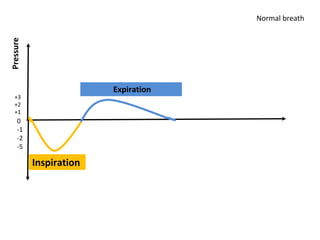
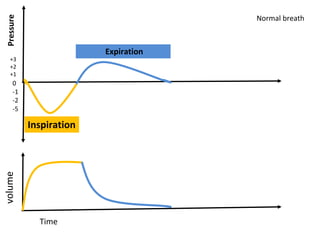
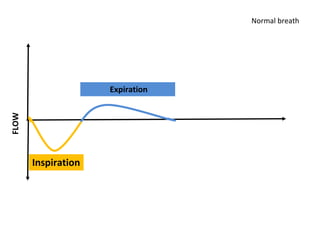
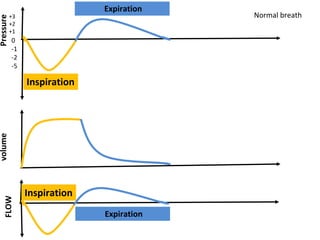
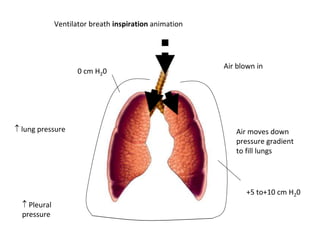
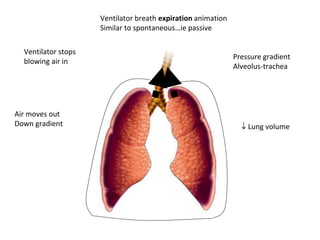
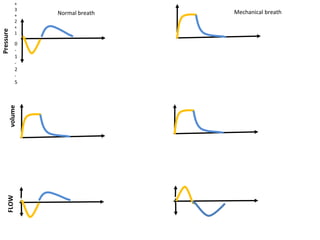
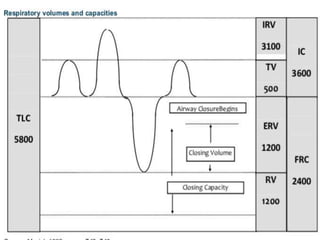
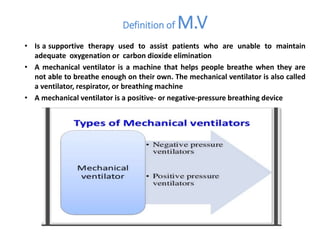
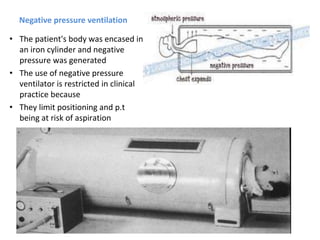
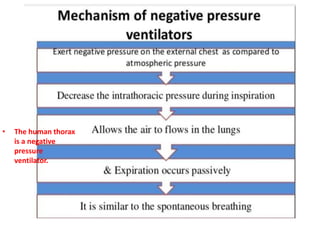
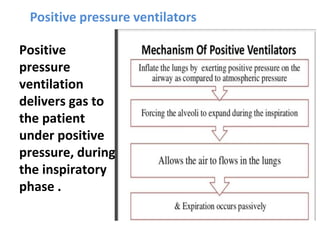
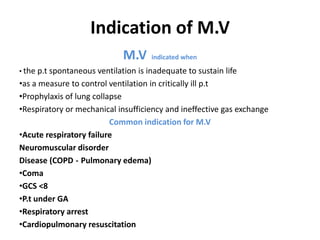
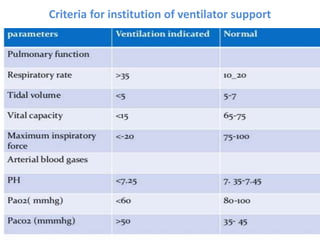
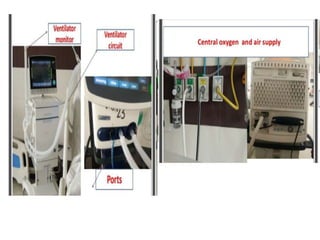
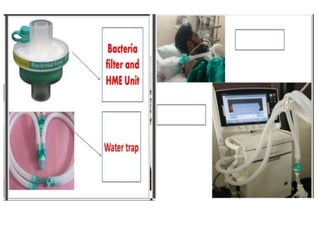
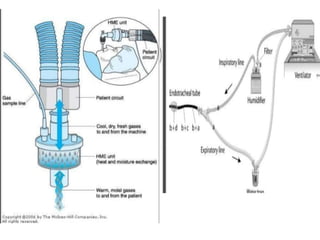
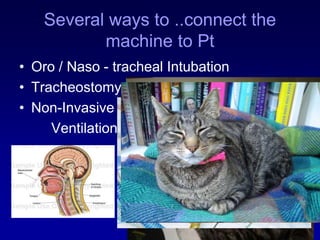
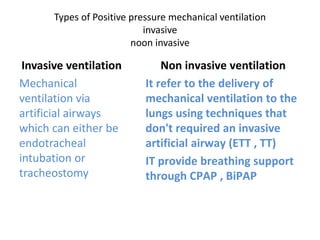
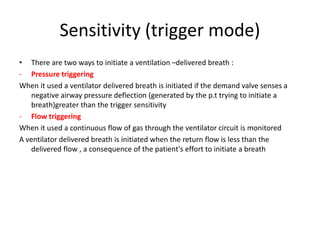
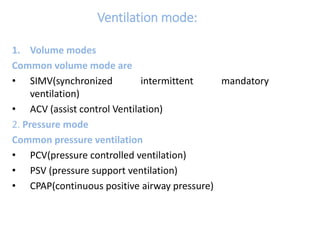
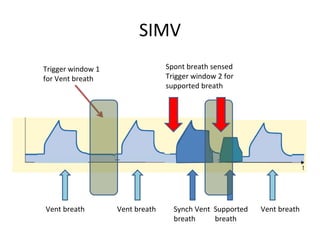
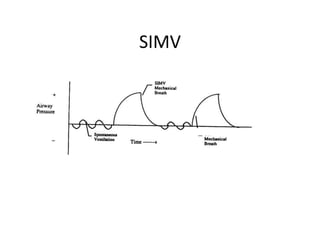
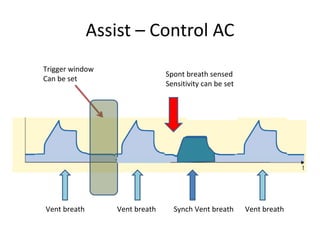
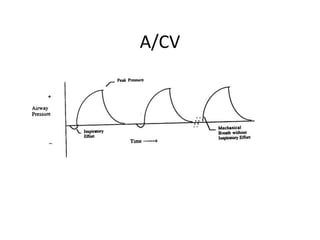
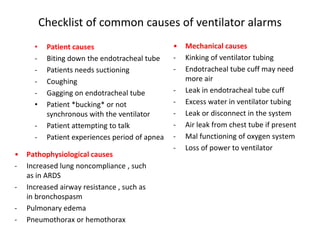
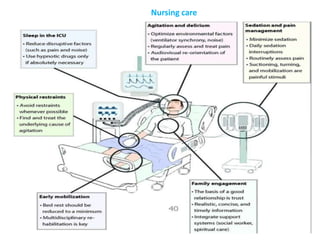
This document discusses mechanical ventilation, including its definition, goals, indications, equipment, types, modes, parameters, alarms, weaning guidelines, complications, and nursing care. The main goals of mechanical ventilation are to maintain adequate oxygenation and carbon dioxide elimination. It is indicated when a patient's spontaneous breathing is inadequate. Common types include invasive ventilation via endotracheal tubes or tracheostomies, and non-invasive ventilation like CPAP and BiPAP. Modes include volume-cycled, pressure-cycled, and high frequency ventilation. Nursing care focuses on maintaining a patent airway and monitoring the patient's condition.