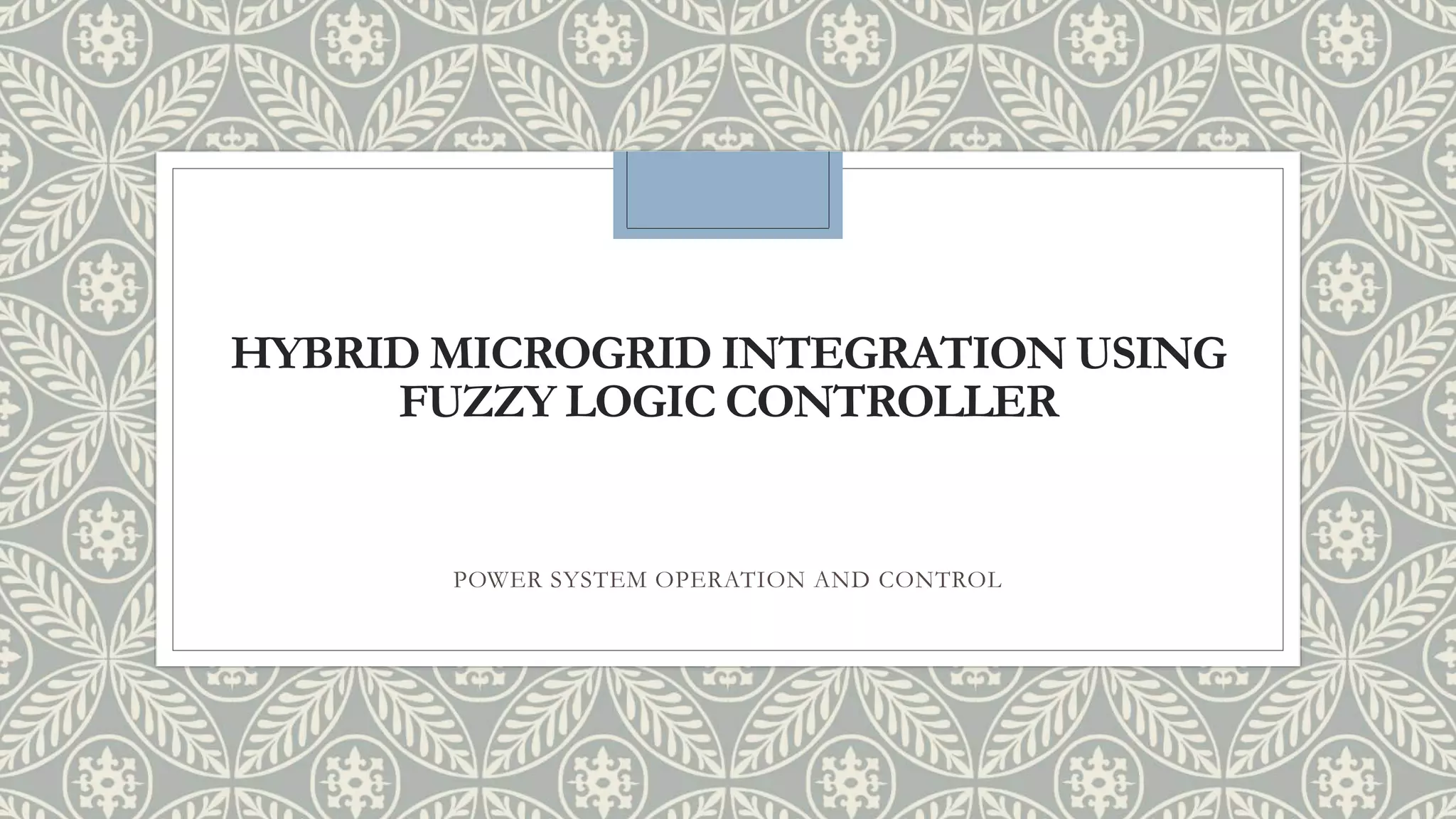
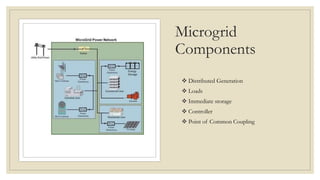
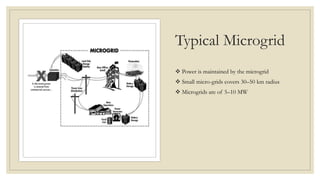
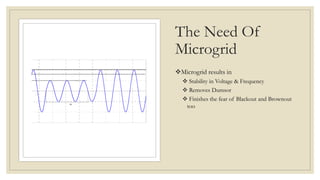
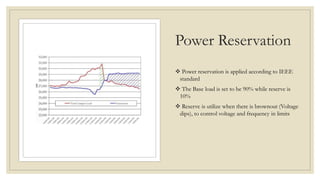
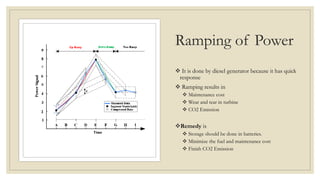
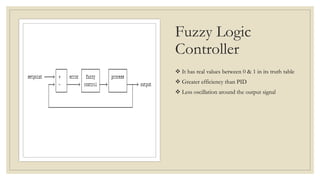
The document discusses the concept of microgrids, which are small-scale power systems that provide local energy generation for communities. It details the components, sources, and advantages of microgrids, including improved voltage stability and reduced blackout risks, while also addressing challenges such as energy storage and synchronization. A fuzzy logic controller is highlighted for its efficiency in managing microgrid operations, despite some limitations in terms of space and technical synchronization.