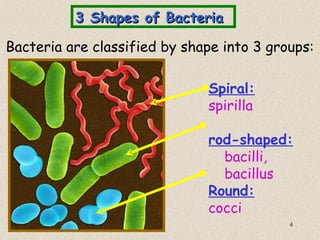
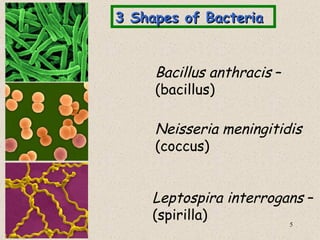
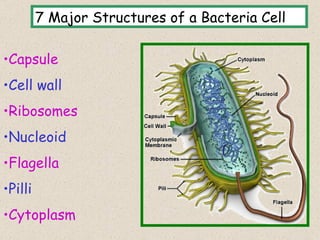
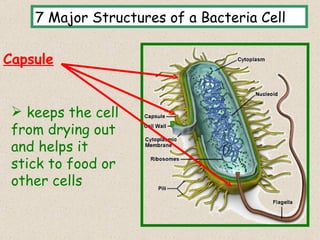
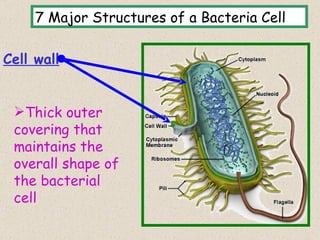
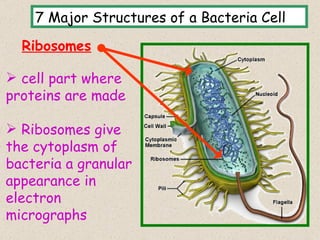
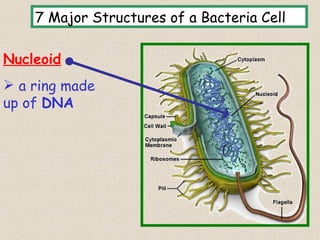
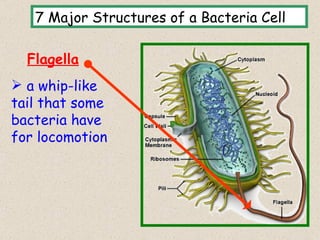
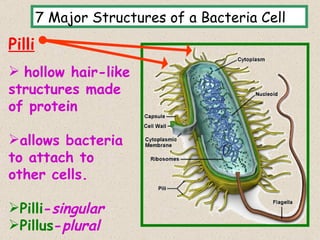
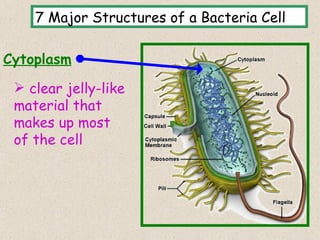
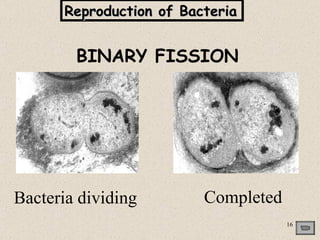
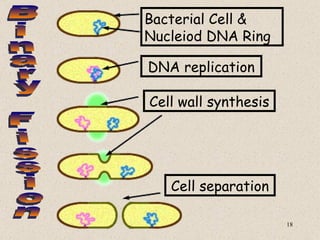
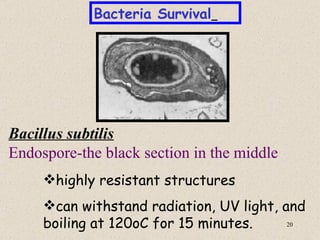
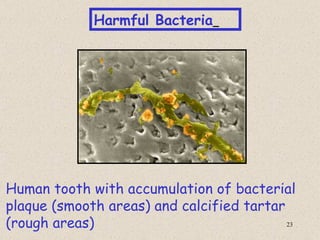
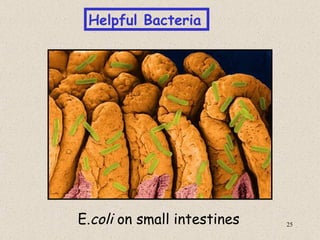
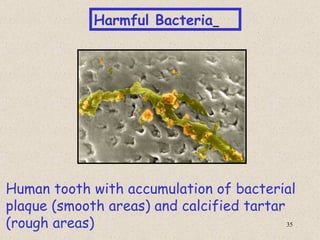
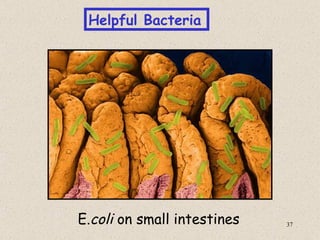
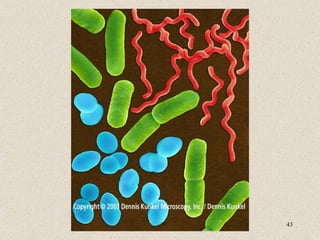
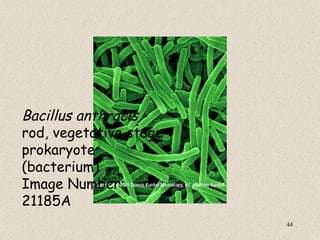
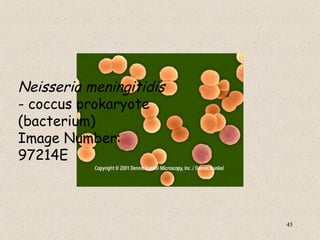
The document provides an overview of bacteria, including their structures, types, shapes, reproduction, how they obtain food, and ways to control bacteria. It discusses that bacteria are single-celled organisms that can be harmful or helpful. Blue-green bacteria are notable as they perform photosynthesis to produce their own food.