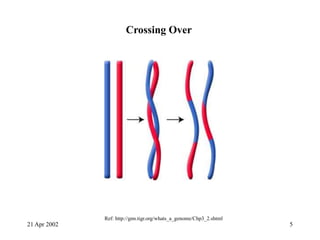
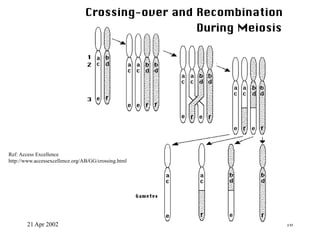
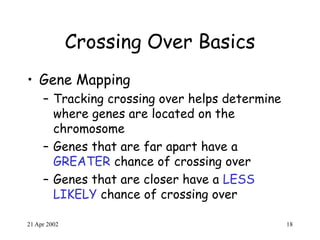
Crossing over occurs during prophase I of meiosis in eukaryotes. It involves the exchange of genetic material between paired homologous chromosomes, resulting in genetic variation. Tracking crossing over helped scientists determine that genes located farther apart on a chromosome have a greater chance of being exchanged than genes closer together, establishing the concept of genetic linkage. Crossing over ensures the combination of maternal and paternal genes in offspring.