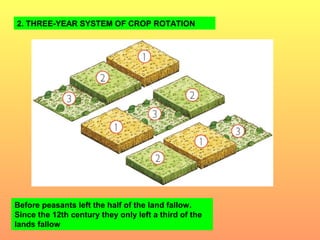
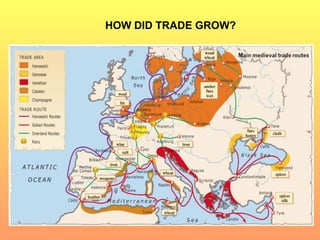
Agricultural improvements led to population growth and the rise of cities in medieval Europe. As cities expanded, trade increased between growing urban centers along major routes like the Mediterranean and Baltic seas. Stronger monarchies also developed as kings gained support from prosperous cities in exchange for autonomy, collecting more taxes to fund royal armies and governments. Guilds organized craftsmen in cities and helped regulate skilled trades that supplied the growing urban markets.