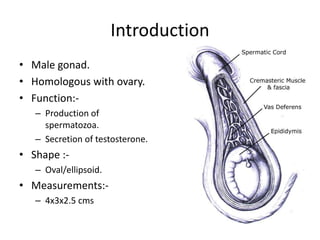
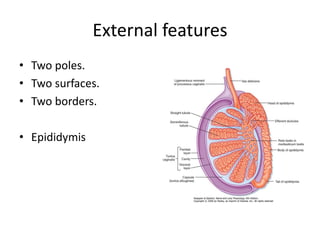
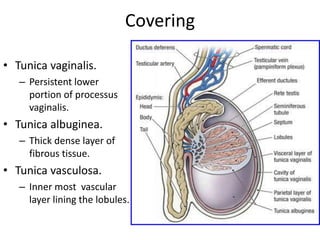
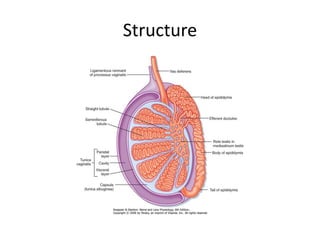
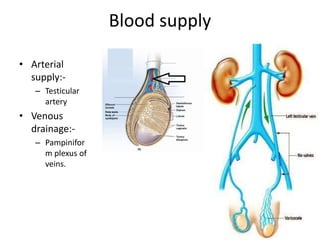
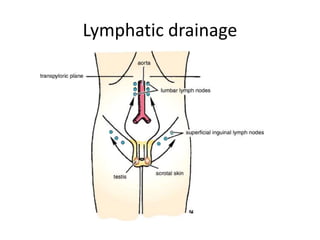
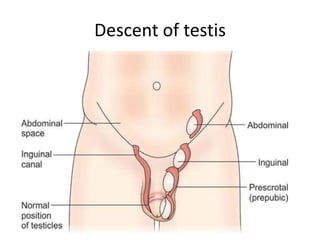
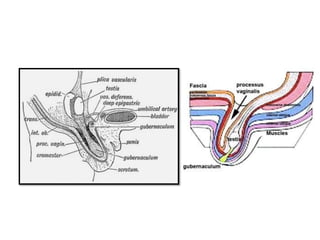
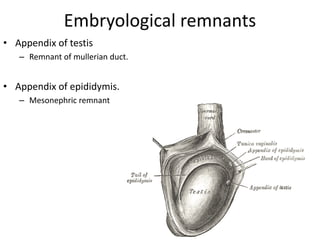
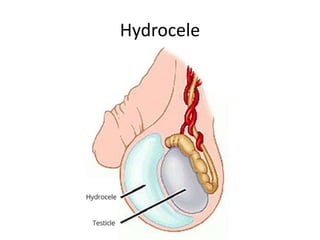
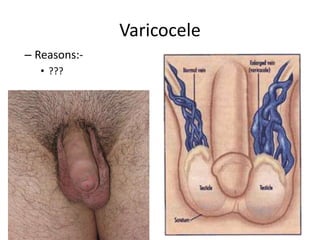
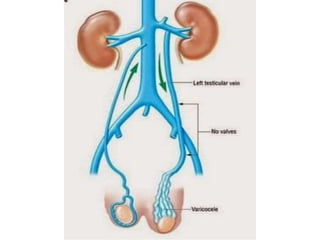
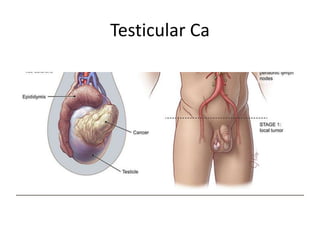
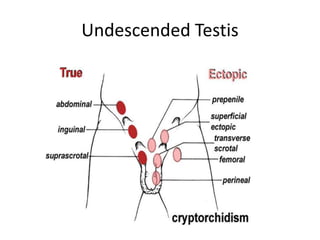
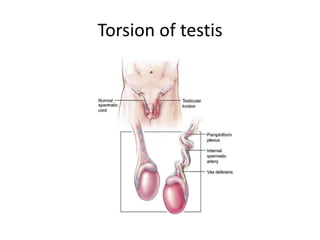
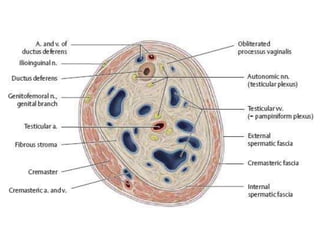
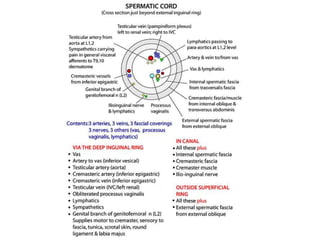
The document provides information about the testis and spermatic cord. It describes the testis as the male gonad that is homologous with the ovary and functions to produce spermatozoa and secrete testosterone. It details the external features, coverings, blood supply, lymphatic drainage, and normal descent process of the testis from abdominal cavity to scrotum during fetal development. Applied topics like hydrocele, varicocele, testicular cancer, undescended testis, and torsion of testis are also mentioned. The epididymis is described as a comma-shaped structure made up of highly coiled tubes that act as reservoirs for spermatozoa.