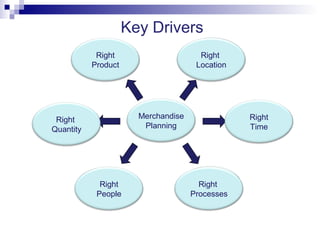
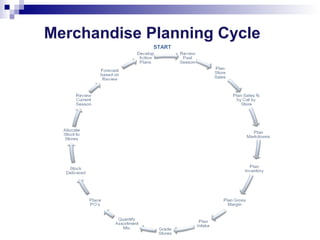
This document outlines the key steps and considerations in a merchandise planning cycle for a retail company. It discusses factors such as reviewing past performance, creating sales forecasts, developing product and financial plans at the department and store level based on trends and benchmarks, optimizing suppliers and supply chains, allocating stock, and reviewing in-season sales performance. It also provides frequently asked questions about each step in the planning process and how the company approaches various merchandising decisions.