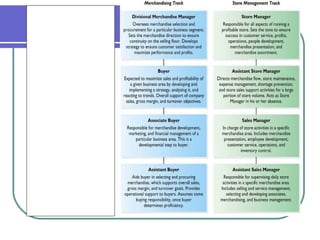
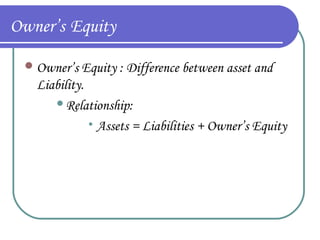
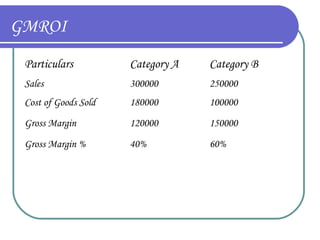
This document provides an overview of retail merchandising concepts. It outlines the objectives of understanding merchandising philosophy, merchandise plans, category management, and buying organization formats. It then defines key merchandising terms and discusses the role and responsibilities of merchandisers, including planning, directing, coordinating, and controlling merchandising activities. The document also summarizes concepts related to merchandise management, accounting, and financial analysis, including sales forecasting, determining merchandise requirements, income statements, and calculating gross margin return on investment.