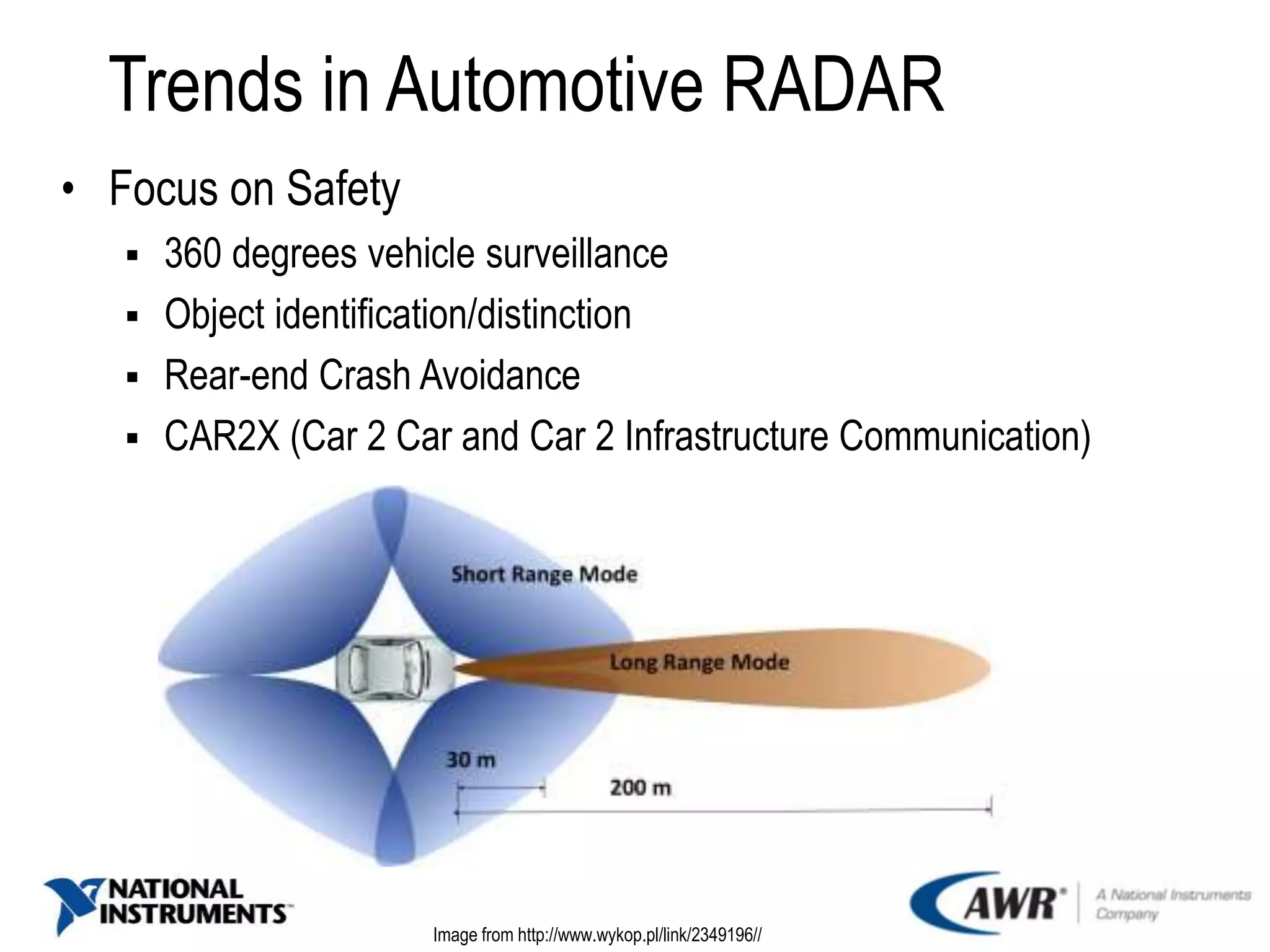
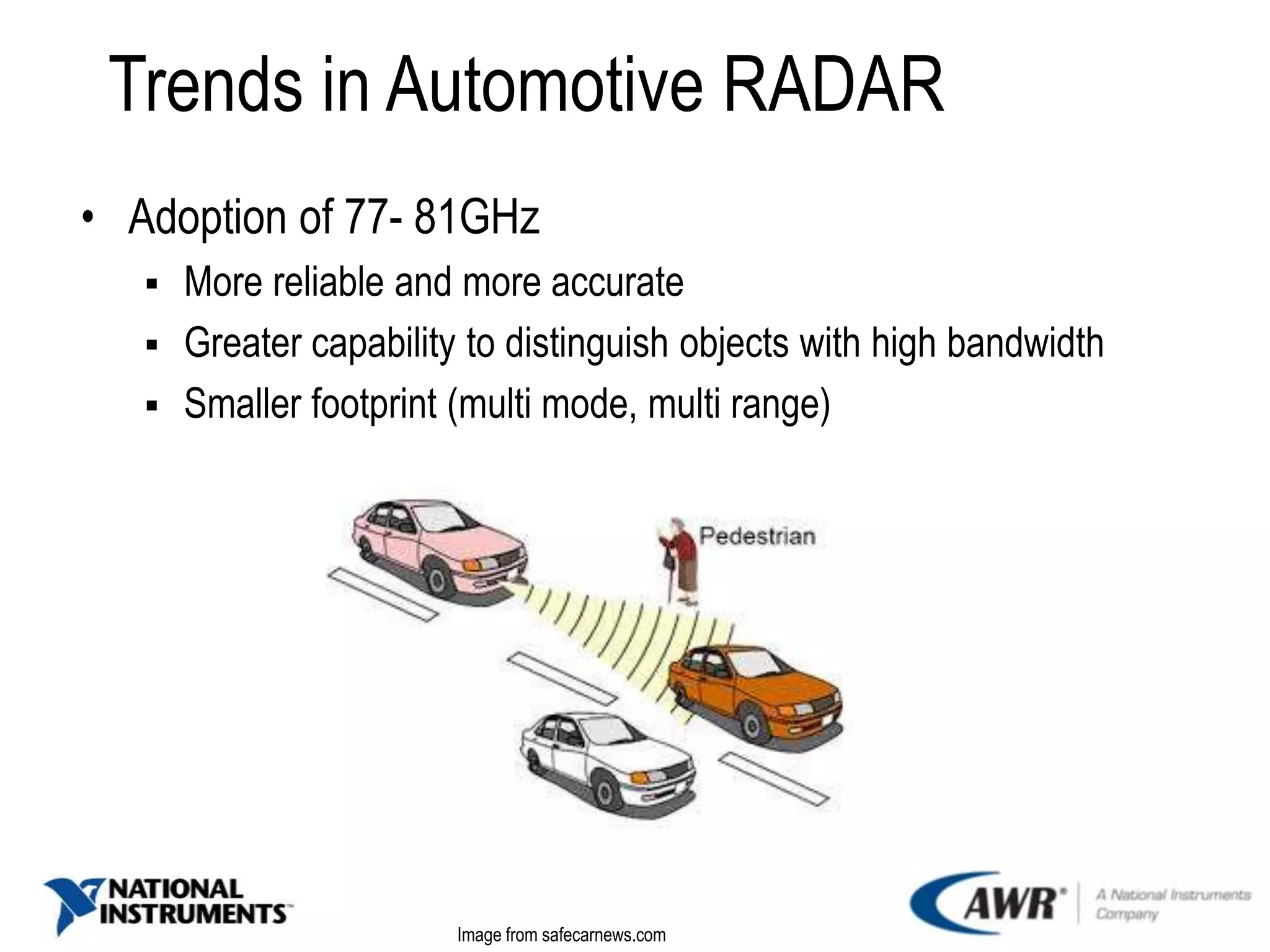
The document provides an overview of automotive radar technology, highlighting its function in detecting and ranging objects using electromagnetic systems. It discusses the trends in automotive radar adoption, emphasizing safety features, advancements in sensor technology for autonomous vehicles, and the shift towards high-frequency bands for improved reliability. Key use cases include adaptive cruise control and collision avoidance systems, positioning radar as integral to advanced driver assistance systems.