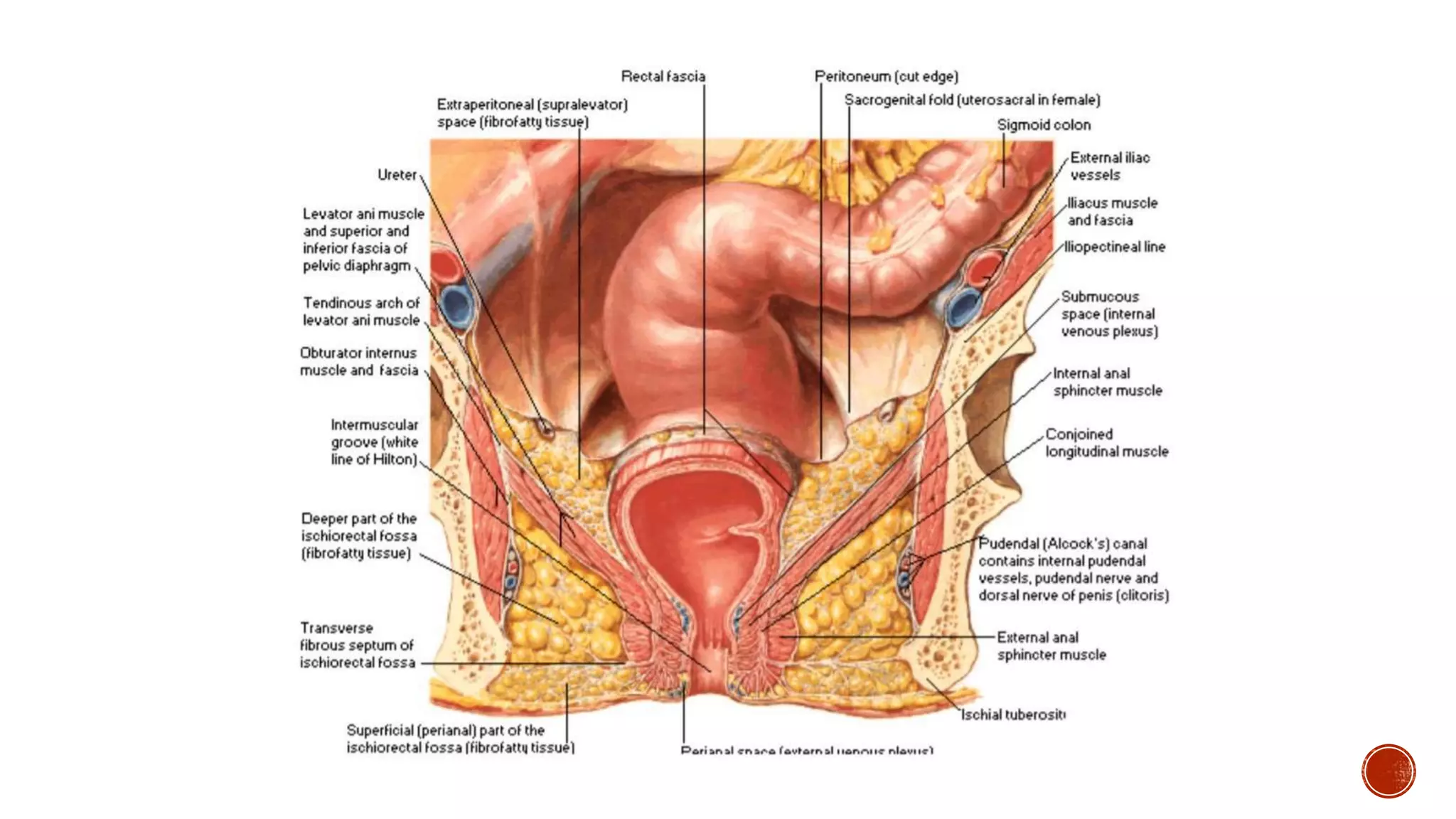
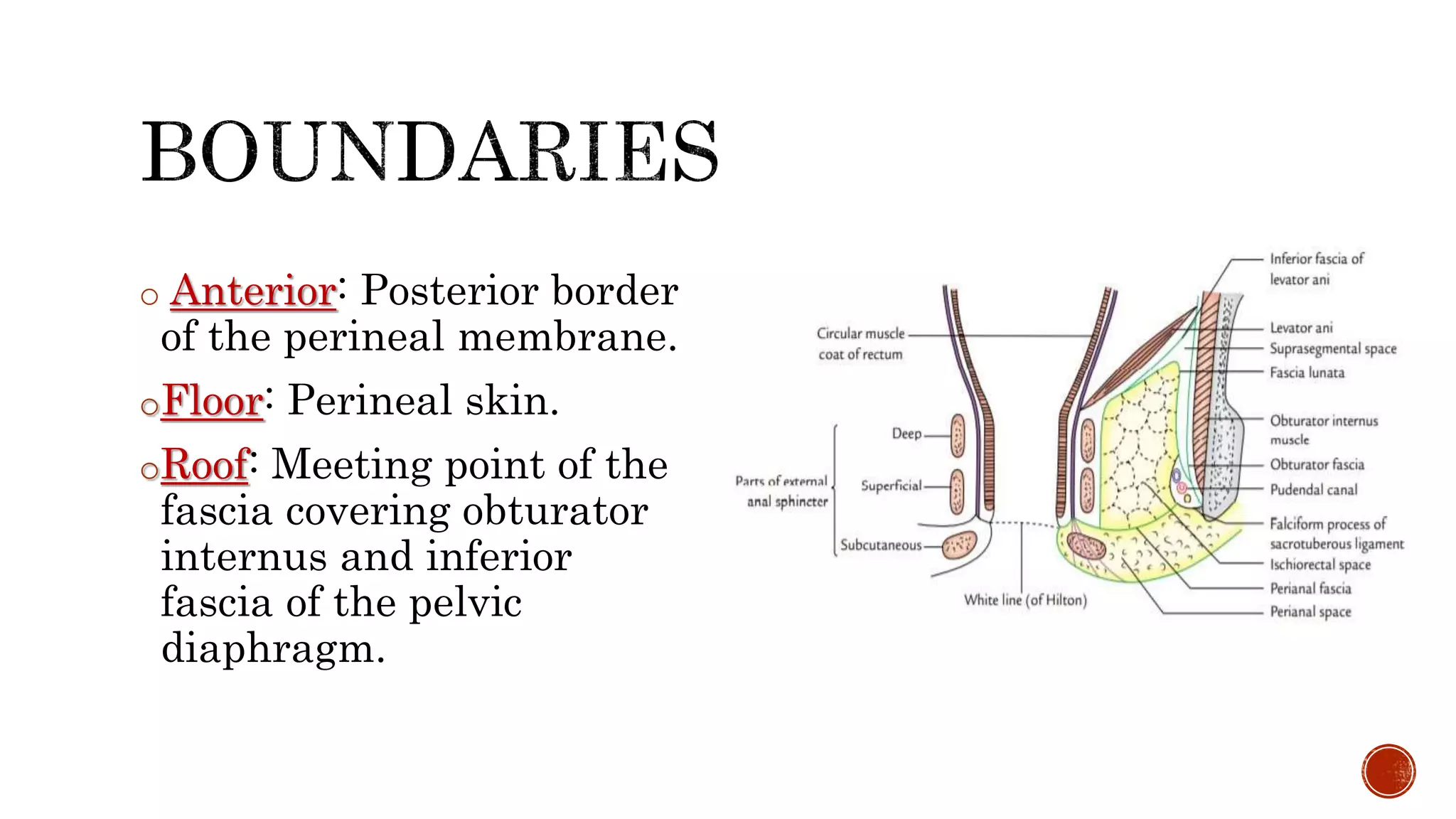
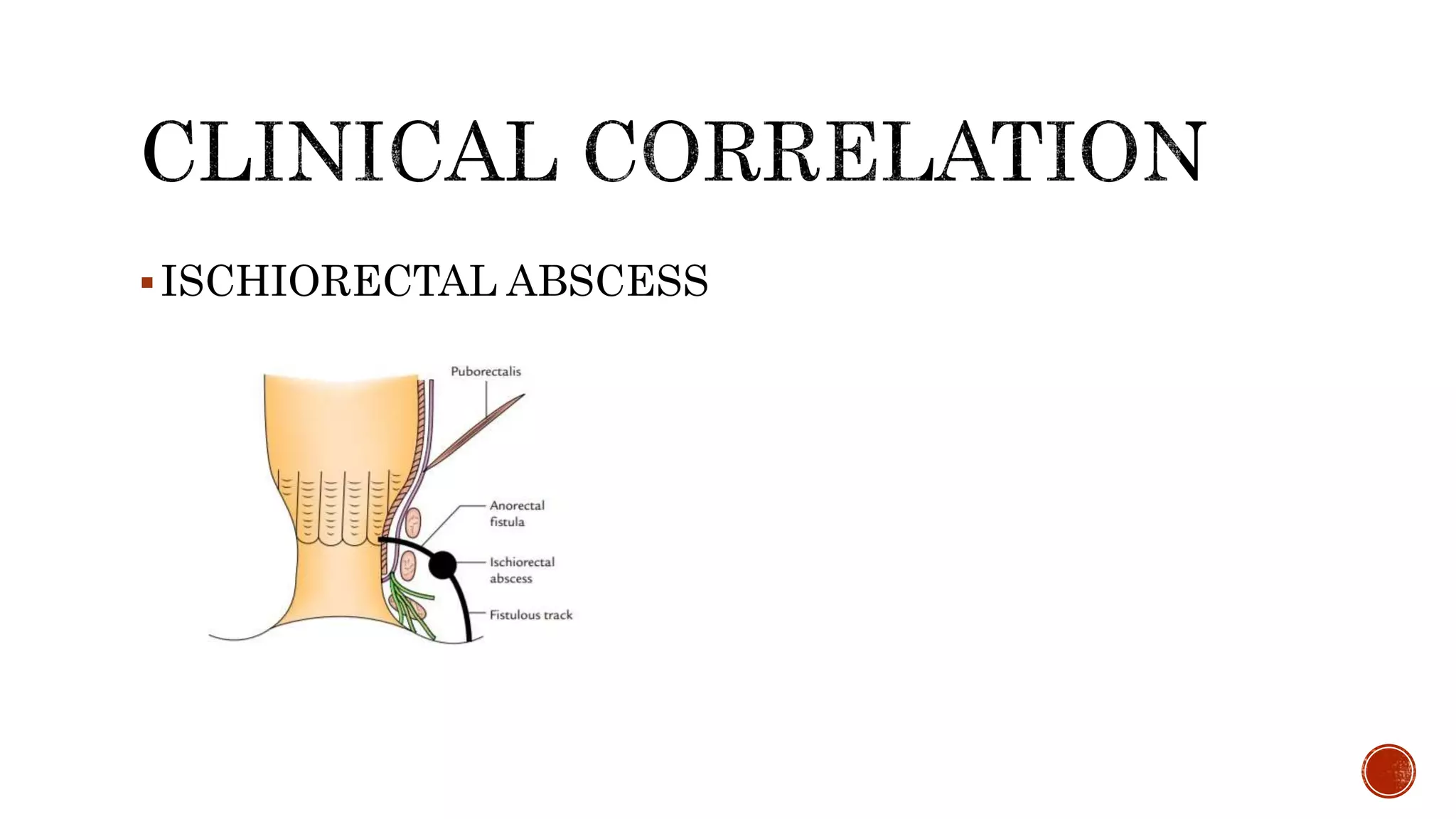
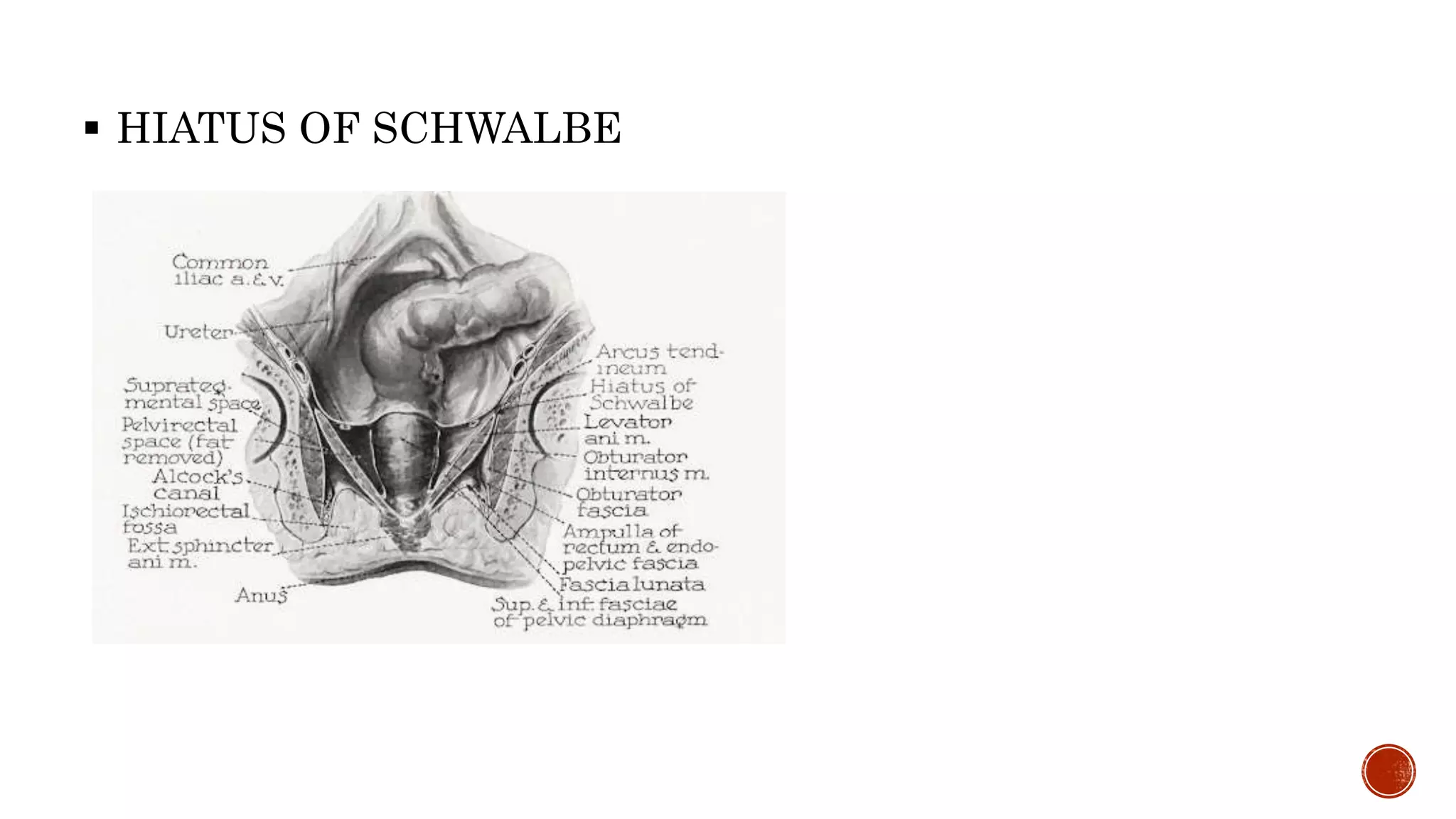
The ischioanal fossa is a wedge-shaped, fat-filled space located lateral to the anal canal below the pelvic diaphragm. It has boundaries formed by fascia covering nearby muscles. Within the fossa are the perianal space and ischioanal space, separated by the perianal fascia. The ischioanal space contains large fat deposits and structures like the pudendal canal, which contains the pudendal nerve and vessels. Infection of the fat deposits can lead to a painful ischioanal abscess.