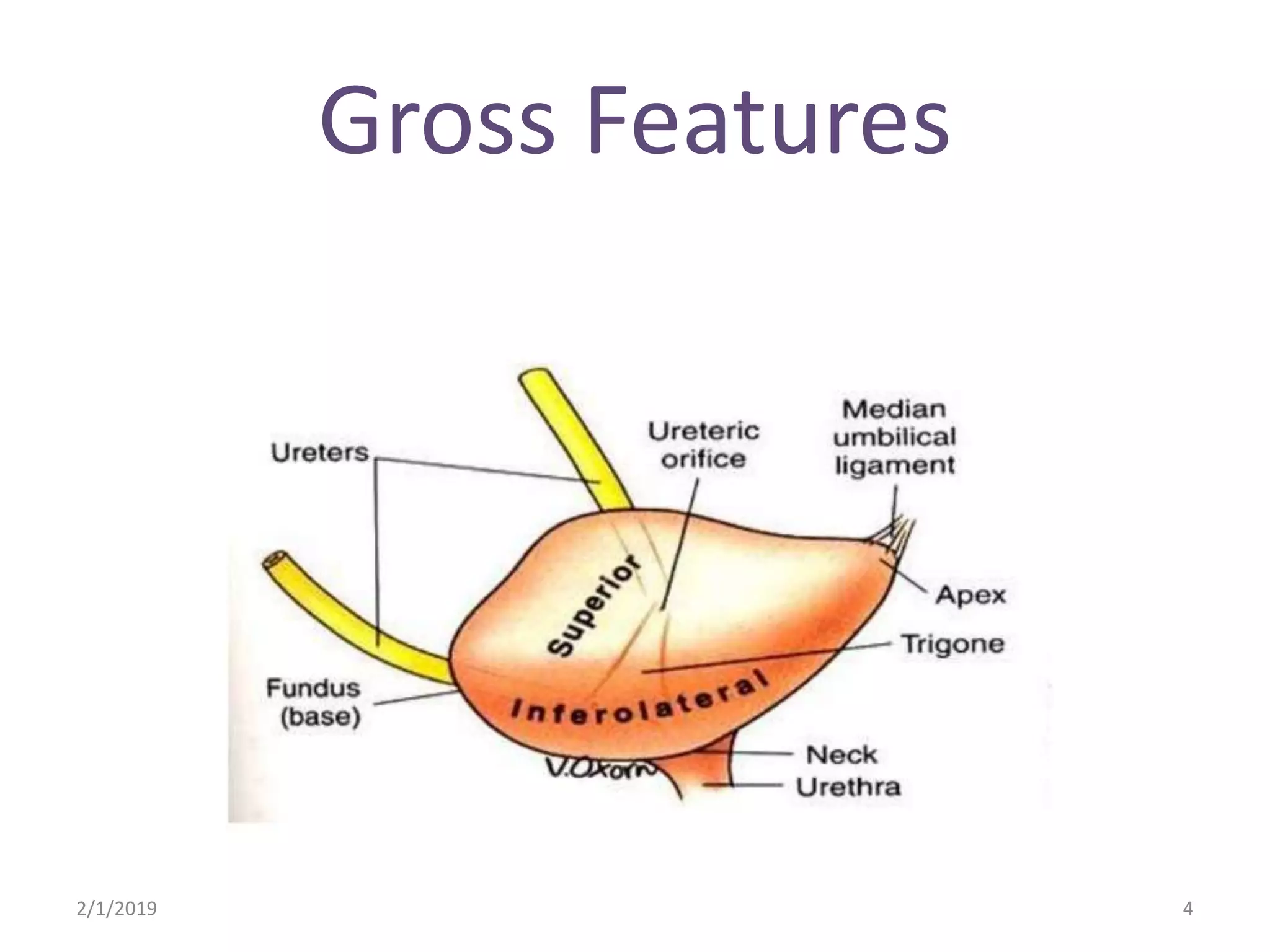
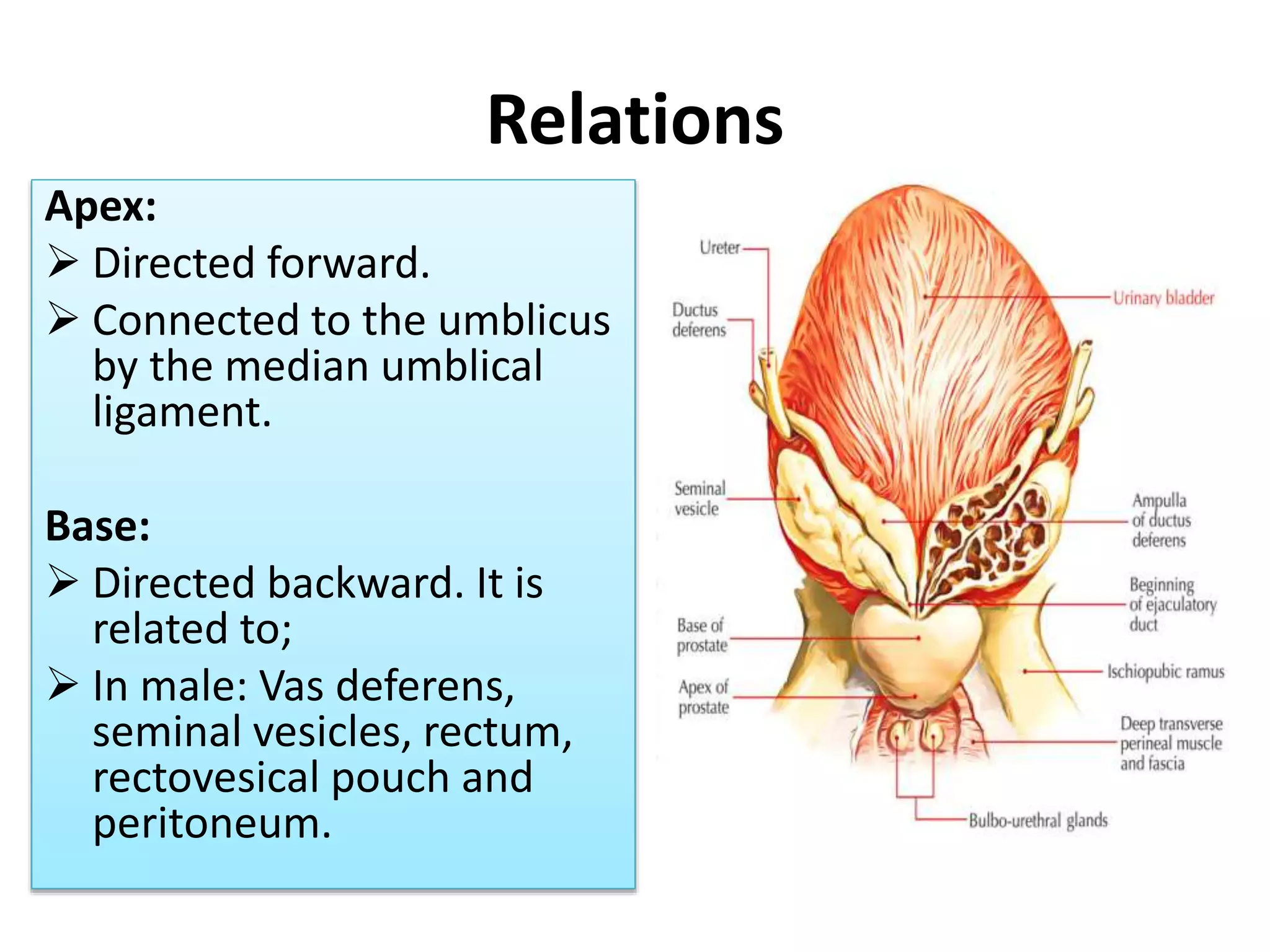
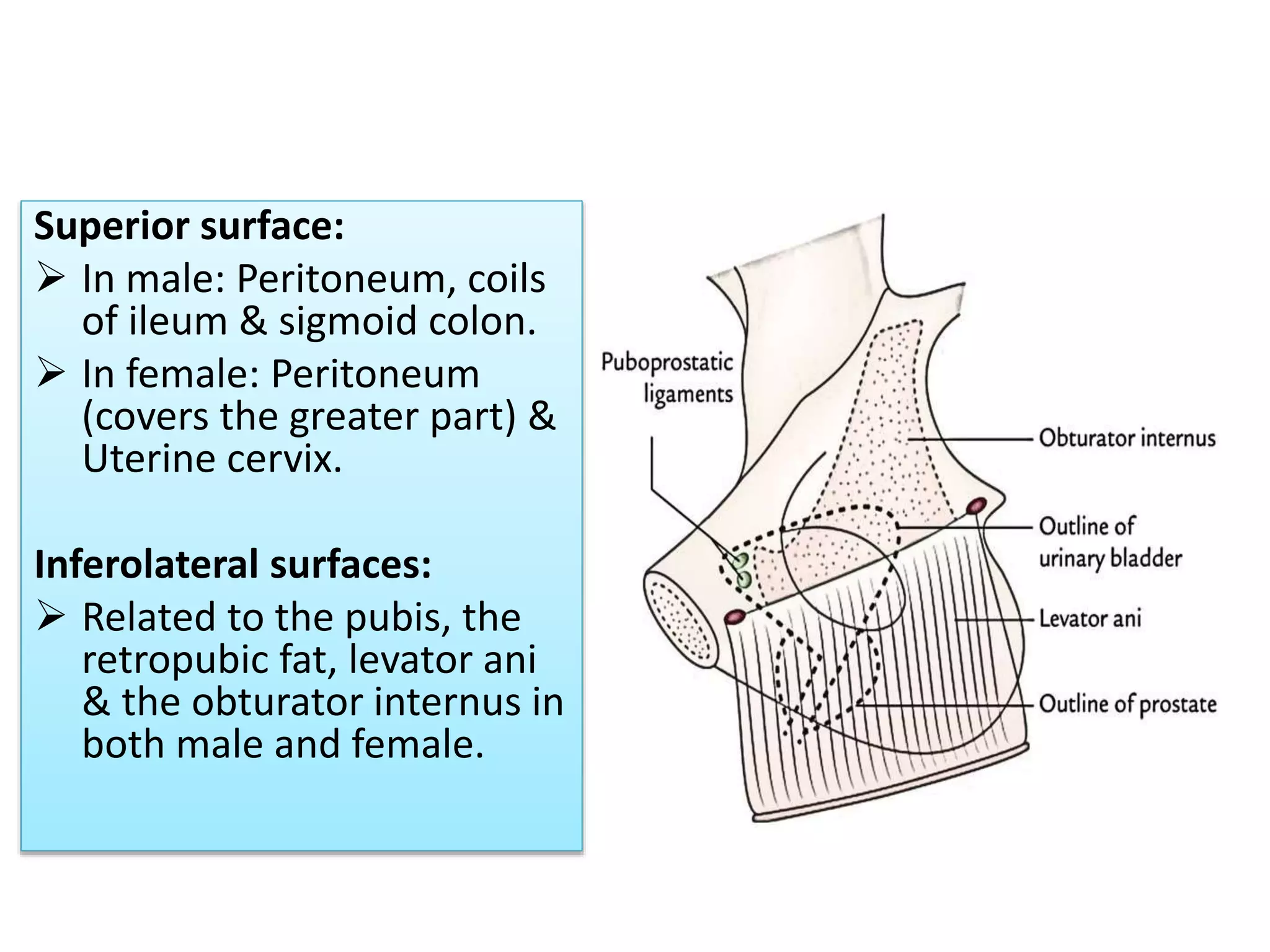
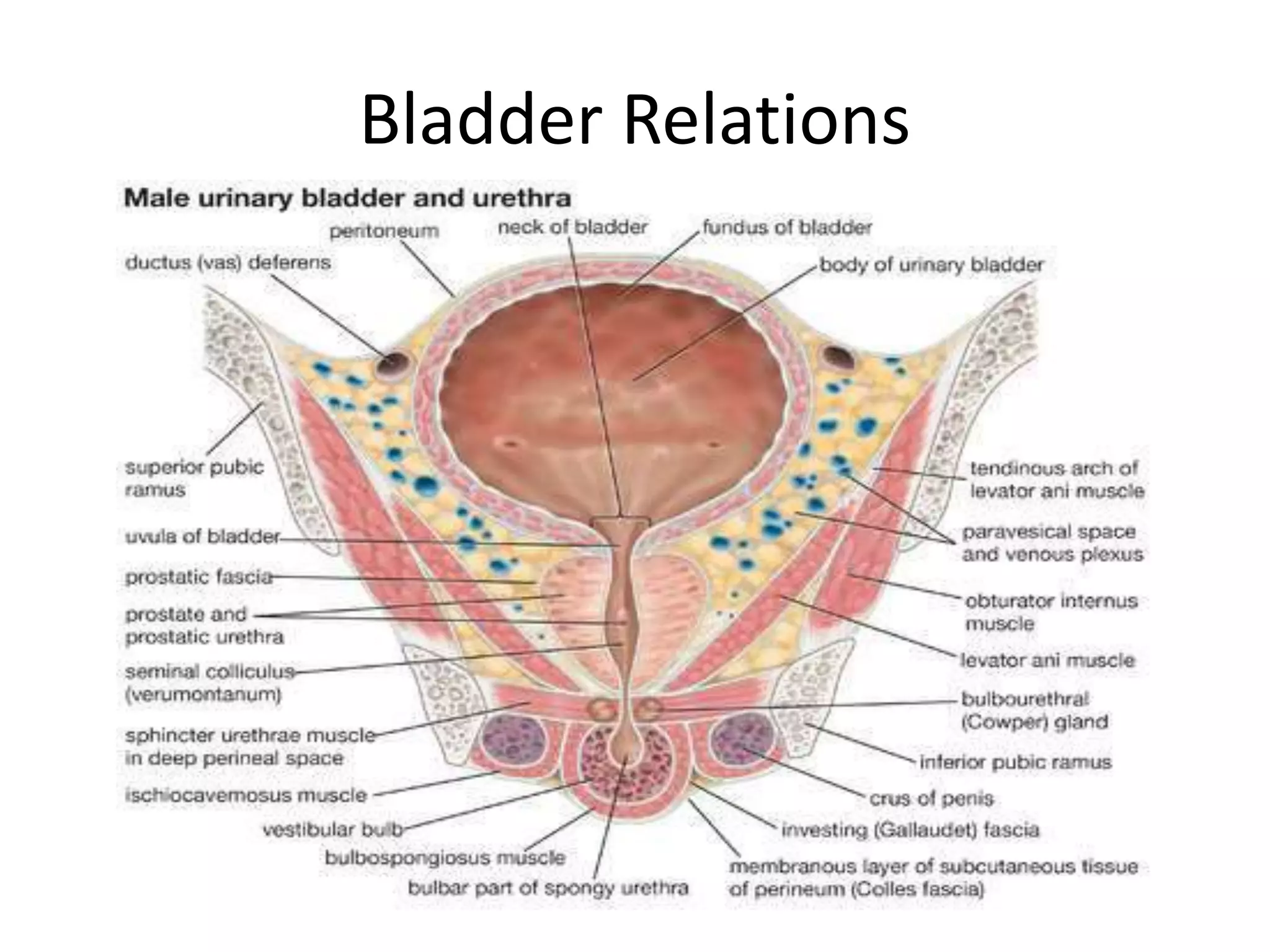
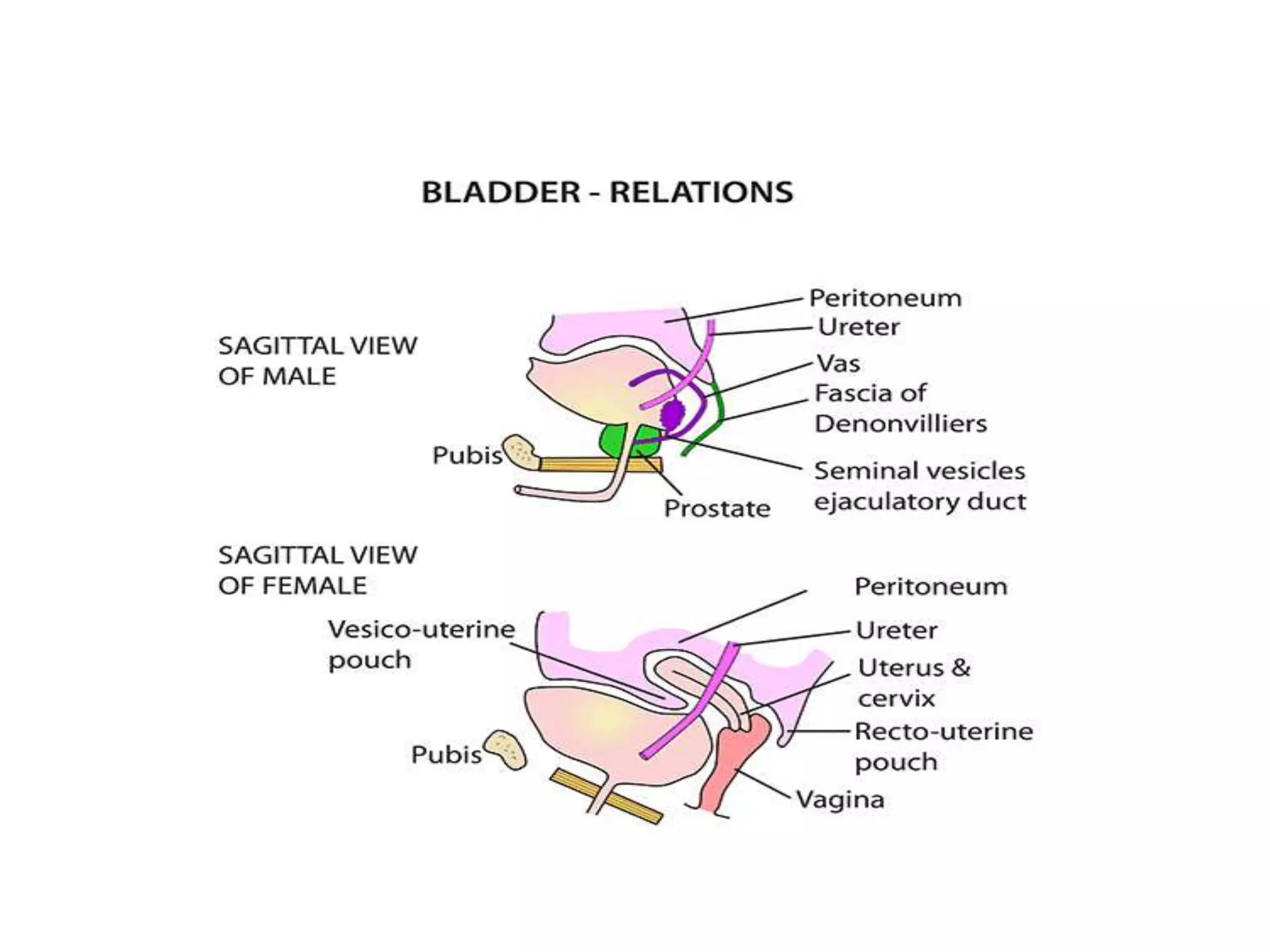
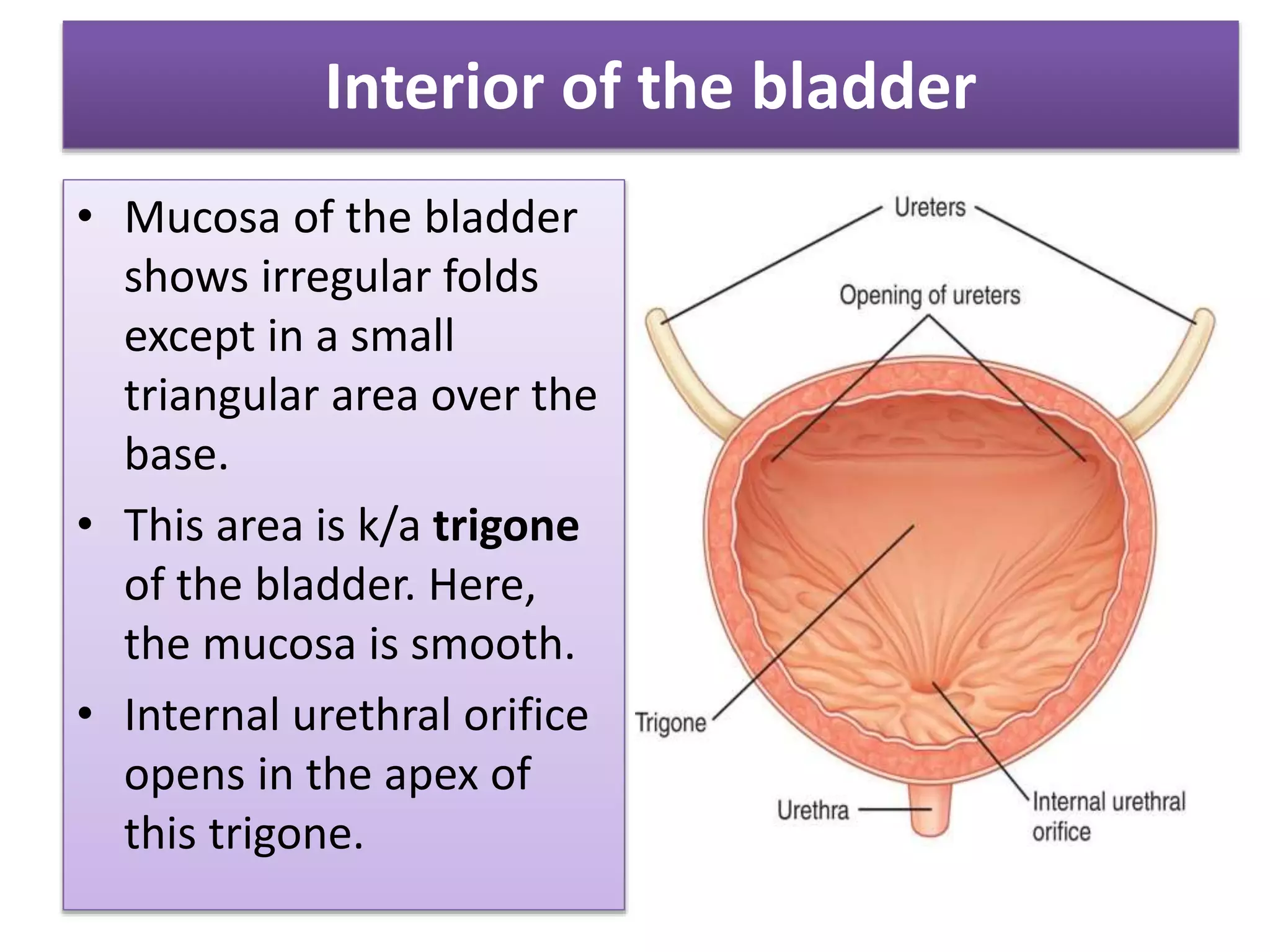
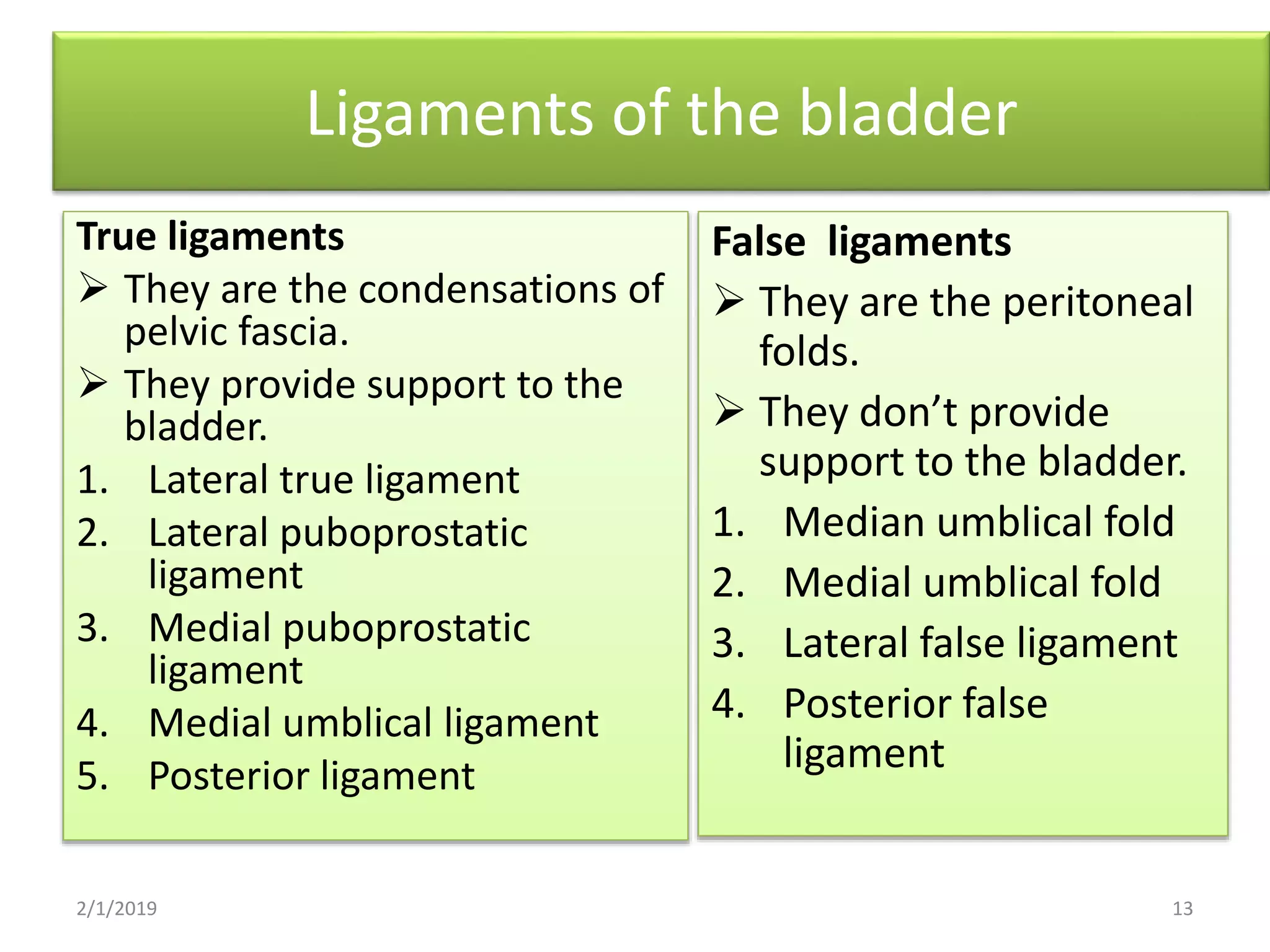
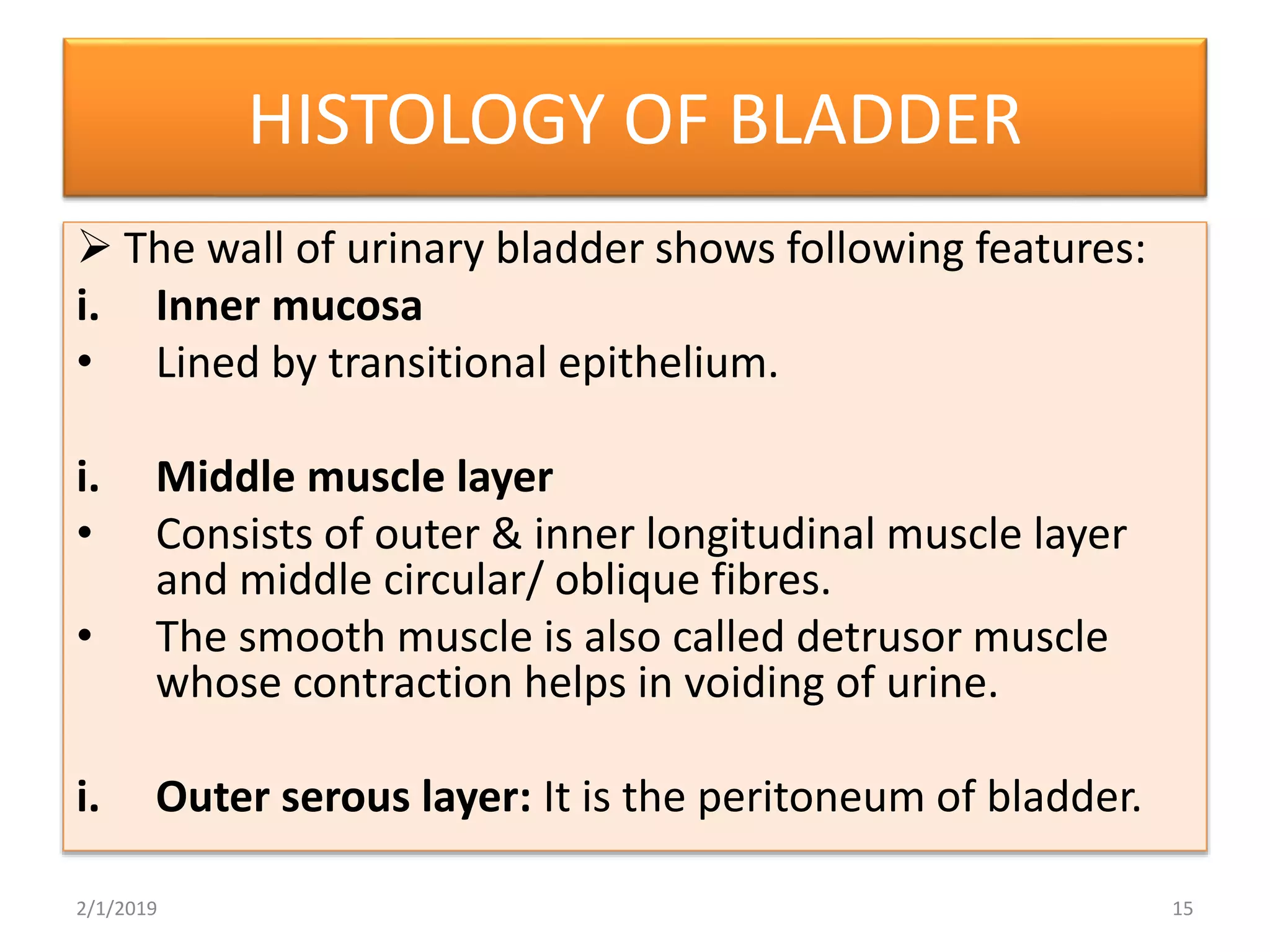
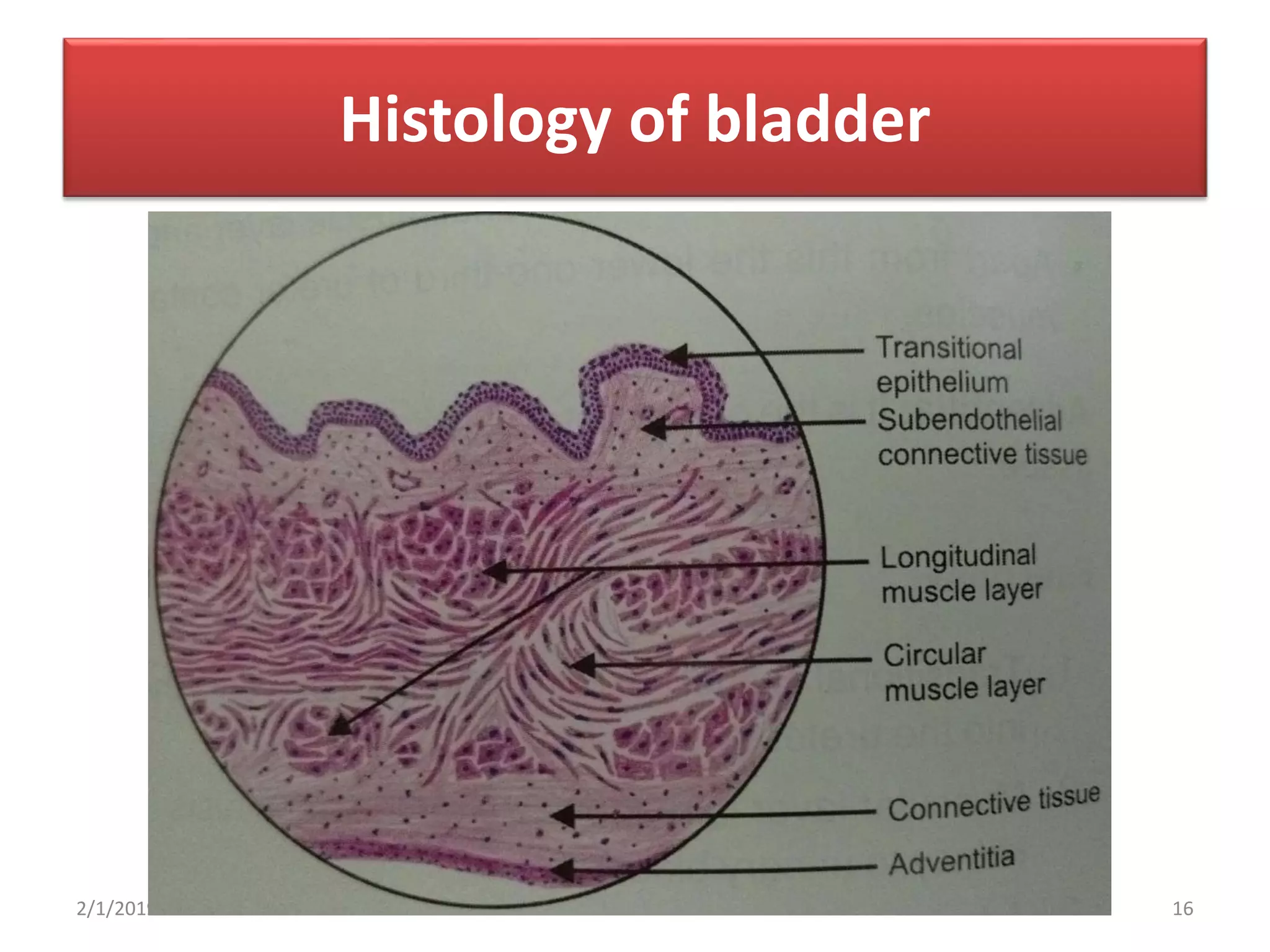
The urinary bladder is a muscular organ located in the pelvic cavity that stores urine, with its shape and size varying based on the urine volume. It has a tetrahedral shape when empty and presents features such as the apex, base, neck, and various surfaces and borders, with specific relations in males and females. The bladder's interior contains a smooth area called the trigone and is supported by true ligaments formed by pelvic fascia and false ligaments that are peritoneal folds.