This document provides details about a Biomedical Instrumentation course, including:
- The instructor's contact information and course code/name.
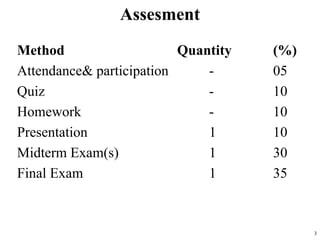
- Assessment will include attendance, quizzes, homework, presentations, midterms and a final exam.
- Topics will include human physiology, biomedical signals and sensors, amplifiers, medical device safety, and measurements of body systems.
- The objective is for students to understand how to measure, test and acquire biological data to design medical systems and devices.