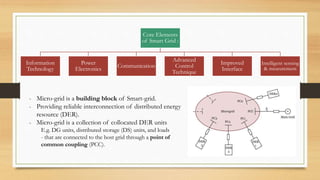
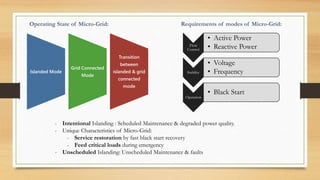
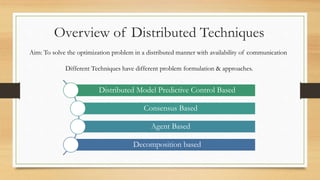
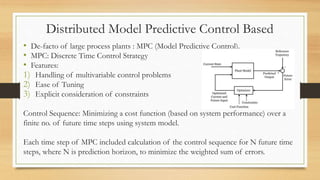
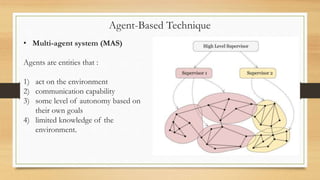
The document discusses distributed control techniques in micro-grids, highlighting the characteristics, operation modes, and control strategies such as decentralized control and droop control. It emphasizes the importance of communication and interaction among distributed energy resources (DERs) for optimizing performance while also addressing the limitations of current methods. Proposed modifications and various distributed approaches, including model predictive control, consensus-based, and agent-based techniques, are presented for improving control system efficiency and stability.