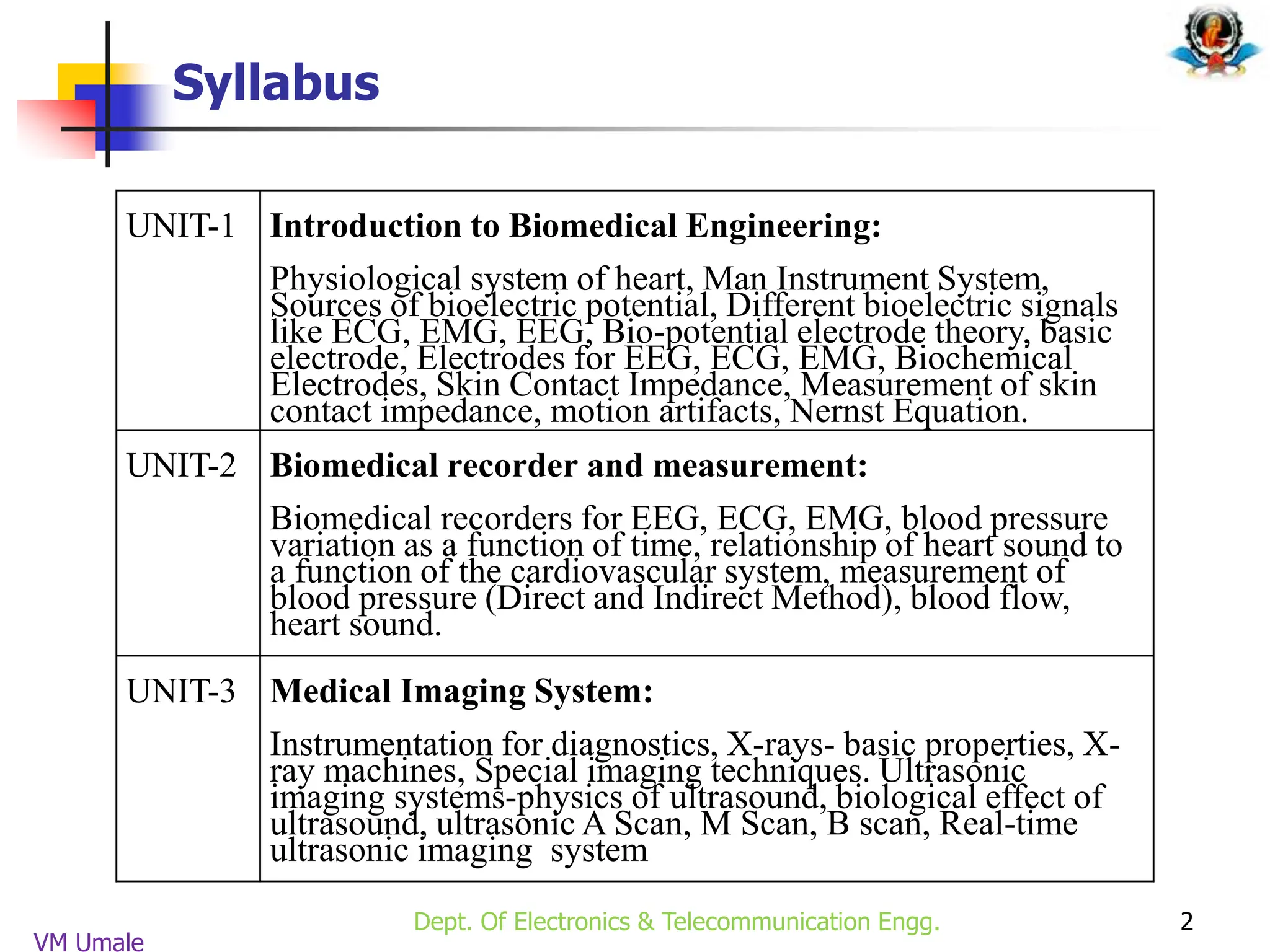
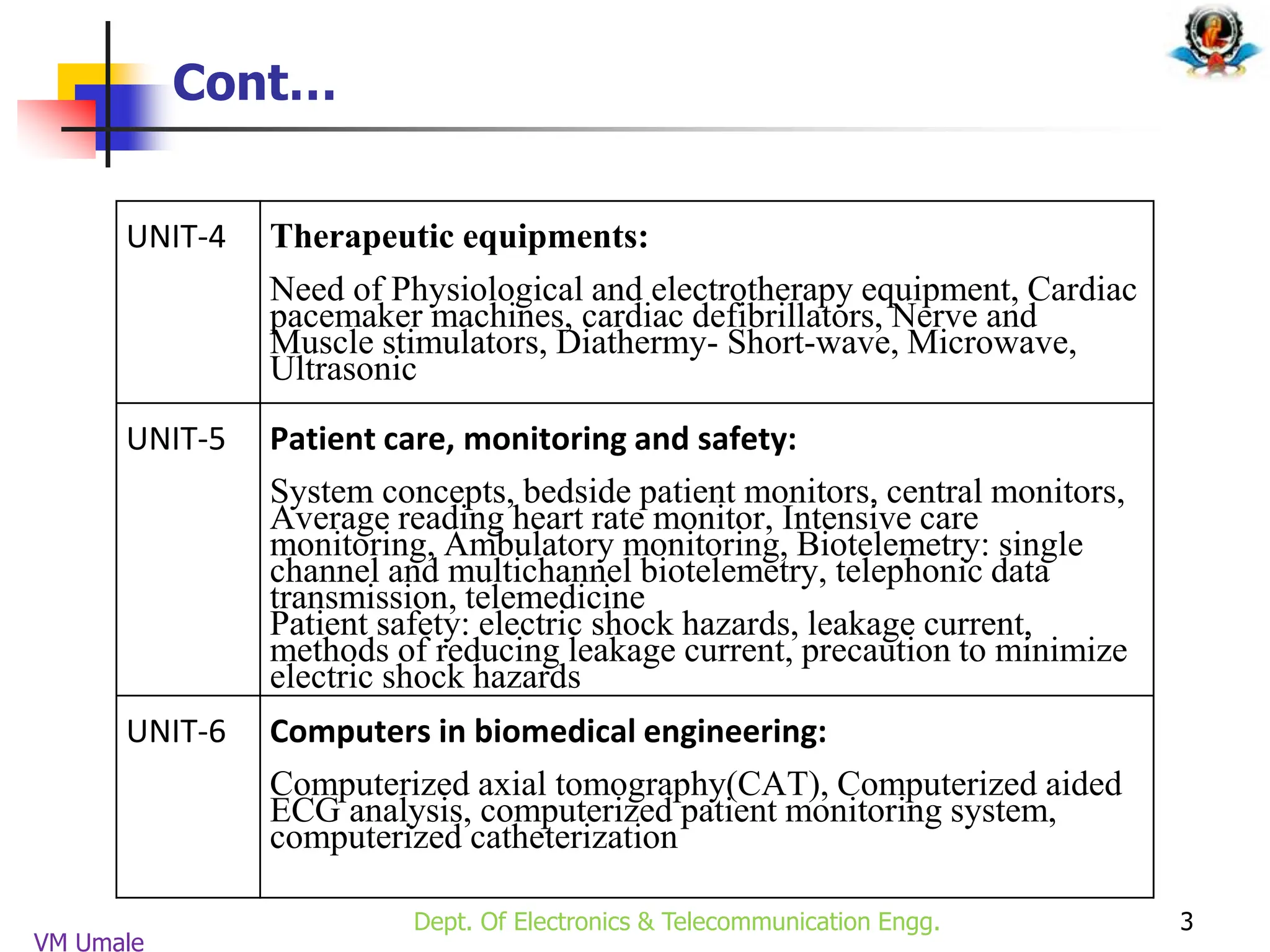
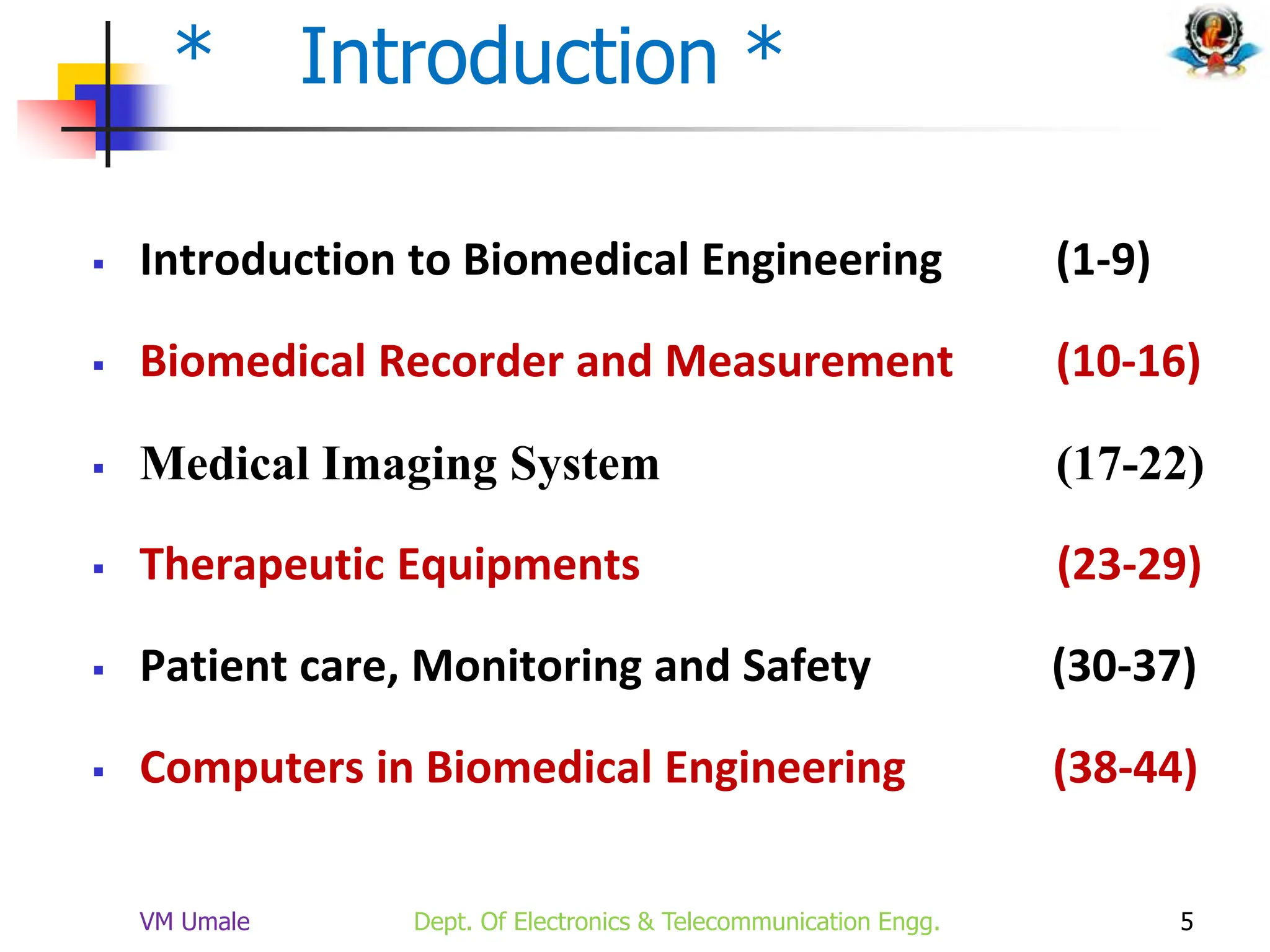
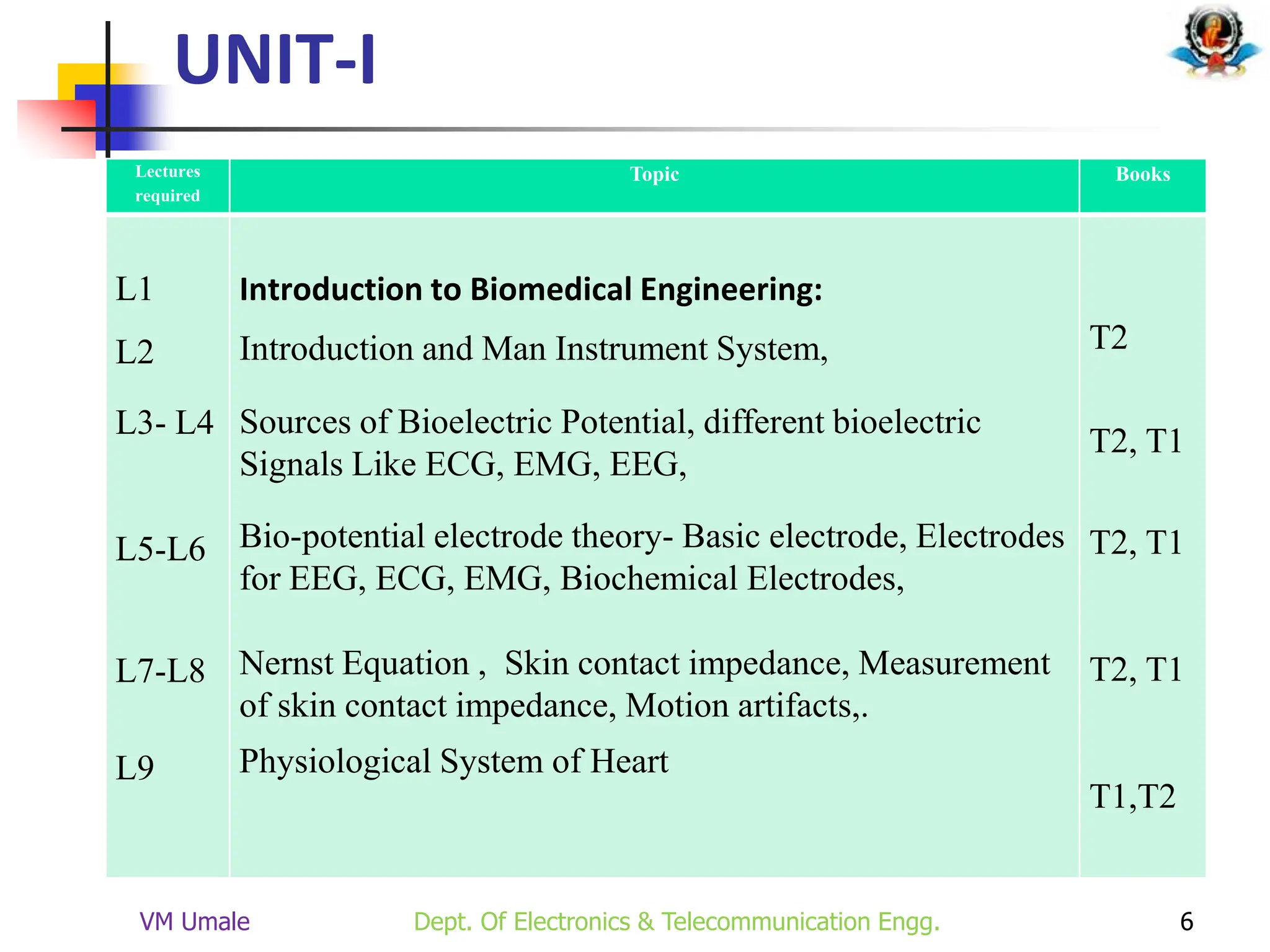
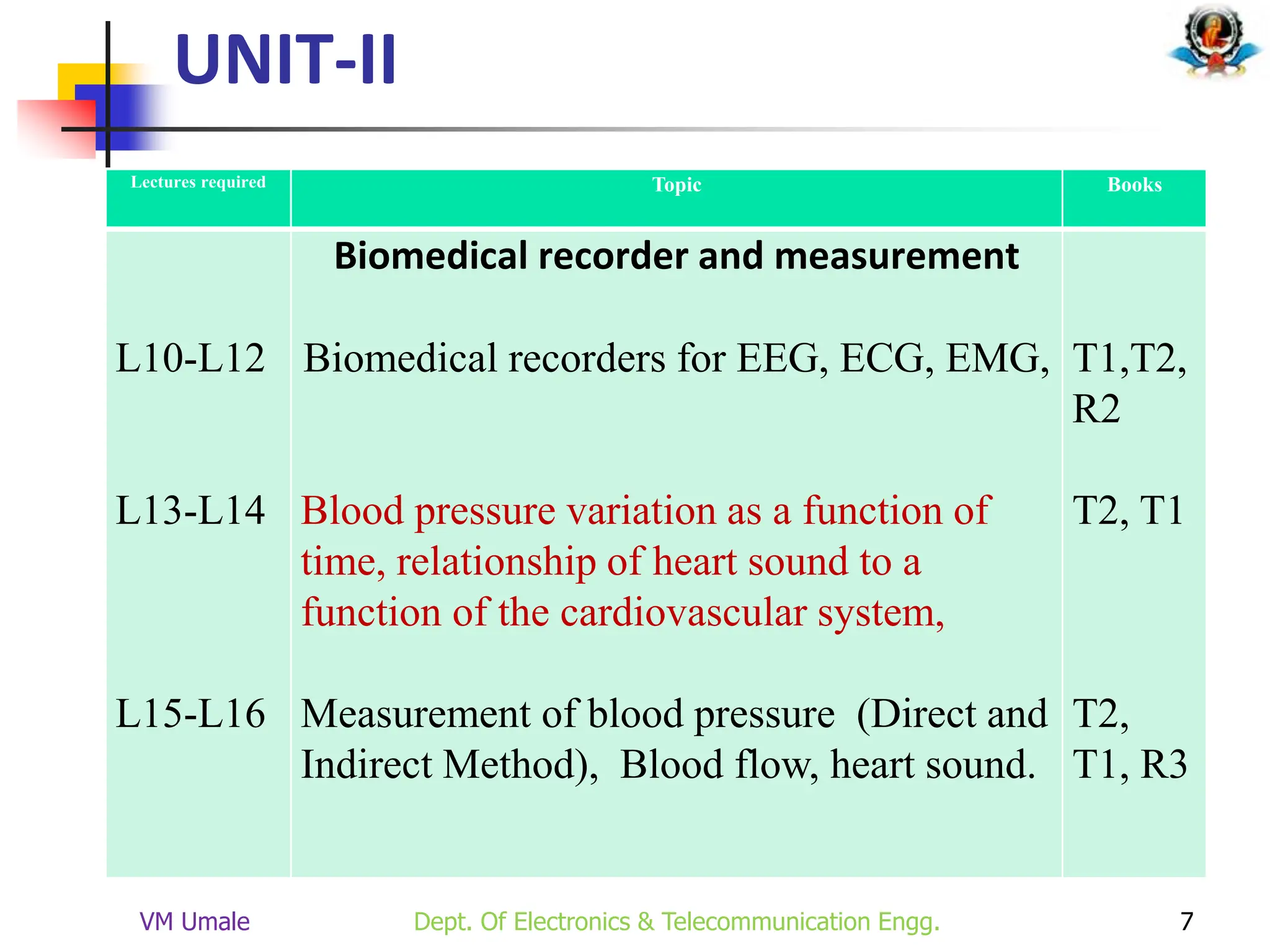
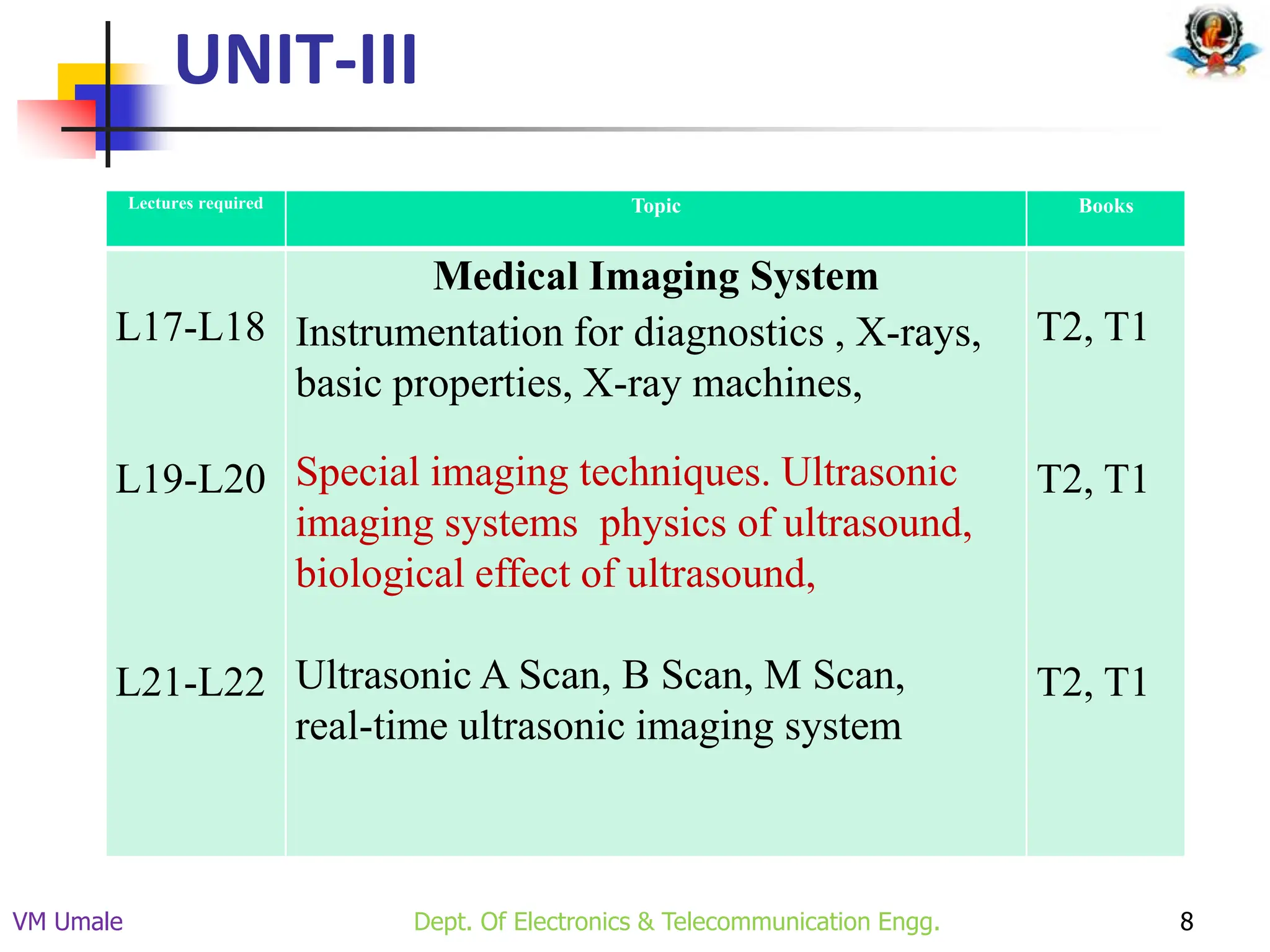
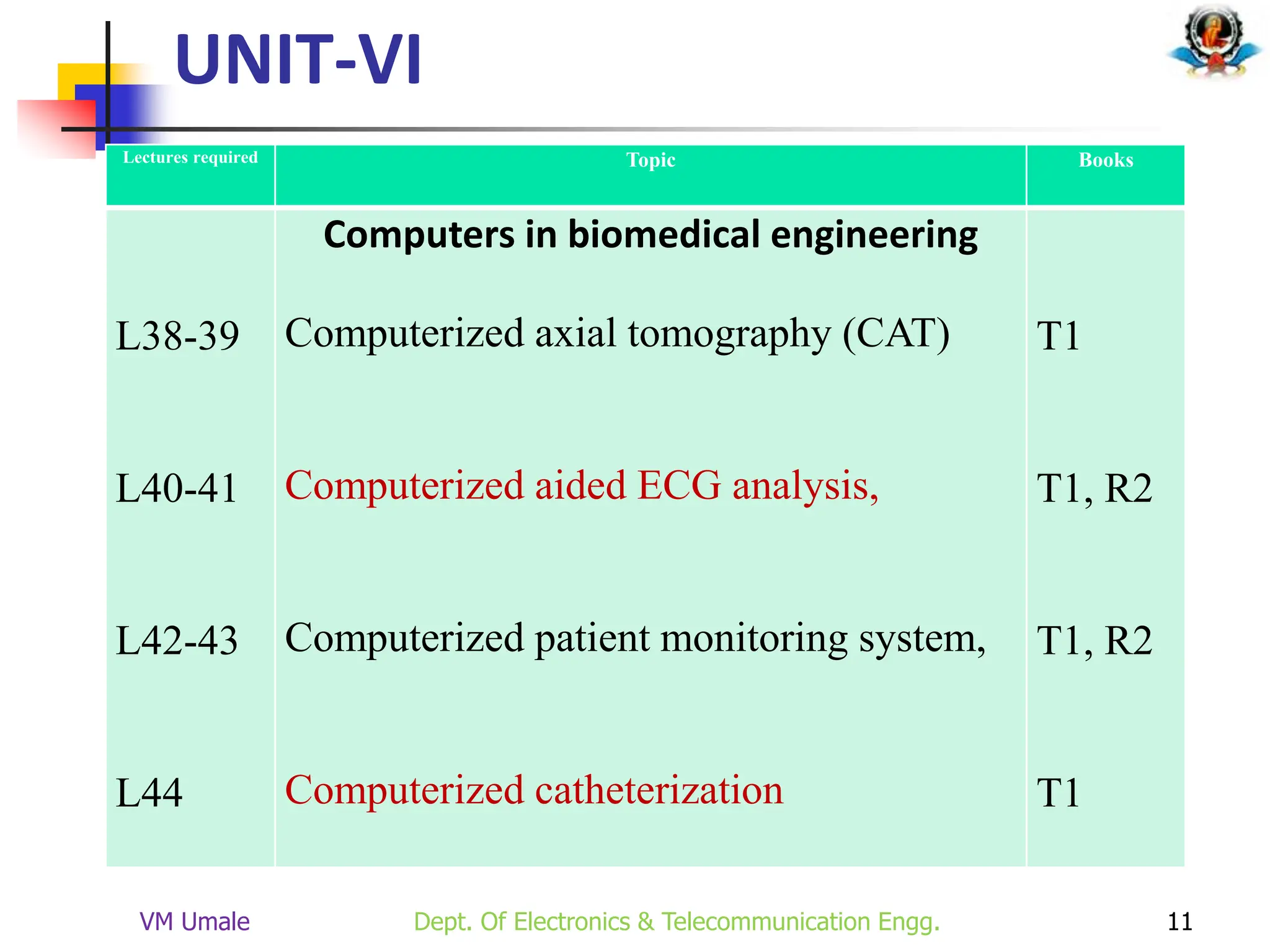
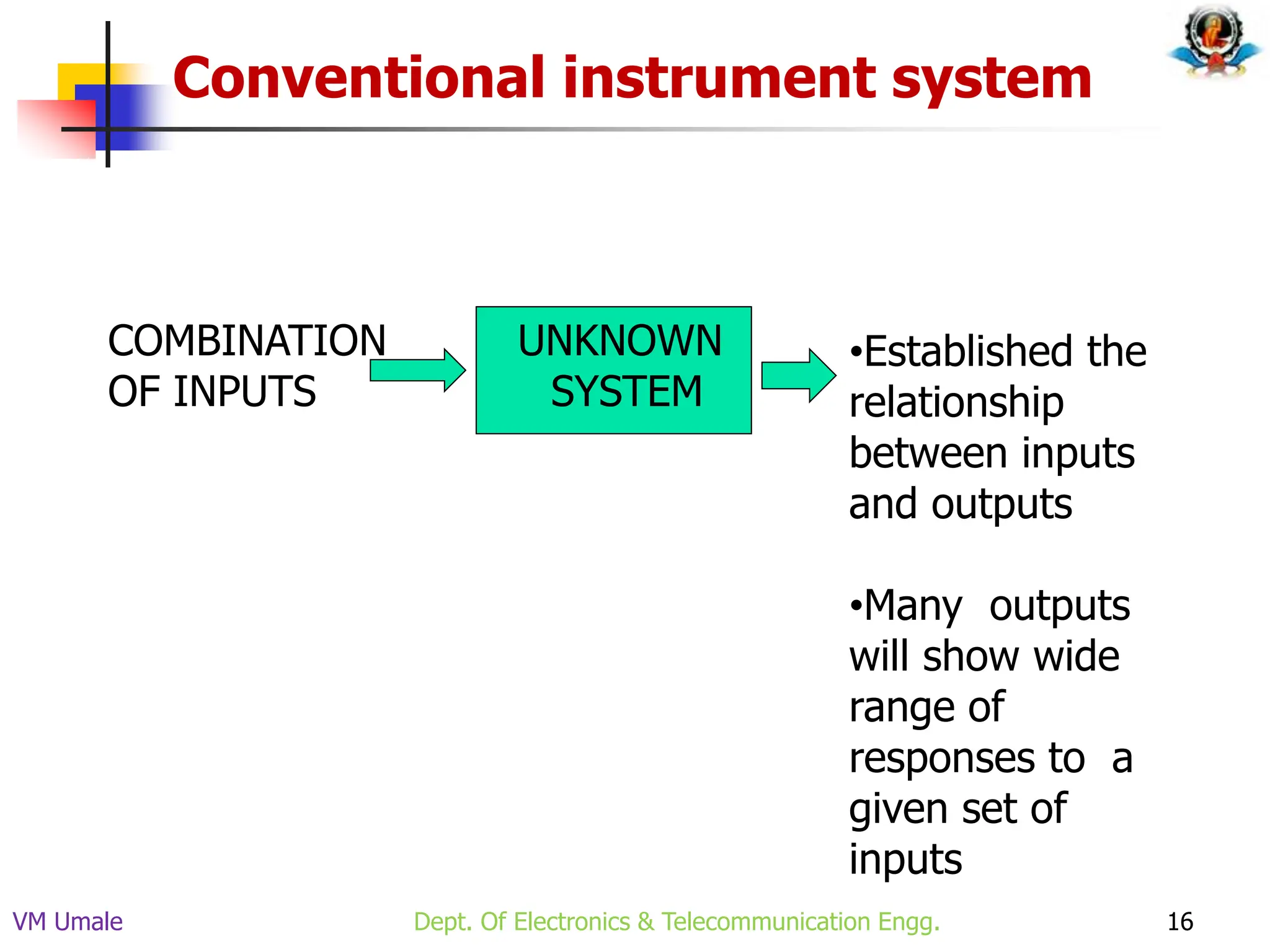
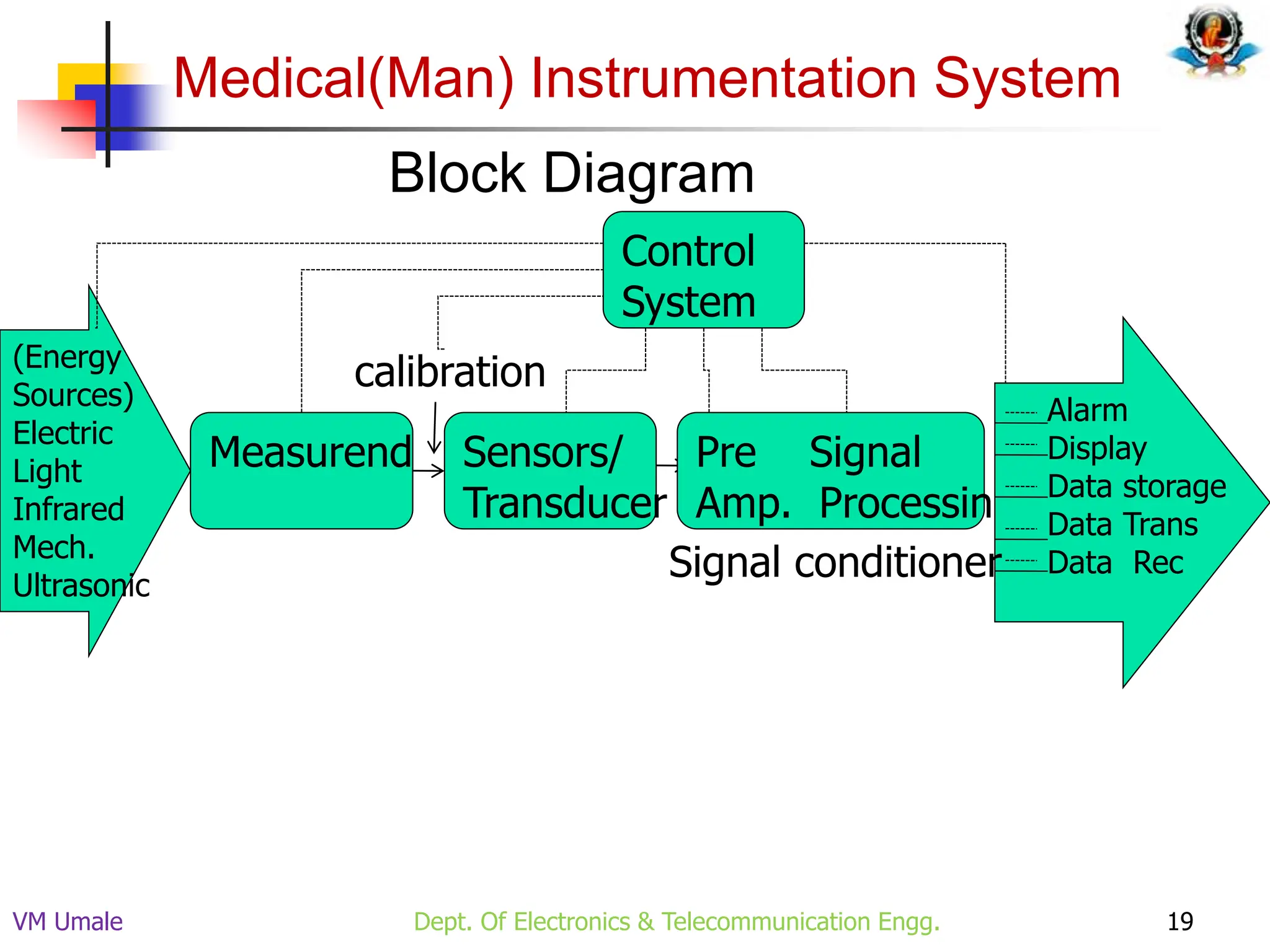
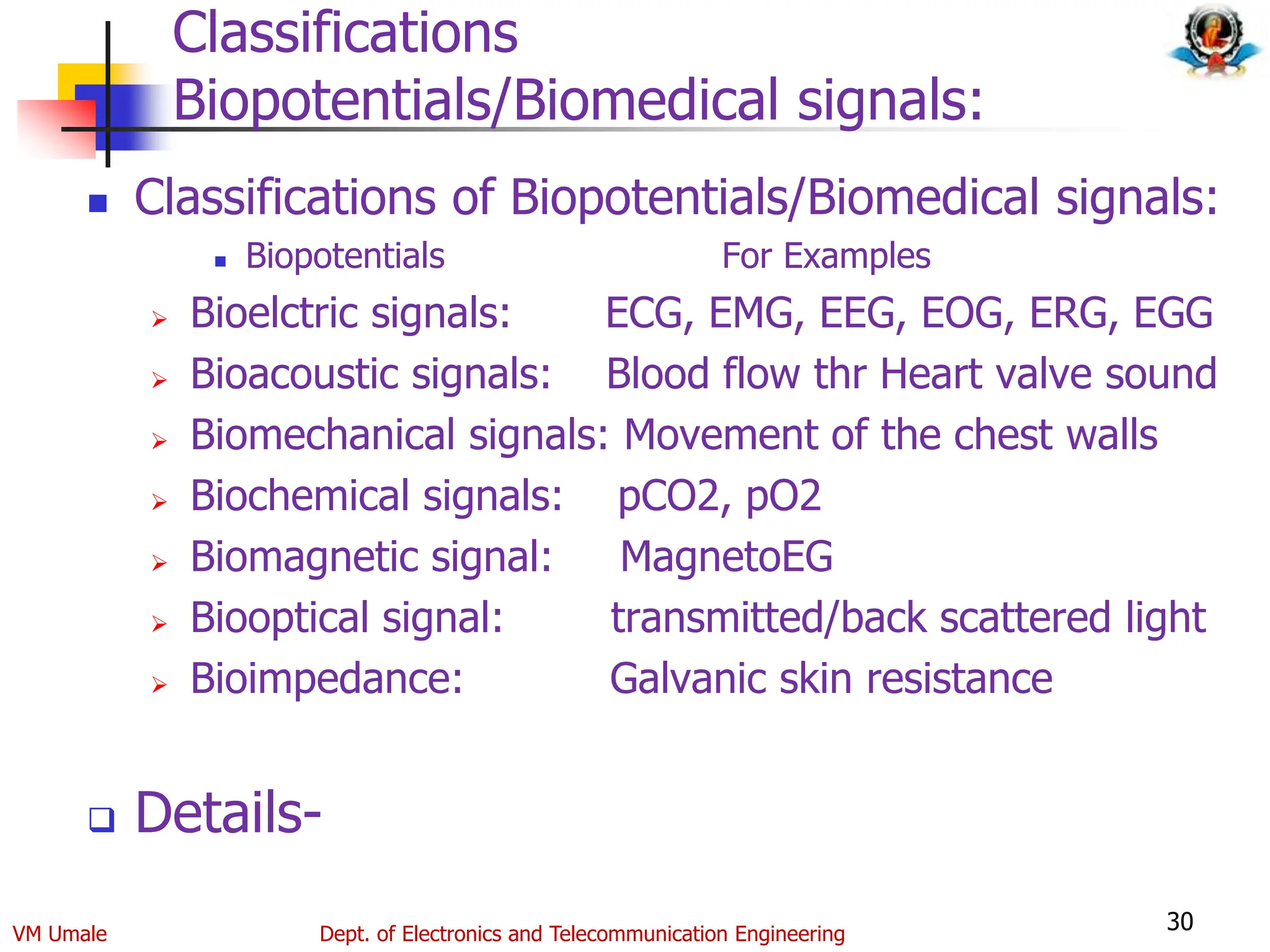
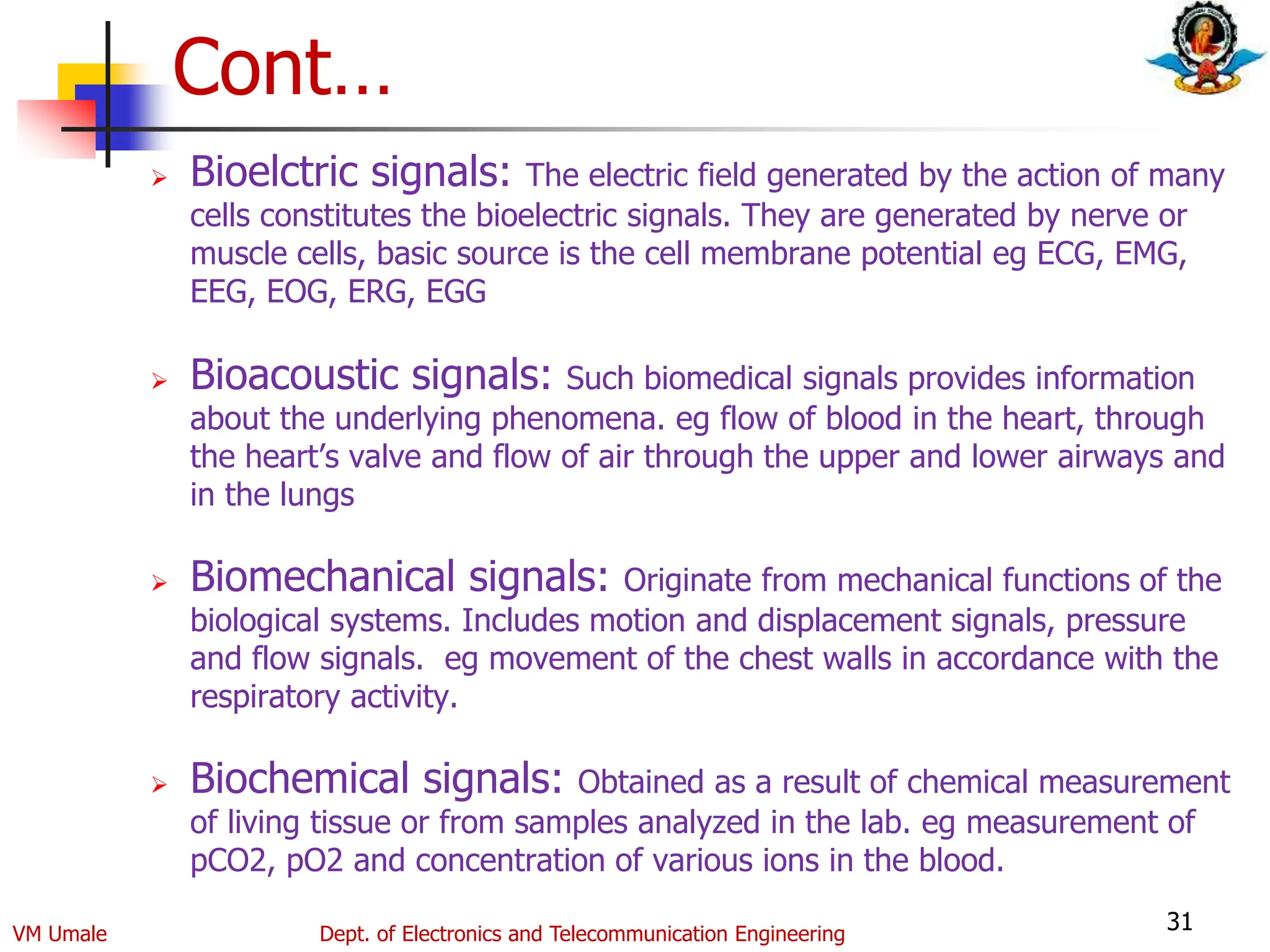
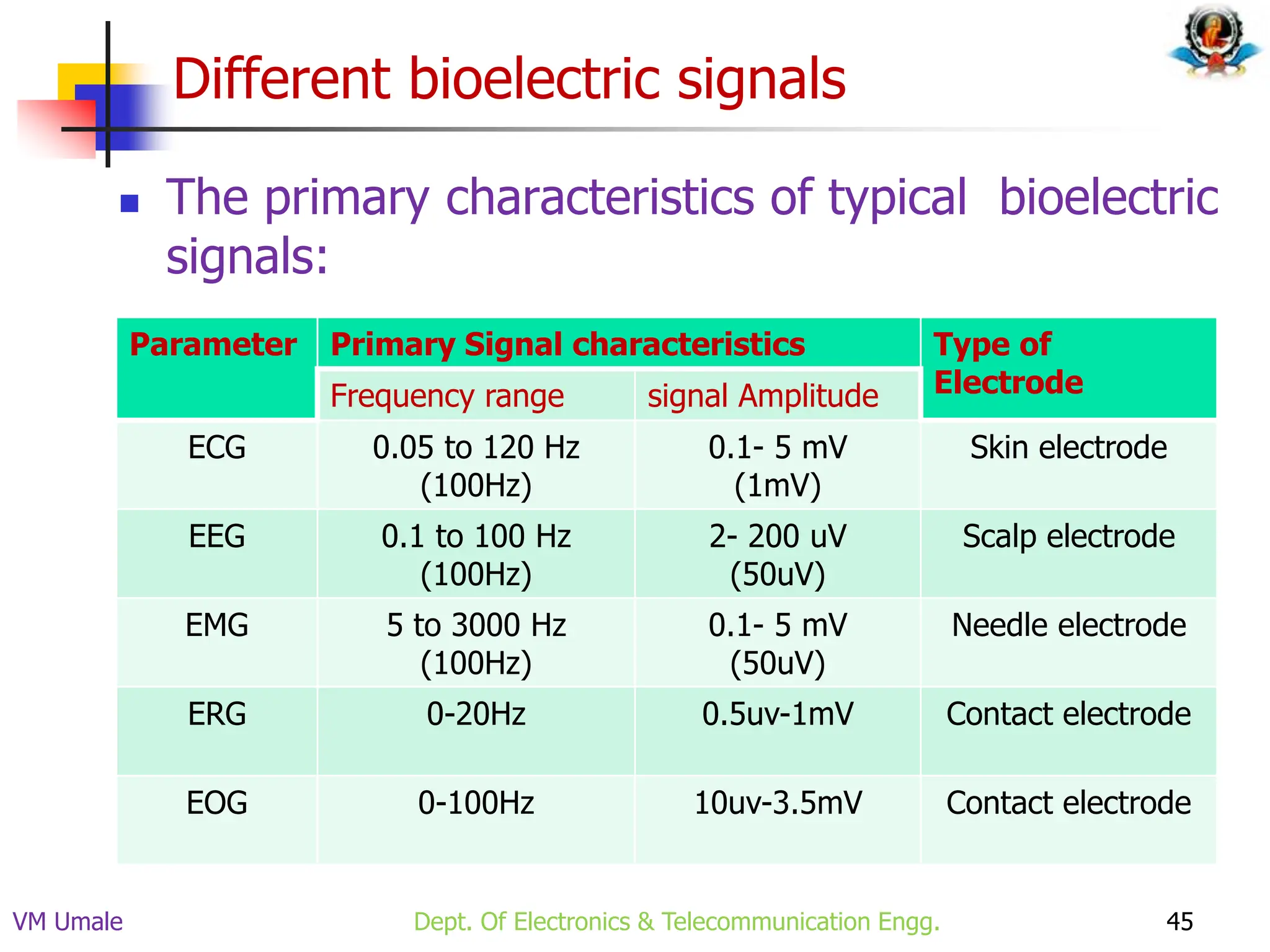
The document outlines the syllabus and lecture plan for a Biomedical Engineering course intended for final year electronics and telecommunications engineering students. It covers various topics including physiological systems, biomedical recorders, medical imaging systems, therapeutic equipment, patient monitoring and safety, and the role of computers in biomedical engineering. The document also delineates course objectives, outcomes, and recommended reading materials.