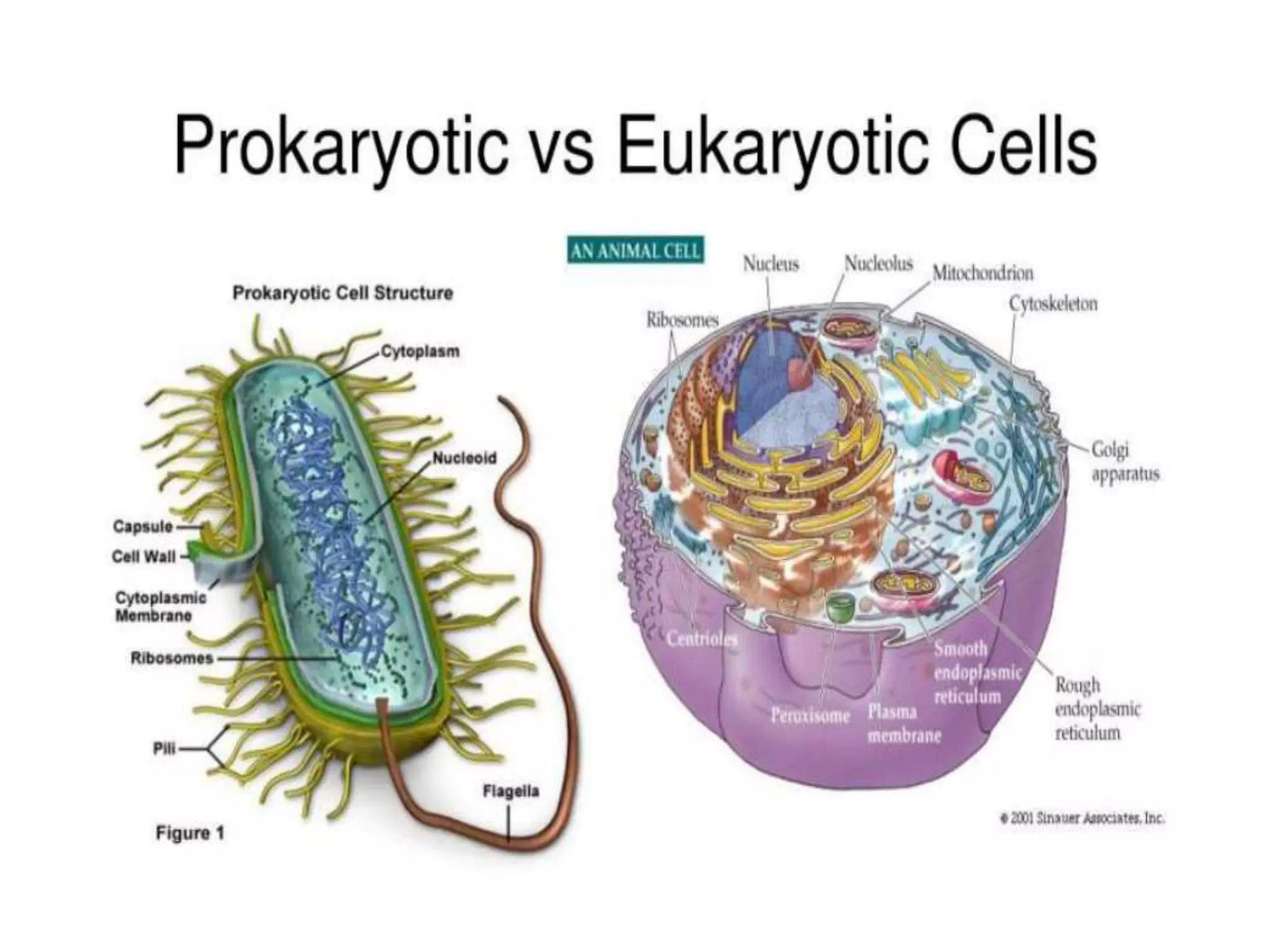
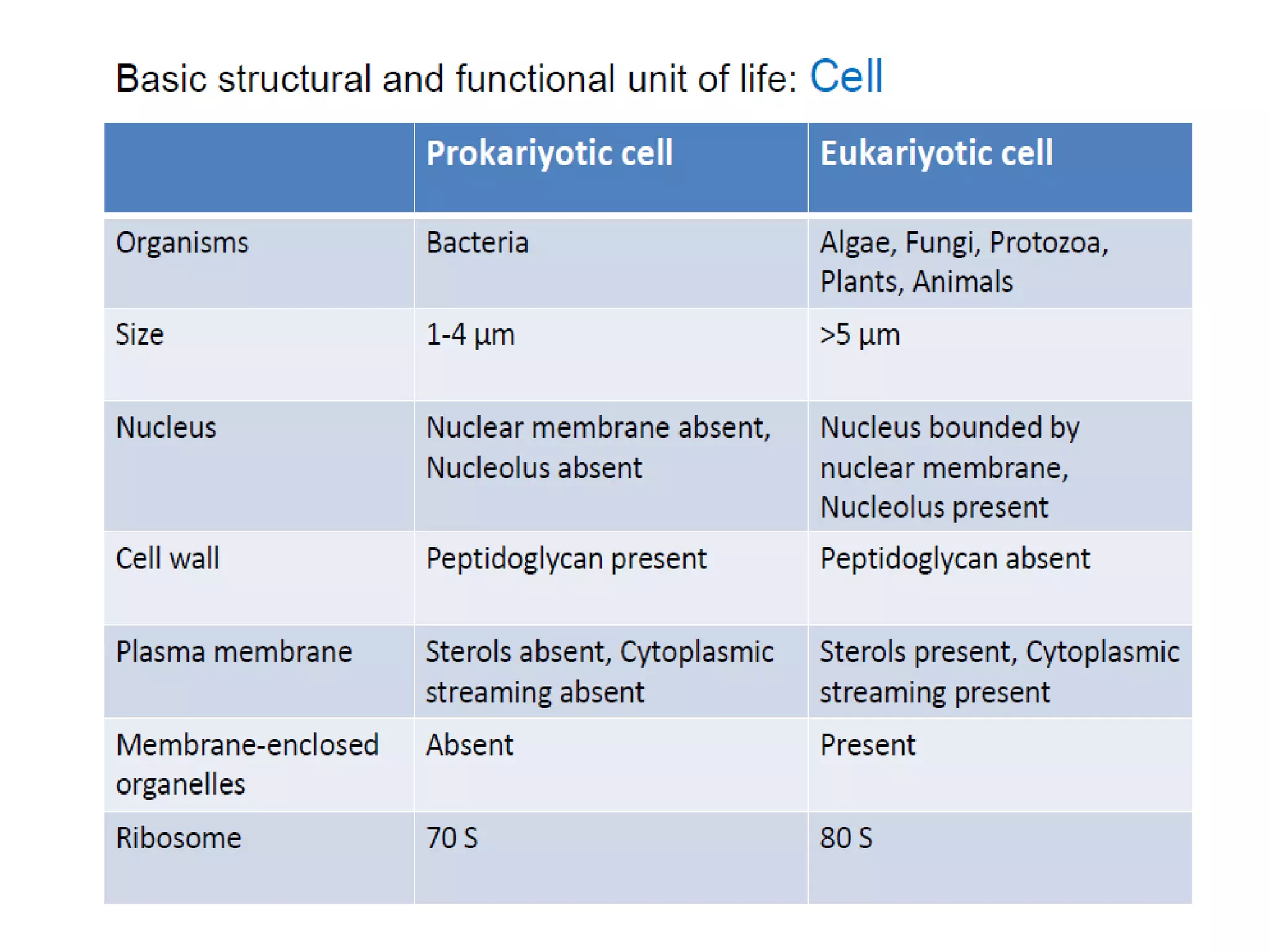
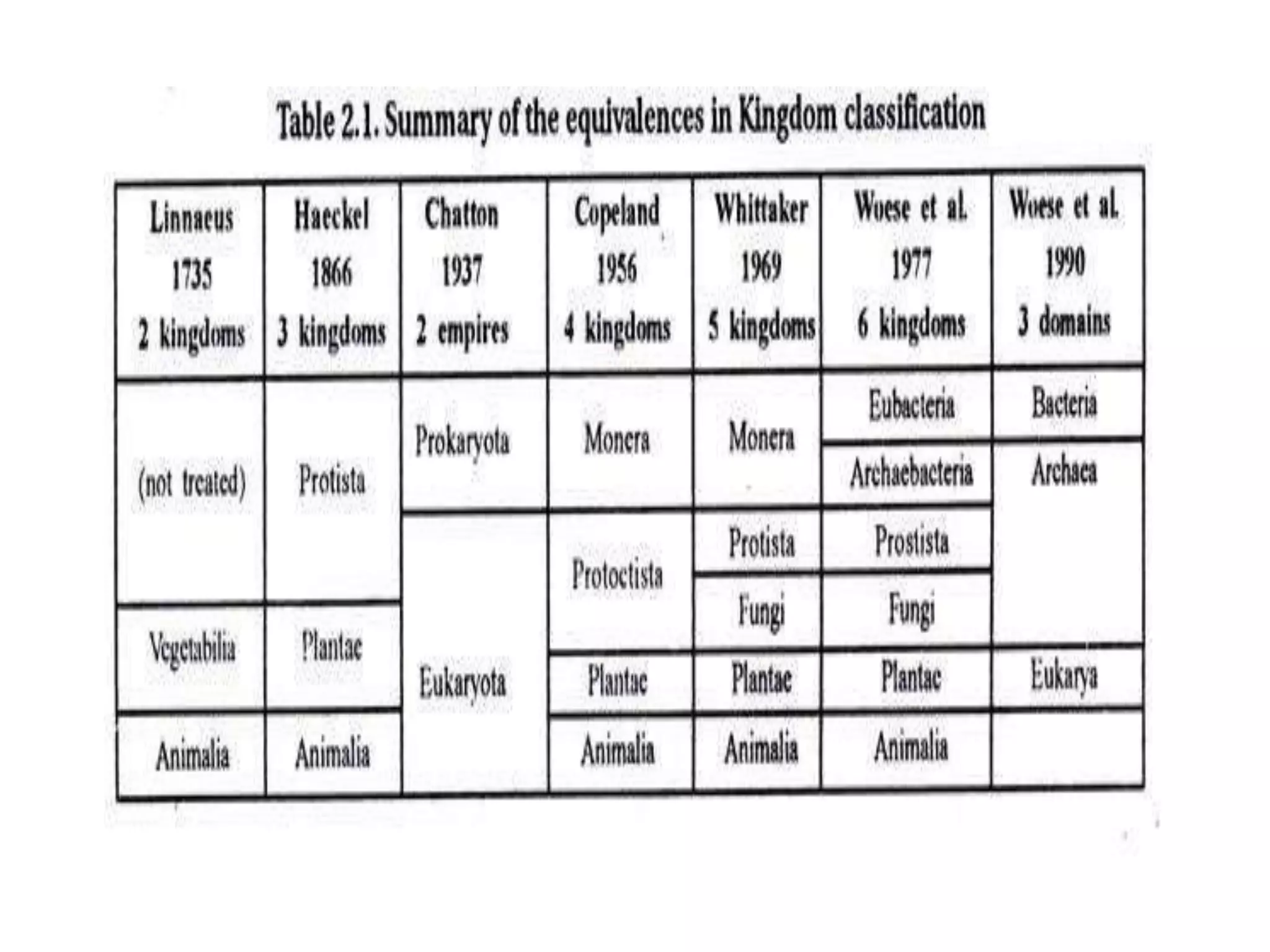
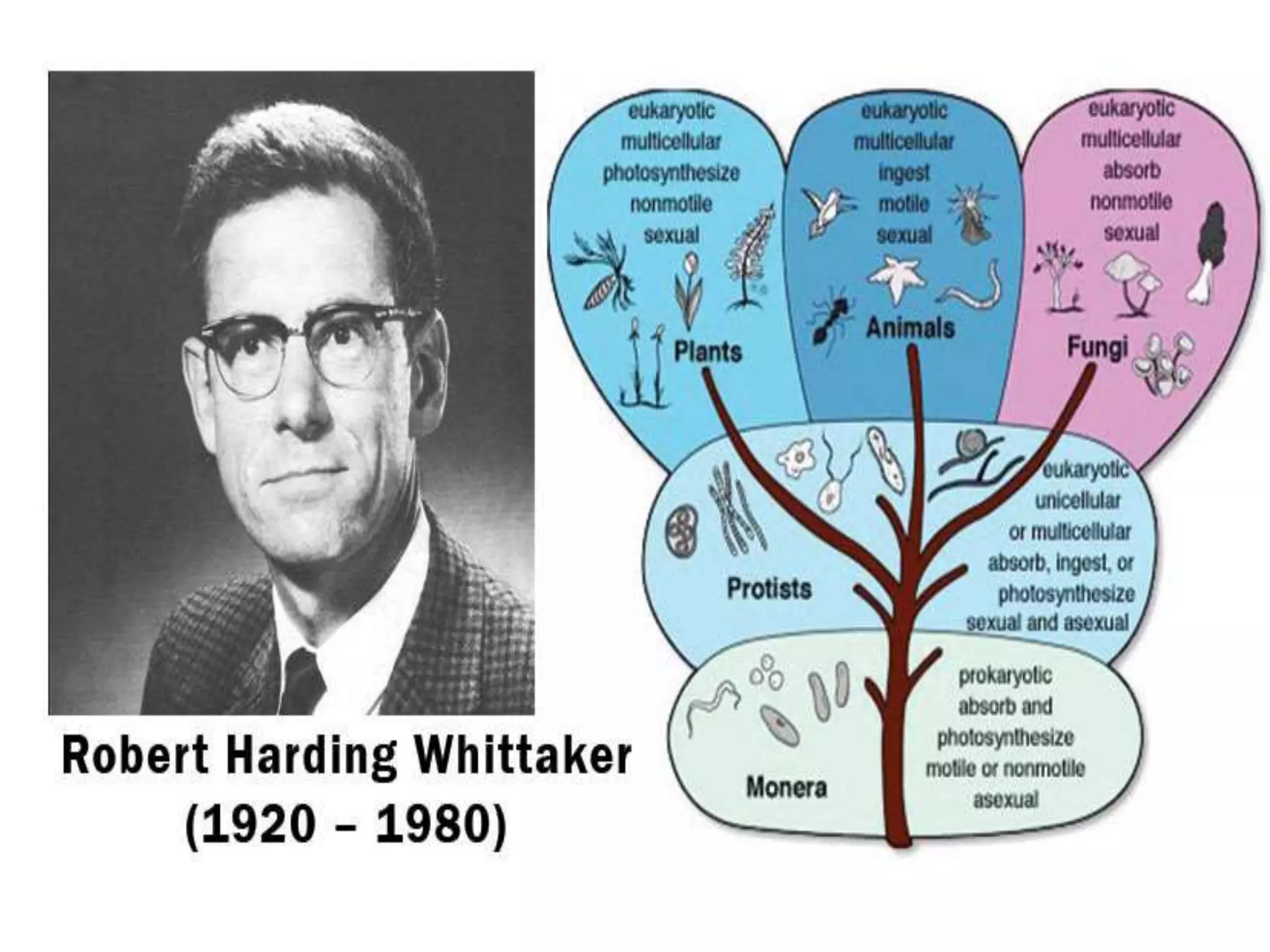
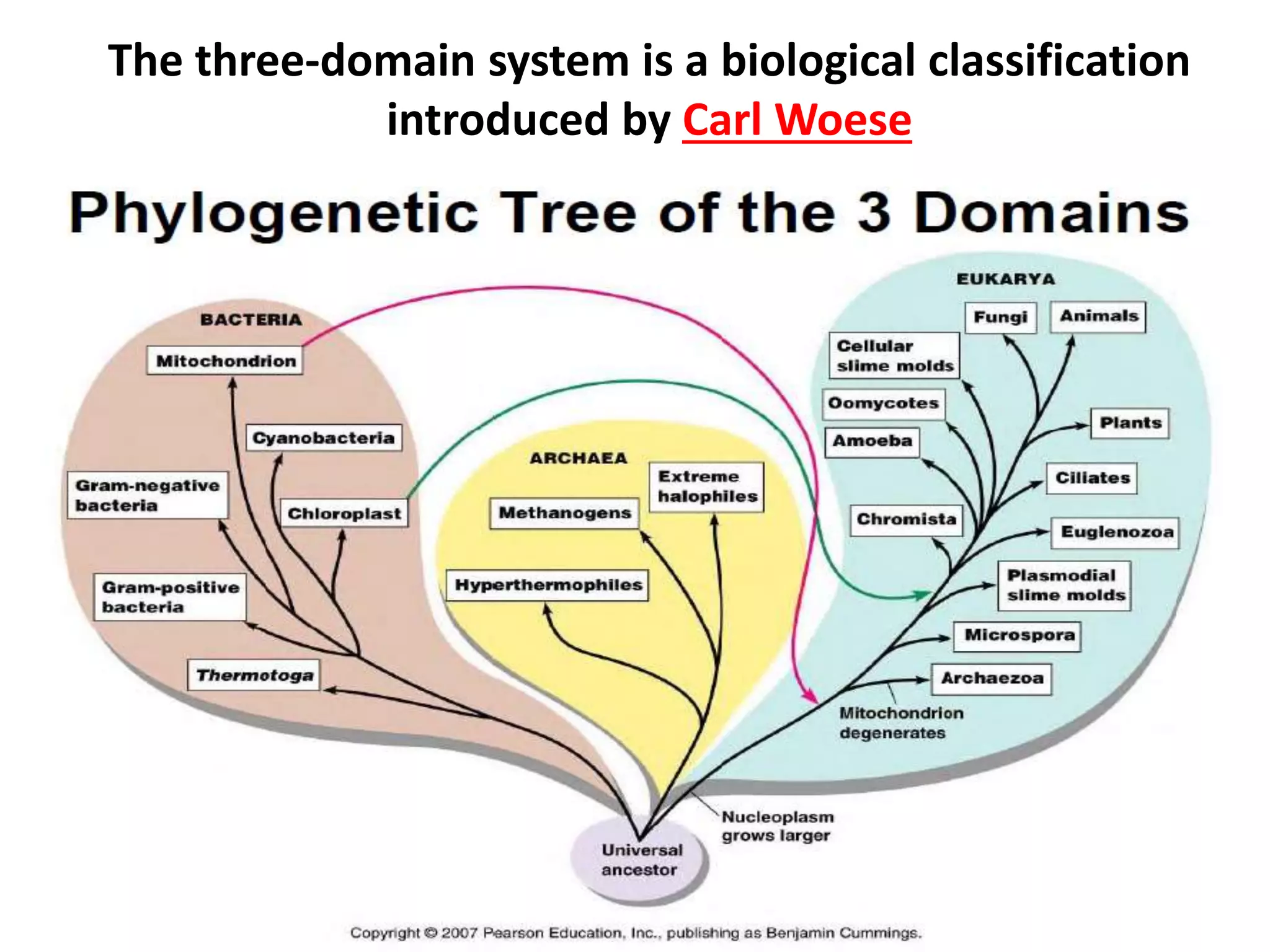
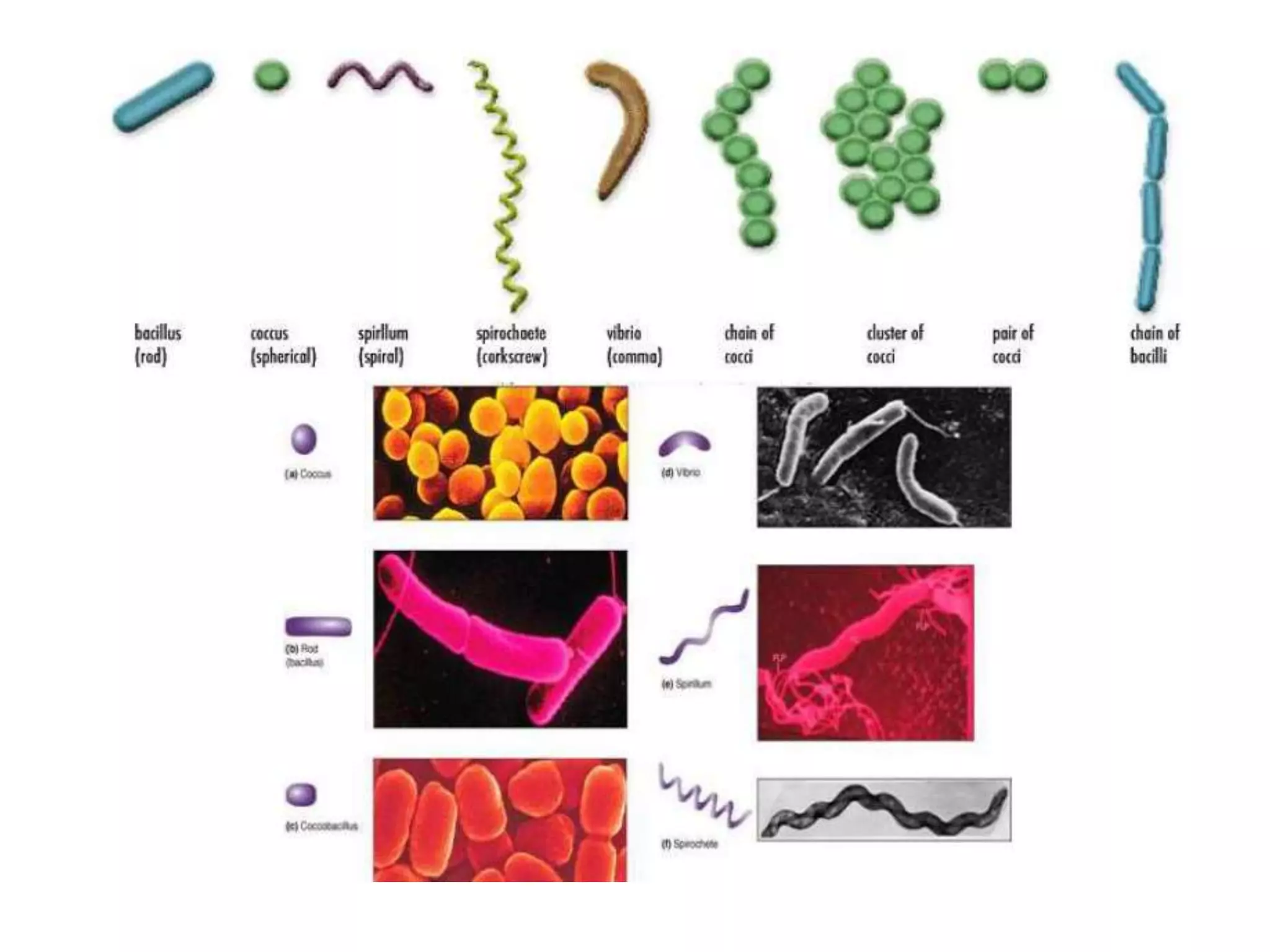
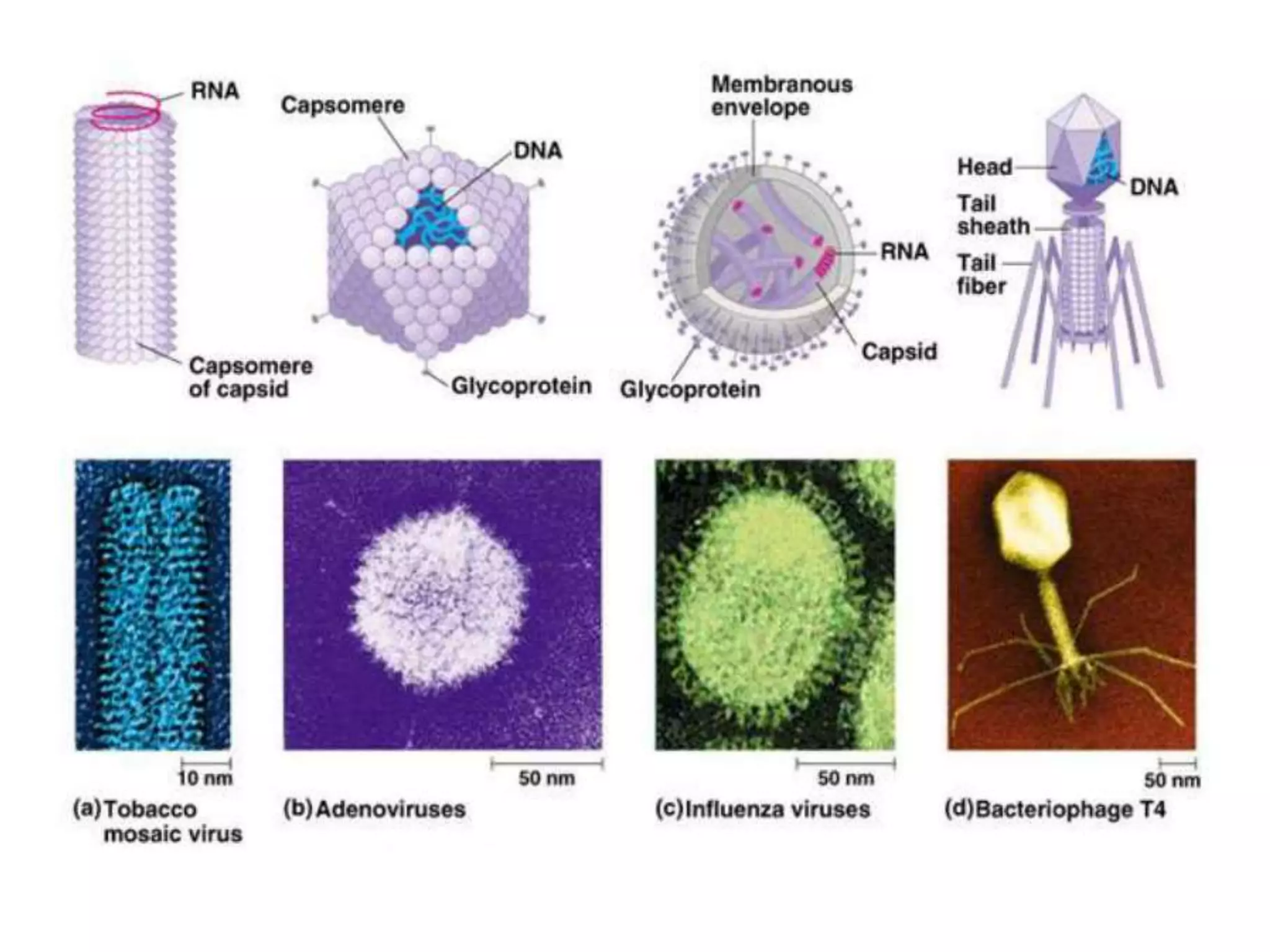
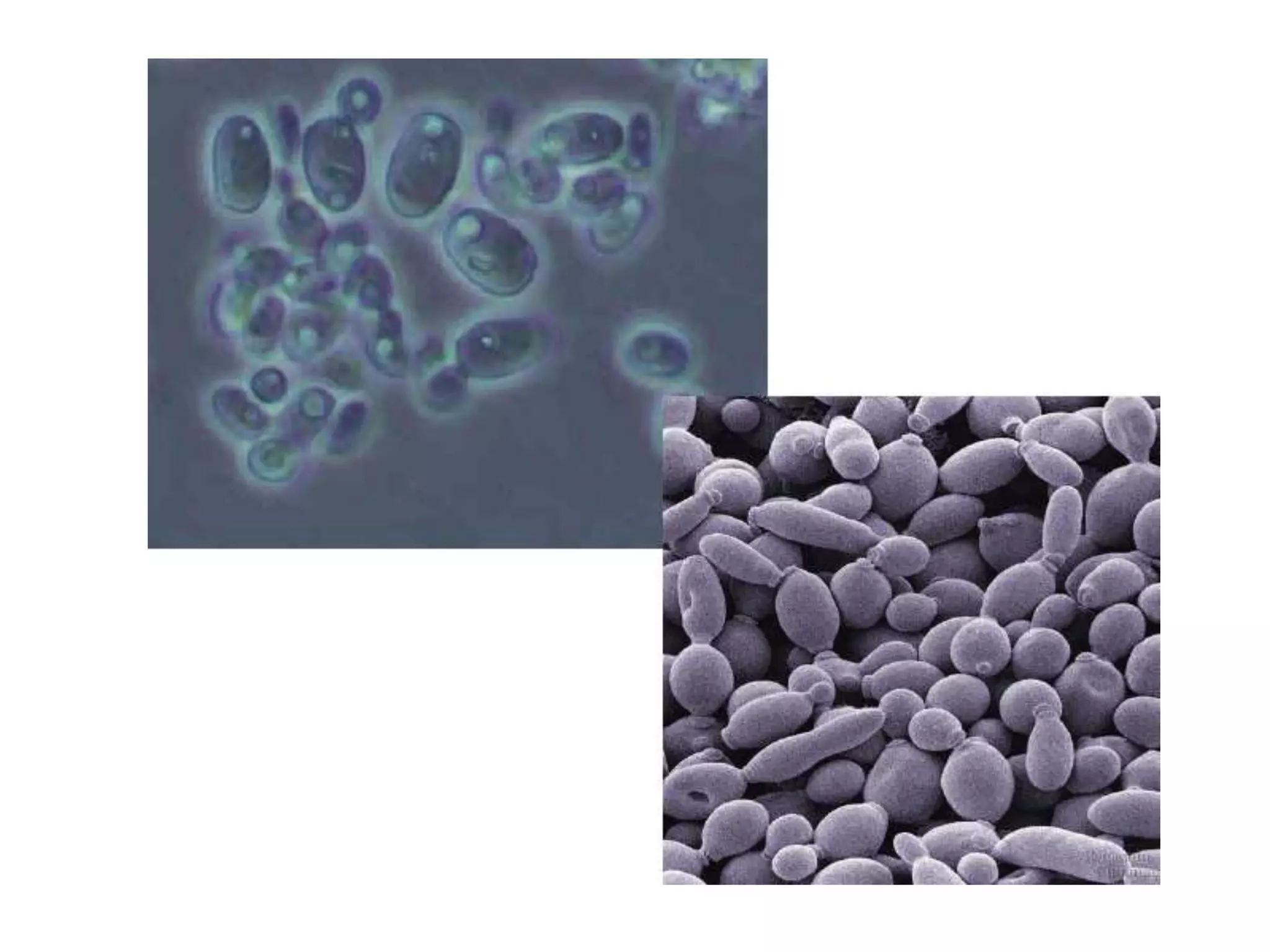
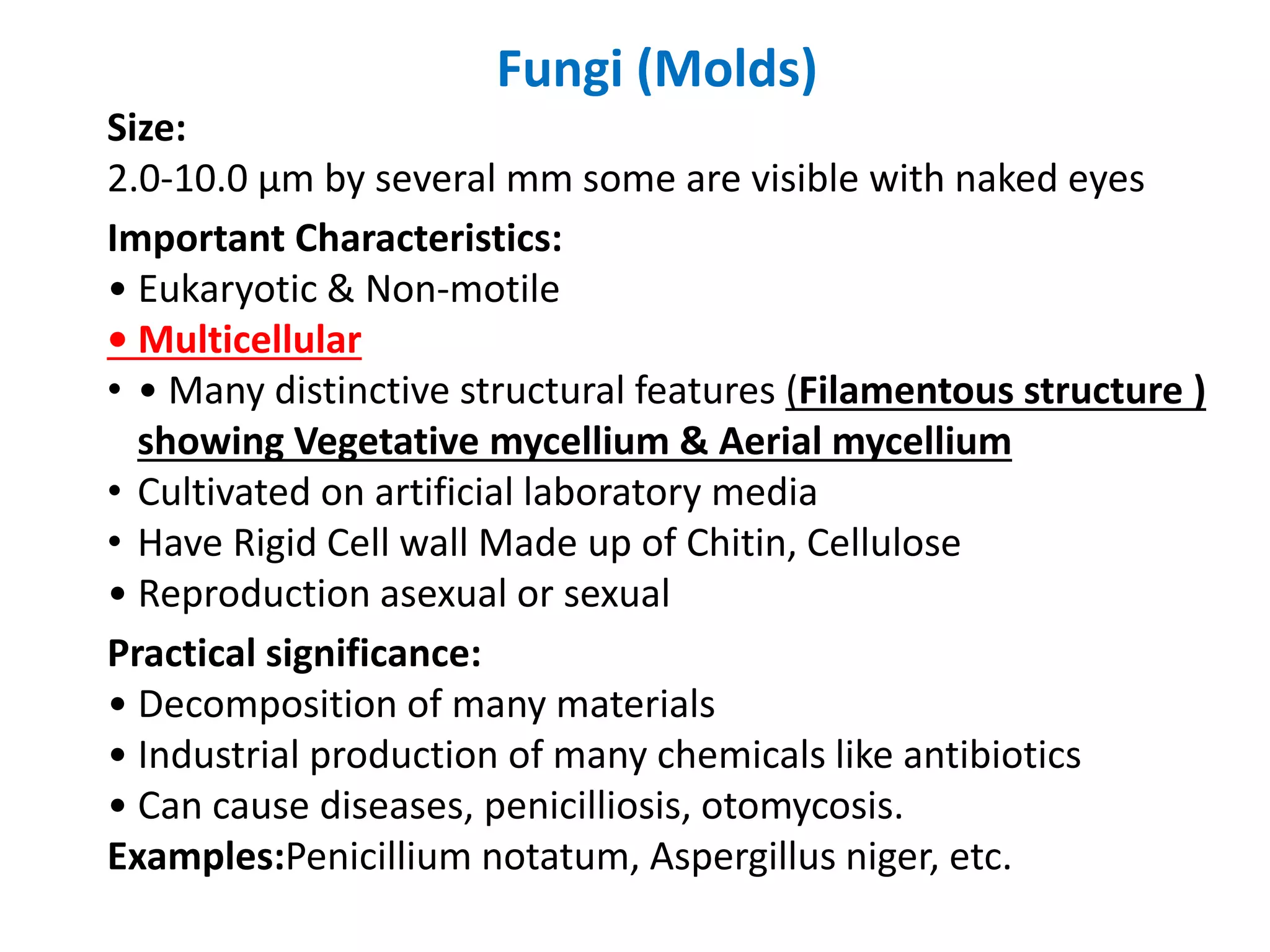
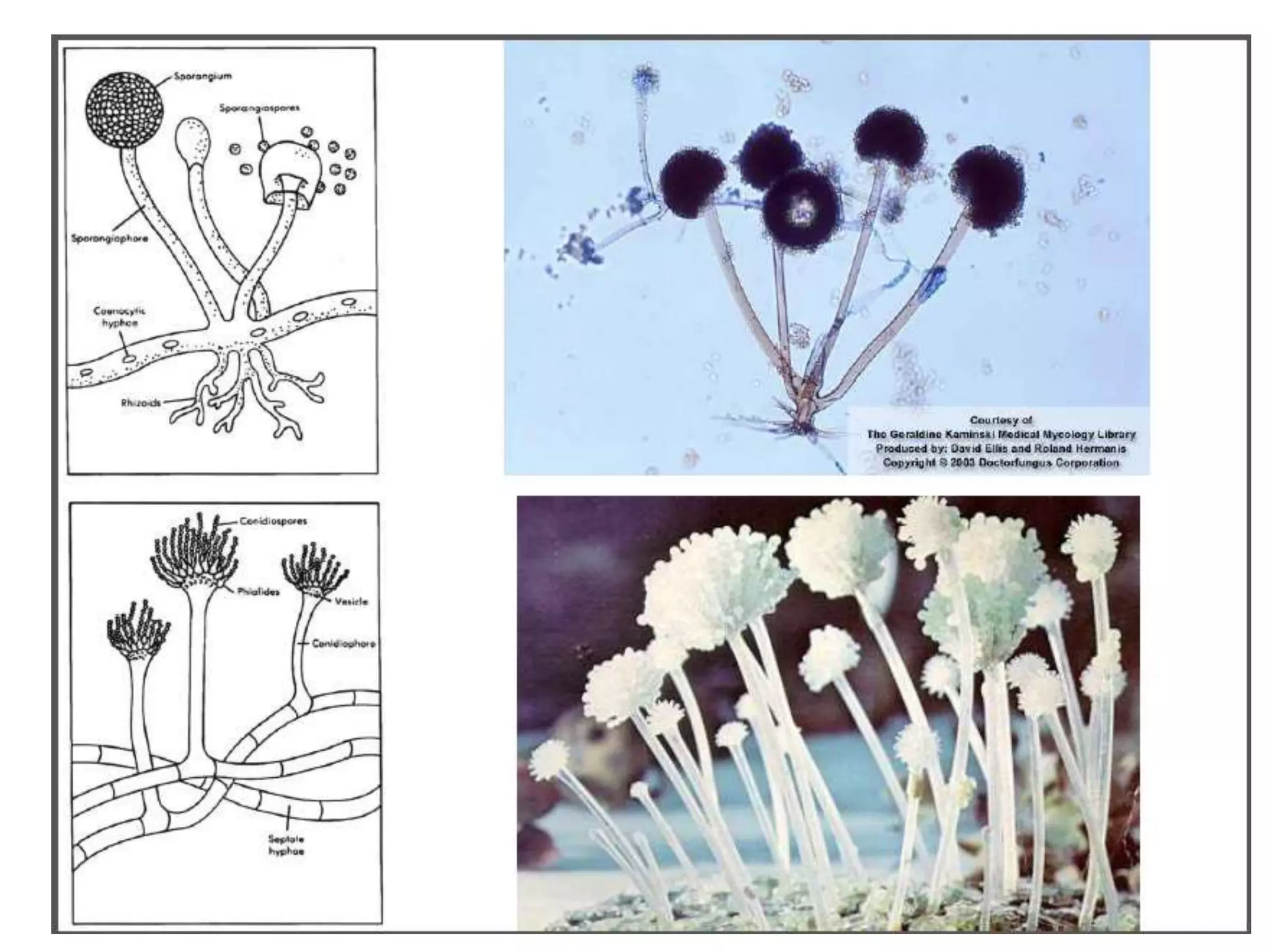
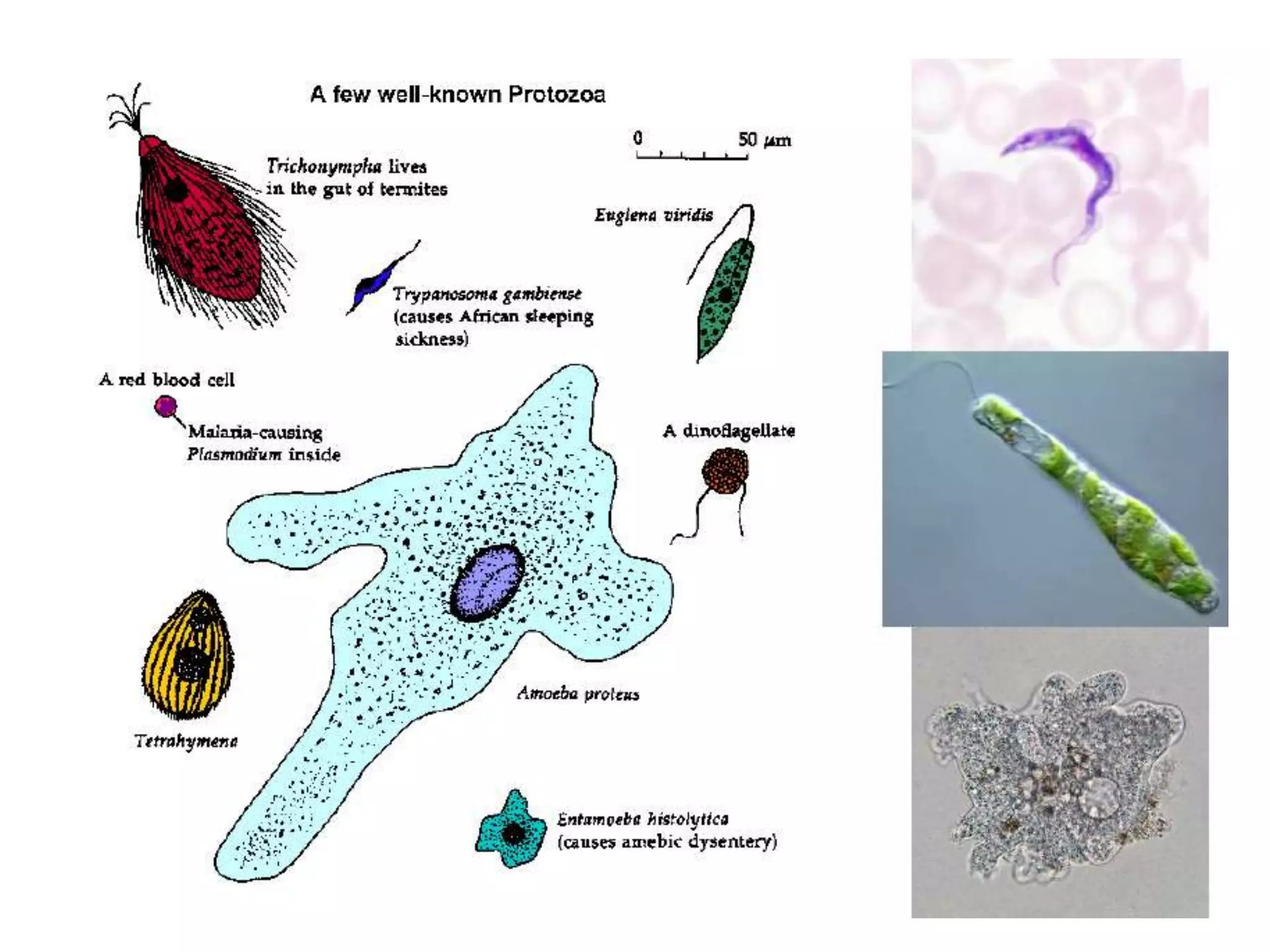
The document presents a classification of microorganisms, detailing the taxonomy and characteristics of different groups, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, and algae. It discusses the historical development of classification, highlighting the three-domain system proposed by Carl Woese, which classifies life into Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Each type of microorganism is characterized by their size, structural features, mode of reproduction, and practical significance in environments and industries.