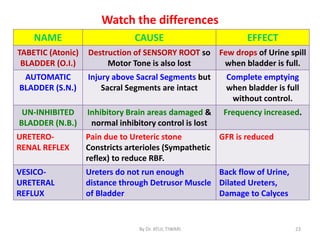
The document discusses micturition (urination) including the physiology, anatomy, and abnormalities involved. It begins with the anatomical structures of the bladder including the detrusor muscle and internal and external sphincters. It then describes the micturition reflex initiated by stretch receptors in the bladder wall. This reflex involves afferent and efferent pathways through the pelvic nerves and sacral micturition center. Higher brain centers provide voluntary control. Abnormalities discussed include the atonic bladder due to sensory fiber destruction, and the tabetic bladder caused by syphilis.