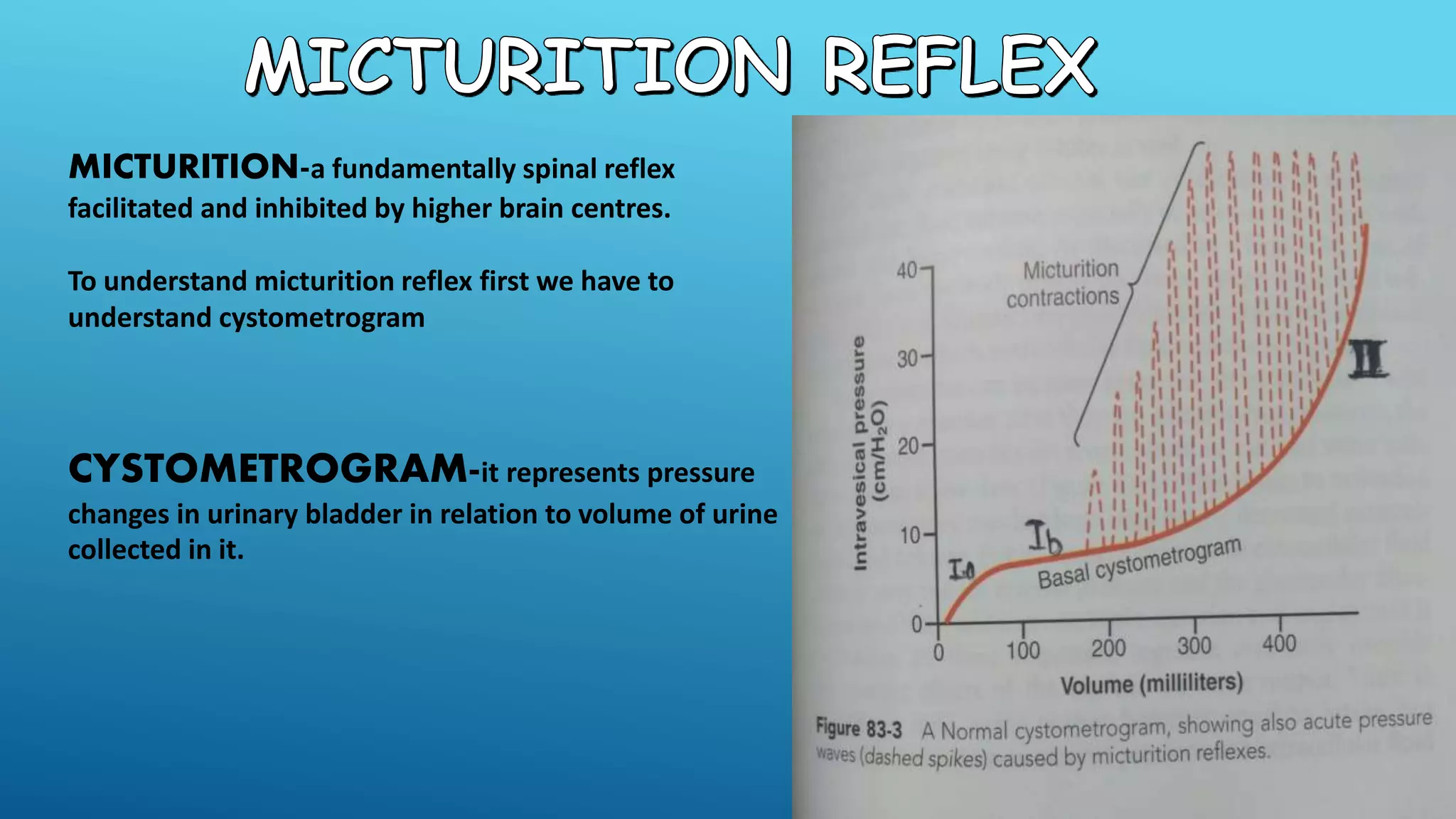
This document summarizes the physiology of the urinary bladder and micturition reflex. It begins with the anatomical components of the bladder, including the body, trigone, internal sphincter, and external sphincter. It then describes the nerve supply to the bladder, including sympathetic, parasympathetic, and somatic nerves. The micturition reflex is a spinal reflex facilitated by higher brain centers that is initiated when urine fills the bladder and stretches its receptors, causing inhibition of the external urethral sphincter and allowing urination. Precise control of micturition involves a balance between inhibitory centers in the midbrain and cortex and facilitatory centers in the pons. Applied aspects discuss conditions like