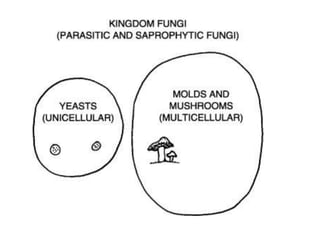
This document provides information about microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. It discusses the key characteristics of bacteria such as being unicellular and prokaryotic. The document describes the structures of bacterial cells and how they reproduce through binary fission. Both harmful and helpful roles of bacteria are outlined. Fungi are described as eukaryotic and non-photosynthetic. The structures and modes of reproduction for fungi are also summarized. Finally, viruses are defined as obligate intracellular parasites lacking the characteristics of life that can cause diseases in humans like AIDS and chicken pox.