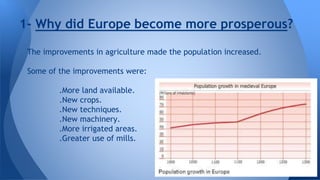
This document summarizes key developments in medieval European cities between the 12th and 15th centuries. It discusses how improved agriculture led to population growth and increased trade between different routes. This stimulated the development of banking and finance. More people migrated to cities for work opportunities and freedom, causing urban populations to expand. Cities became centers of trade, crafts, and governance, though they remained small overall. Craftsmen organized themselves by street and trade, while citizens represented a diversity of social classes and religions. Monarchies grew stronger by collecting more taxes, creating professional armies, and establishing parliaments to reduce noble power and approve budgets and legislation.