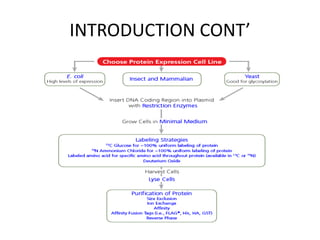
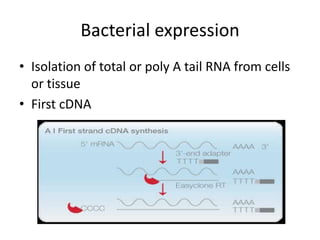
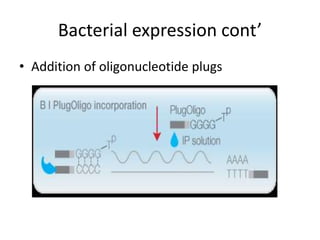
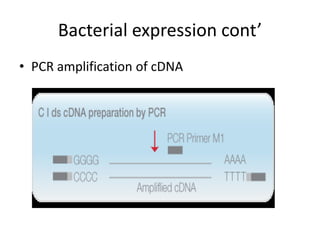
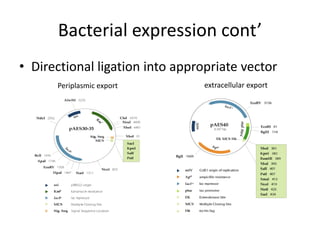
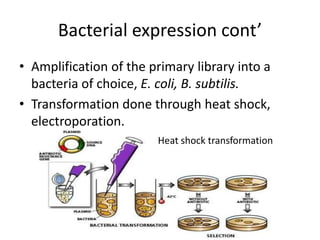
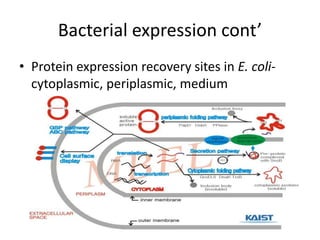
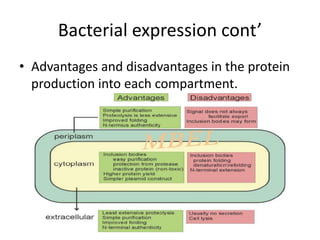
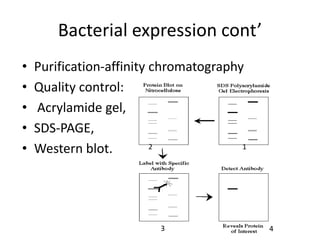
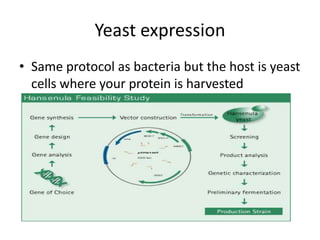
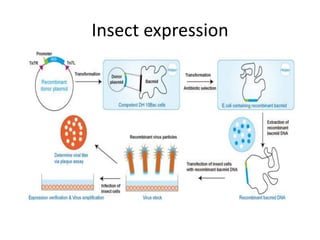
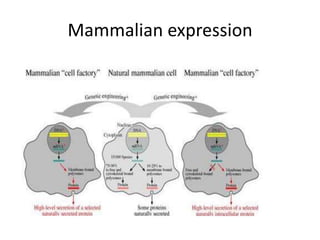
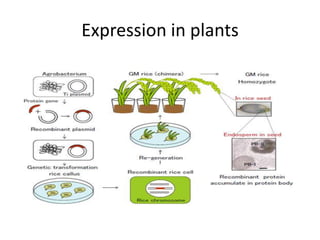
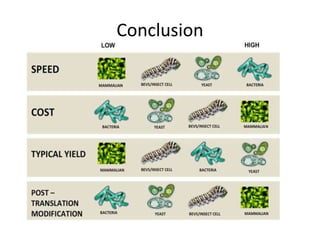
This document discusses recombinant protein expression in different systems including bacterial, yeast, insect, mammalian and plant systems. It provides details on the process of recombinant protein expression which involves isolation of mRNA, cDNA synthesis, cloning into an expression vector, transformation into a host cell, protein expression and recovery. The advantages and disadvantages of expressing proteins in different cellular compartments like cytoplasm, periplasm and culture medium are also mentioned. Quality control methods like SDS-PAGE and western blotting are discussed.