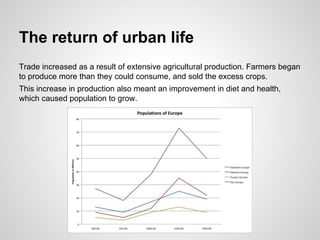
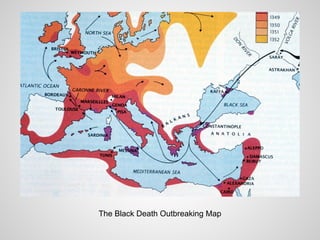
Medieval cities experienced a period of growth and development between the 12th and 13th centuries. Advances in agriculture led to increased food production and population growth, allowing cities to reemerge as centers of trade, artisan production, and new social classes like the bourgeoisie. However, the 14th century brought crises like wars, famine, plague, and subsequent social unrest that marked the Lower Middle Ages. Despite this, Gothic art and architecture flourished as new styles emphasized taller, lighter structures like cathedrals.