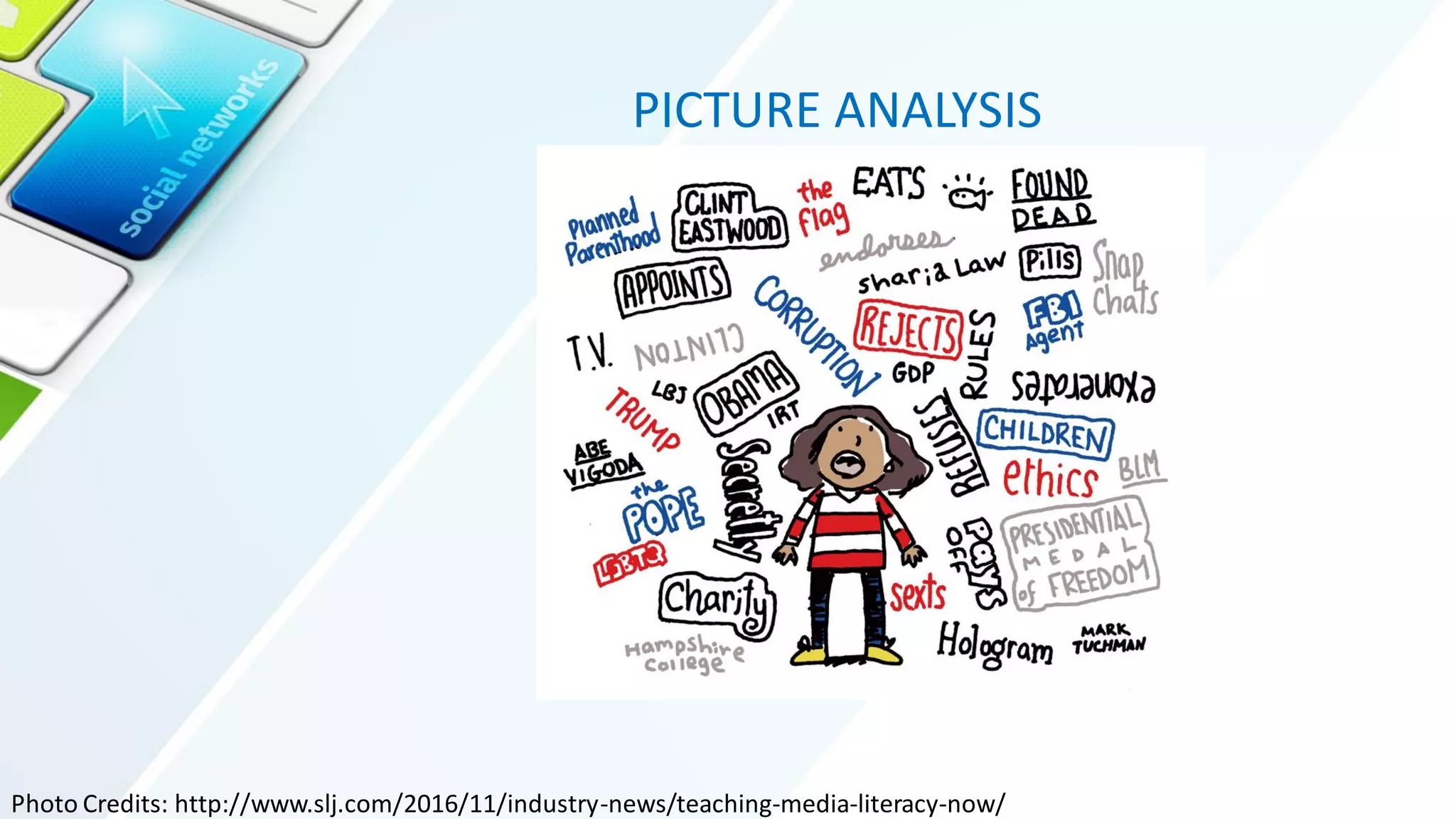
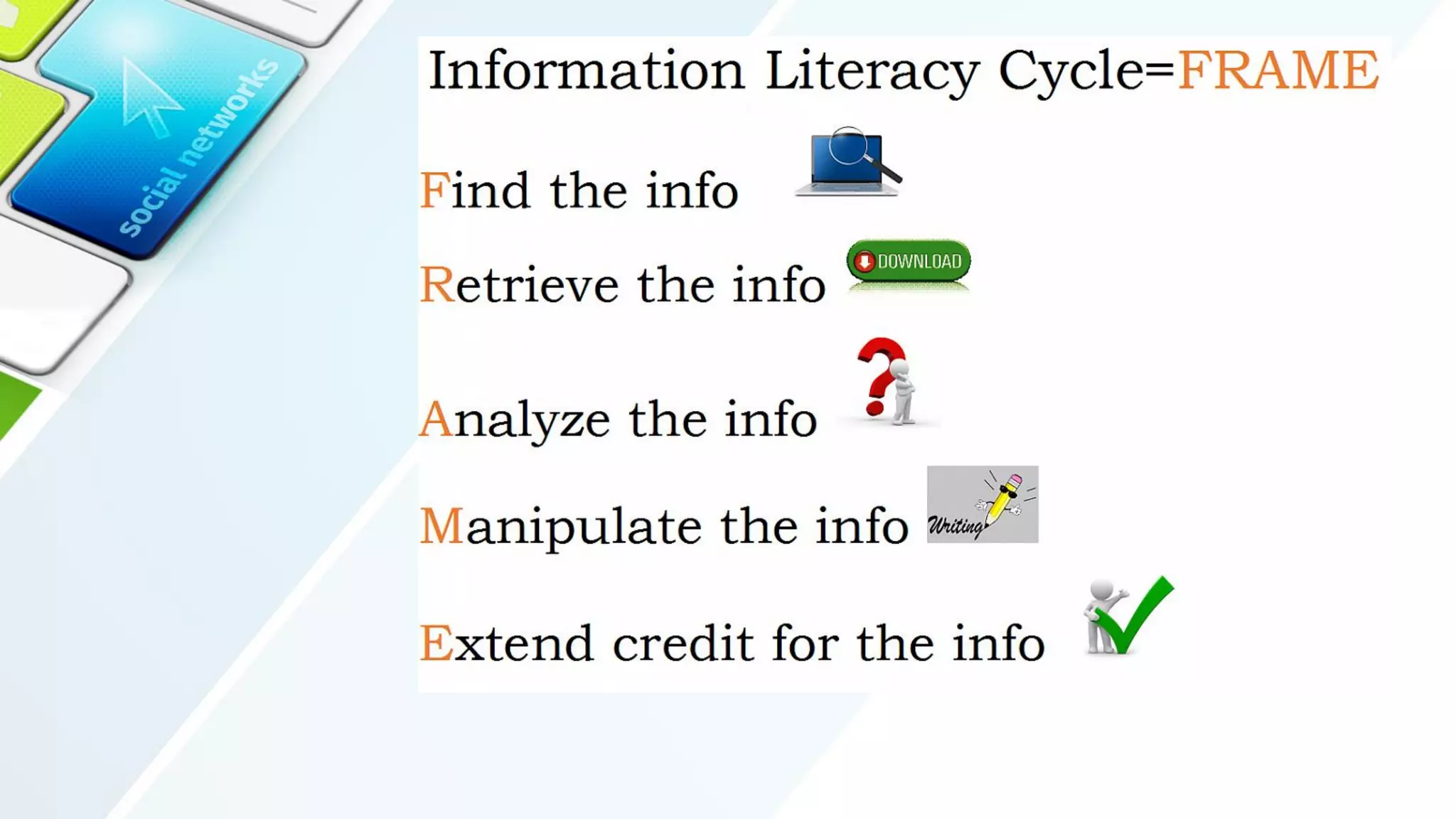
The document outlines the importance of media and information literacy, highlighting key competencies such as identifying information needs, locating and assessing resources, and demonstrating ethical use of information. It describes the five components of information literacy: identifying, finding, evaluating, applying, and acknowledging information. Additionally, it suggests an activity to create a video presentation to educate others about information literacy.