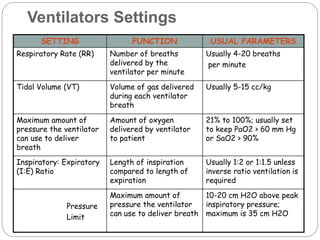
This document provides information on mechanical ventilation management. It discusses the goals of airway management and indications for mechanical ventilation. The roles of nurses include monitoring patients on ventilators and notifying respiratory therapists when issues arise. There are two main types of ventilators and settings must be individualized. Modes of ventilation are described along with weaning and extubation processes. Alarms are addressed and their common causes.